Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC)
APEC Free Trade Area (Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation)
The objective of the Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC) is to strengthen free and open trade and investment in the Asia-Pacific region.
APEC has twenty-one members, representing 41% of the world’s population, 57% of the World's GDP and 44% of global trade.
The member economies of APEC are Australia, Brunei, Canada, Chile, Hong Kong, Indonesia, Japan, Korea, Malaysia, Mexico, New Zealand, Papua New Guinea, Peru, Philippines, Russia, Singapore, Chinese Taipei (Taiwan), Thailand, United States, and Vietnam.
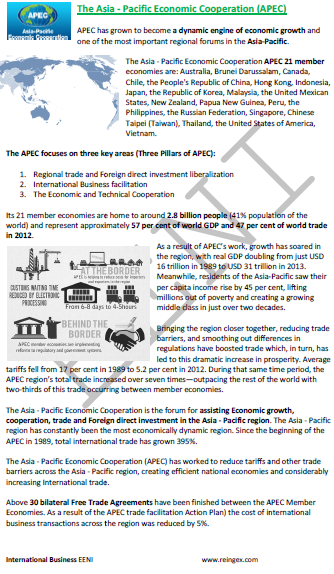
APEC focuses on three key areas (the three pillars of APEC):
- Regional Trade and Foreign Direct Investment liberalization
- International Business facilitation
- Economic and technical cooperation
1- Introduction to APEC
- Introduction to APEC ©
- APEC Structure
- Bogor Goals
- Osaka Action Agenda
- Trade and Investment Liberalization
- Business Facilitation
- Economic and technical cooperation
- Achievements and Benefits of APEC
- Free Trade Area of the Asia-Pacific (FTAAP)
- Pacific Economic Cooperation Council
Sample - Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC)
2- Committee on Trade and Investment of APEC
- Introduction to APEC Committee on Trade and Investment
- Principles for Cross-Border Trade in Services in APEC region
- Principles of Foreign Trade Facilitation
- Automotive and Chemical Dialogue
- Business Mobility Group
- Investment
- Group on Services
- TRIPS
- E-commerce
- Market Access
- Rules of Origin
- Customs Procedures
- Standards and Conformance
- Economic Impact of the Enhanced Multimodal Connectivity in APEC Region
3- Economy, Trade, and Investment in the Asia-Pacific Region (APEC)
4- APEC Telecommunications and information.

The educational aims of the Subject “Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC)” are the following:
- To understand the Bogor Goals and the functions of APEC
- To assess the benefits for the member countries of APEC as well the cooperation areas
- To learn about role of APEC Commission on Trade and Investment
- To research the economic integration process and trade among the member countries of APEC (Free Trade Area of the Asia-Pacific)
- To understand trade liberalization, Trade Facilitation and investment flows between APEC Countries
- To know Trade Agreements between APEC Countries

The Subject “APEC (Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation).” is included within the curriculum of the following academic programs at EENI Global Business School:

Masters: International Business, Foreign Trade.

- Subject Credits “Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC)”: 2

Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC).
The Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation is a forum for assisting economic growth, cooperation, Foreign Trade, and Foreign Direct Investment in the Asia-Pacific region.
- The Asia-Pacific region has consistently been the most economically dynamic region
- Since the beginning of APEC in 1989, total International Trade has grown 395%
The Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation has three official observers Organizations:
- ASEAN Secretariat
- Pacific Economic Cooperation Council
- Pacific Islands Forum Secretariat
APEC has worked to reduce tariffs and other trade barriers across the Asia-Pacific region, creating efficient national economies and considerably increasing International Trade.
The pillars of the Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation are the Bogor Goals of free and open Foreign Trade of Foreign Direct Investment in the Asia-Pacific region by 2010 for industrialized economies and 2020 for developing economies. These objectives were adopted by APEC Leaders in 1994 in Bogor (Indonesia).

Religions and Global Business -
Religious diversity
Main religions in the Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation Forum member countries:
- Christian Countries: Australia, Canada, Chile, the United States, the Philippines, Mexico, New Zealand, Papua New Guinea, Peru, and Russia
- Muslim Countries: Brunei, Indonesia, and Malaysia
- Buddhist Countries: Japan, Thailand, Taiwan, and Vietnam. In Singapore, 42% of the population is Buddhist
Above thirty bilateral Trade Agreements have been finished between APEC member economies. As a result of APEC Trade Facilitation Action Plan, the cost of International Business transactions across the region was reduced by 5%.
(c) EENI Global Business School (1995-2025)
Top of this page










 WhatsApp
WhatsApp or
or 

