Greater Mekong Subregion. Corridors
Economic Area Greater Mekong, Cambodia, China, Laos, Myanmar, Thailand, Vietnam

The Greater Mekong Subregion (GMS) is an Asian economic area near the Mekong River formed by:
The main objective of the Greater Mekong Subregion is to boost the economic cooperation between the member economies.

- Introduction to the Greater Mekong Subregion (GMS)
- Strategic Framework
- Economic Profile of the Greater Mekong Subregion: Cambodia, China (Yunnan and Guanxi Zhuang), Laos, Myanmar, Thailand, and Vietnam
- Areas of activity:
- Transport (Cross-Border Transport Agreement)
- Tourism
- Regional Trade
- Agriculture
- Investment
- Energy
- Telecommunications
Greater Mekong Subregion (GMS):
The educational aims of the Subject “Greater Mekong Subregion” are:
- To understand the purposes of the Greater Mekong Subregion
- To assess the benefits for the member countries and cooperation areas (logistics corridors, agriculture, trade) of the Greater Mekong Subregion
- To learn about economic profile of the Greater Mekong Subregion

The Subject “Greater Mekong Subregion (GMS)” is included within the curriculum of the following academic programs at EENI Global Business School:
Masters: International Business, Foreign Trade.


Course: Buddhism and Business.
Languages:  (or
(or  Subregión del Gran Mekong
Subregión del Gran Mekong  Sous-région du Grand Mékong
Sous-région du Grand Mékong  ).
).
Credits of the Subject “Greater Mekong Subregion”: 1  .
.

- All Countries, except China, belongs to ASEAN
- Main religion of the countries of the Greater Mekong is Buddhism
- The Greater Mekong Subregion belongs to the Sinic - Buddhist Civilization
Economic Profile of the Greater Mekong Subregion (GMS)
- Total population: 326 million people
- Area: 2.6 million km²
- The Greater Mekong Subregion was founded in 1992 by the Asian Development Bank
- Rich in natural resources: minerals, petroleum, and coal
- Great hydro-power potential
- Main economic sectors are agriculture and fisheries
- Access to the Asia-Africa Logistics Corridor
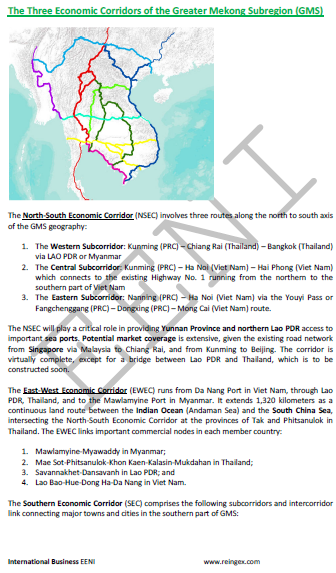
Economic Corridors Development.
- East-West Economic Corridor
- Phnom Penh-Ho Chi Minh City Highway
- East-West Corridor (Myanmar-Vietnam)
- Bangladesh-Myanmar Logistics Corridor
- China-Russia Logistics Corridor
- Trans-Siberian Railway (Russia, North Korea)
- Nanning-Singapore Logistics Corridor

(c) EENI Global Business School (1995-2025)
Top of this page










 WhatsApp
WhatsApp