Business in Myanmar, Yangon. Burmese Economy
Burmese International Trade, Logistics. Business in the Union of Myanmar. Port of Yangon

The Republic of the Union of Myanmar is rich in resources (hardwood timber, natural gas, fishery reserves, gems, and jade)
The agricultural sector (agriculture, livestock, fisheries, and forestry) represent 50% of Burmese GDP
Main Burmese export products of Myanmar are natural gas (38%), agricultural export products (18%), precious stones, timber and forest products, and marine products
The Port of Yangon is the largest port in the Union of Myanmar (90% of Foreign Trade -exports and imports-)
Aung San Suu Kyi (Nobel Peace Prize)
- Introduction to the Union of Myanmar (Burma) - Southeast Asia ASEAN.
- Burmese economy
- Doing Business in Yangon
- Burmese International Trade
- Transport and Logistics
- Port of Yangon
- Investment in Myanmar
- Case Study:
- Myanmar Brewery
- Waaneiza
- Mobilemate Telecommunications
- Access to the Burmese market
- Business Plan for Myanmar
International Trade and Business in Myanmar:

The purposes of the subject “Foreign Trade, Logistics and Business in the Union of Myanmar” are:
- To analyze the Burmese Economy, Logistics and Global Trade
- To conduct research on business opportunities in the Union of Myanmar
- To explore the Burmese trade relations with the student's country
- To learn about Burmese Trade Agreements
- To examine the profile of Burmese companies
- To develop a business plan for the Burmese market

The Subject “Foreign Trade, Logistics and Business in Myanmar” is included within the curriculum of the following academic programs at EENI Global Business School:

Masters: International Business, Foreign Trade.

Masters
adapted to  Burmese students.
Burmese students.
Languages:  or
or  Myanmar
Myanmar  Myanmar.
Myanmar.
- Subject Credits “Doing Business in Myanmar”: 1

International Trade, Logistics and Business in Myanmar (Burma).

- Port of Yangon
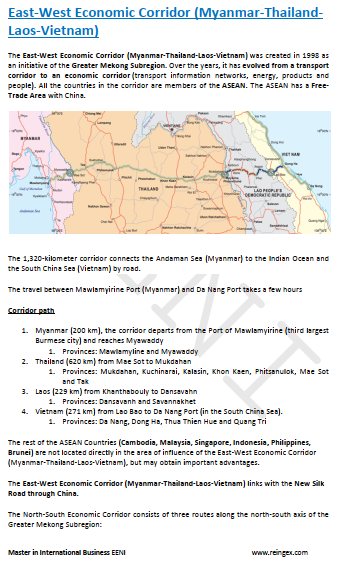
- East-West Corridor (Myanmar-Vietnam)
- Bangladesh-Myanmar Logistics Corridor
- Asia-Africa Logistics Corridor
- Access to the Nanning-Singapore Economic Corridor

Burmese Trade Agreements and preferential market access:
- Myanmar and the Buddhist Economic Area
- ASEAN
- ASEAN Economic Community
- ASEAN Free Trade Area
- Trade Agreements (as a member of ASEAN): Australia-New Zealand, India, Canada, China, the EU, Japan, South Korea, the United States, Australia- New Zealand and Pakistan
- Mekong Economic Cooperation
- Mekong River Commission (dialogue partner)
- Greater Mekong Subregion
- Bay of Bengal Initiative
- Asian Clearing Union
- Regional Comprehensive Economic Association
- GSP
- Trade Agreements with Bangladesh, Israel, and Sri Lanka
- Global System of Trade Preferences
- South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (Observer)

- World Trade Organization (WTO)
- Agreement on Trade in Services (GATS)
- Agreement on Sanitary Measures
- Agreement on Technical Barriers to Trade
- Agreement on Preshipment Inspection
- Agreement on Safeguards
- Trade Facilitation Agreement
- World Customs Organization (WCO)
- Kyoto Convention
- BIC (Containers)
- Chicago Convention (ICAO)
- International Maritime Organization
- Istanbul Convention - not a member
- Customs Convention on Containers - not a member

- Boao Forum for Asia
- Asia Cooperation Dialogue
- Economic Commission for Asia (ESCAP)
- Asian Development Bank
- Colombo Plan
- East Asia-Latin America Cooperation
- Africa-Asia Partnership
- Asia-Middle East Dialogue

- United Nations
- World Bank
- World Trade Organization (WTO)
- International Monetary Fund
- Borders of the Republic of the Union of Myanmar: China, Laos, Thailand, Bangladesh, and Bharat (India)
- Capital of Burma is Naypyidaw
- The largest city of Myanmar: Yangon (Rangoon)
- Burmese is the official language (32 million speakers)
- 68% of the population of Myanmar are Burmese
- Burmese population: 51.4 million people
- Area of Myanmar: 676,578 km²
- Type of Government of Myanmar: Unitary Parliamentary Republic
- Burmese Independence: 1948 (United Kingdom)
Main religion in Burma: Theravada Buddhism (89% of the Burmese population - 60 million people).
- Christianity is the second religion (7%)
- 1 million of Baptists
Burma belongs to Buddhist Civilization

Burmese Economy:
- The Government controlled the activity in the strategic sector of the Burmese economy: energy, heavy industry, and International Trade of rice (control local rice prices)
- The Military commercial entities dominate the economy of Myanmar
- in recent years, the Union of Myanmar has liberalized local and International Trade, promoting private sector and opening the country to the FDI
- Burmese Currency: Kyat (K) (MMK)

International Trade of Burma.
- Rice exports of Burma hit a record
- The largest export markets of Myanmar are Thailand (40%), Singapore (13%), Hong Kong and India (11%), China (8%), and Malaysia
- Main imports products of Myanmar are petroleum, textiles, machinery parts, steel, iron, and bars
- The largest Burmese import markets of Myanmar are Singapore (30%), China (18%), the Bahamas (13%), Thailand, and Japan
Sample:
(c) EENI Global Business School (1995-2025)
Top of this page








 WhatsApp
WhatsApp