Business in Singapore, Port, ASEAN
Singapore: second most competitive economy in the World. Singaporean Foreign Trade, Logistics

Singapore is the second most competitive economy in the World and the most competitive small economy in the World.
- Singapore consistently scores at the top levels in global and regional rankings. These range from political Risk to workforce productivity, from quality of life to forecasts for making profits
- More than 26,000 international firms are established in Singapore

Religions and Global Business -
Religious diversity
- Introduction to Singapore (Southeast Asia, ASEAN)
- Singaporean Economy
- Advantages of Singapore
- Key Singaporean industry sectors
- International Trade of Singapore
- Transport and Logistics
- Port of Singapore
- Investment in Singapore
- Setting up a company in Singapore
- Case Study:
- Hyflux
- Temasek
- Made in Singapore
- Access to the Singaporean Market
- Business Plan for Singapore

The educational aims of the Subject “Foreign Trade, Logistics and Business in Singapore” are:
- To analyze the Singaporean Economy, Logistics and Global Trade
- To conduct research on business opportunities in Singapore
- To understand the role of Singapore as a gateway to the Southeast Asian markets (ASEAN)
- To explore the Singaporean trade relations with the student's country
- To learn about Singaporean Trade Agreements
- To examine the profile of the Singaporean companies
- To develop a business plan for the Singaporean Market

The Subject “Business in Singapore” is included within the curriculum of the following academic programs at EENI Global Business School:

Masters: International Business, Foreign Trade.

Course: Taoism, Confucianism & Business.
Masters adapted to  Singaporean Students.
Singaporean Students.
Languages:  (or
(or  Singapur
Singapur  Singapour).
Singapour).
- Subject Credits “Doing Business in Singapore”: 3

International Trade, Logistics and Business in Singapore.

- Port of Singapore
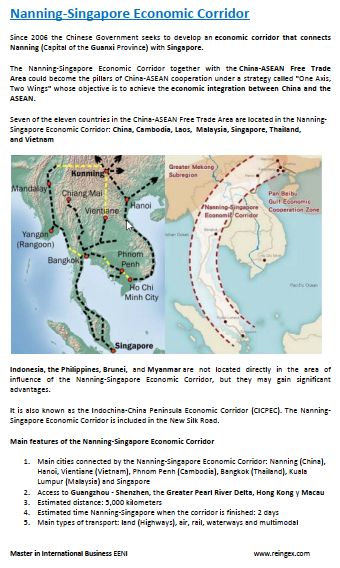
- Nanning-Singapore Logistics Corridor
- Asia-Africa Logistics Corridor
- Access to the East-West Economic Corridor (Myanmar-Thailand-Laos-Vietnam)

Singaporean Free Trade Agreements and Market Access:
- Singapore and the Buddhist Economic Area
- ASEAN
- ASEAN Economic Community
- ASEAN Free Trade Area
- Singaporean Free Trade Agreements (as an ASEAN member): Australia-New Zealand, Canada, China, Hong Kong, India, the EU, Japan, Korea, Russia, and Pakistan
- APEC
- Indian-Ocean Rim Association
- Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership
- Regional Comprehensive Economic Association
- India-Singapore Agreement
- China-Singapore FTA
- Singapore-South Korea Agreement
- Singapore-Australia Agreement
- Singapore-Japan Agreement
- U.S.-Singapore Agreement
- Singapore-New Zealand Agreement
- Singapore-EU Agreement
- Singapore-European Free Trade Association (EFTA)
- Jordan-Singapore Agreement
- Singapore-Peru Agreement
- Singapore-Panama Agreement
- Turkey-Singapore Agreement
- UK-Singapore Free Trade and Economic Integration Agreement
- Costa Rica-Singapore Agreement
- Taiwan-Singapore Agreement
- GCC-Singapore Agreement
- Global System of Trade Preferences
Business in Singapore:


- World Trade Organization (WTO)
- Agreement on Sanitary and Phytosanitary Measures
- Agreement on Trade in Services (GATS)
- Agreement on Technical Barriers to Trade
- Agreement on Preshipment Inspection
- Agreement on Safeguards
- Trade Facilitation Agreement
- World Customs Organization (WCO)
- Kyoto Convention
- Hamburg Rules (Maritime Transport)
- International Road Transport Union (IRU)
- International Chamber of Shipping
- BIC (Containers)
- Chicago Convention (ICAO)
- International Maritime Organization (IMO)
- Istanbul Convention - not a member
- Customs Convention on Containers - not a member


- Asian Development Bank
- Colombo Plan
- Africa-Asia Partnership
- Boao Forum for Asia
- Asia Cooperation Dialogue
- Economic Commission for Asia (ESCAP)
- Asia-Middle East Dialogue
- Forum for East Asia-Latin America Cooperation (FEALAC)

- United Nations
- World Bank
- World Trade Organization (WTO)
- International Monetary Fund
- Pacific Economic Cooperation Council
- Capital of the Republic of Singapore: Singapore City
- Singaporean Population: 5.5 million people
- Singaporean Area: 719.1 km²
- There are four official languages in Singapore: English, Malay, Mandarin, and Tamil
- 74% of the Singaporean population are Chinese, 13% are Malays and 9% Indians
- Type of Government of Singapore: Unitary Parliamentary Constitutional Republic
- Singaporean Independence: 1963 (United Kingdom)
- Near countries to Singapore: Cambodia, Malaysia, Indonesia, Brunei, Thailand
Religions in Singapore:
- Buddhism (33%)
- Christianity (18%)
- Islam (15%)
- Taoism (11%)
- Hinduism (5%)
- Singapore has a significant Confucianism influence on his culture

Singapore belongs to Buddhist Civilization / Sinic Civilization
Singaporean Economy:
- Singapore is the second most competitive economy (World Competitiveness Yearbook), the seventh most competitive economy (Global Competitiveness), and the ninth in the Business Competitiveness Index
- The economy of Singapore is the second freest economy in the World (Heritage Foundation)
- Singapore is a world leader in all the ten fields of economic freedom
- Currency: Singapore Dollar (SGD)
- Singaporean GDP by sector
- Services: 75%
- Industry: 25%


International Trade of Singapore
- Top exports of Singapore: electronics, chemicals, and services
- Top trade partners of Singapore: France, Germany, the UK, Indonesia, Malaysia, Thailand, Japan, Hong Kong, South Korea, Taiwan, China, Saudi Arabia, the United States, and Australia
Singapore has in force several Free Trade Agreements.
Singapore has the most extensive Free Trade Agreement network in Asia. Trade Agreements have been signed with the United States, Japan, Australia, New Zealand, EFTA, Jordan, China, Chile, South Korea, India, and Panama.
Singapore Free Trade Agreements (Concluded/Signed)
- Costa Rica
- Gulf Cooperation Council
Singapore Free Trade Agreements (actual/Negotiations)
- Canada
- Mexico
- Pakistan
- Ukraine.
Sample
(c) EENI Global Business School (1995-2025)
Top of this page








 WhatsApp
WhatsApp