Business in Pakistan, Islamabad, Karachi

Pakistani Foreign Trade. Business in Lahore (Pakistan) Automotive Sector
- Introduction to the Islamic Republic of Pakistan (Central Asia)
- Economy of Pakistan
- International Trade of Pakistan
- Top Pakistani Exports: products and markets
- International Trade Development Authority of Pakistan
- Investment in Pakistan
- Sales promotion in Pakistan
- Business in Karachi, Islamabad, and Lahore
- Case Study:
- Pakistani Information Technology Industry
- Pakistani Automotive Sector
- Hinopak Motors
- Pakistan Telecommunication
- Chawla Group
- Case Study - Pakistani Muslim Businessman:
- Shahid Khan
- Saigol Family
- Mian Muhammad Mansha
- Dewan Farooqui
- Access to the Pakistani market
- Business Plan for Pakistan
The objectives of the subject “International Trade and Business in the Islamic Republic of Pakistan” are the following:
- To analyze the Pakistani Economy and Foreign Trade
- To know the business opportunities in the Islamic Republic of Pakistan
- To explore the Pakistani trade relations with the country of the student
- To know the Pakistani Trade Agreements
- To examine the profile of Pakistani companies and Businessman
- To develop a business plan for the Pakistani market

The Subject “Foreign Trade and Business in Pakistan” belongs to the following Online Programs taught by EENI Global Business School:
Masters: International Business, Foreign Trade.
Doctorate: Islamic Business, World Trade.
Languages:  (or
(or  Pakistan
Pakistan  Pakistán
Pakistán  Paquistão).
Paquistão).
- Credits of the subject “Doing Business in Pakistan”: 2

- Duration: two weeks

Masters adapted to the  Pakistani Students.
Pakistani Students.
International Trade and Business in Pakistan.

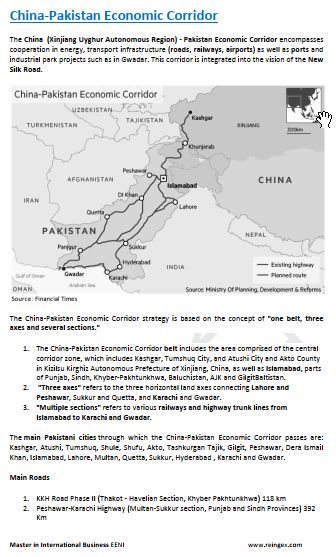
- China-Pakistan Corridor
- Islamabad-Istanbul Corridor
- Almaty-Bishkek Corridor
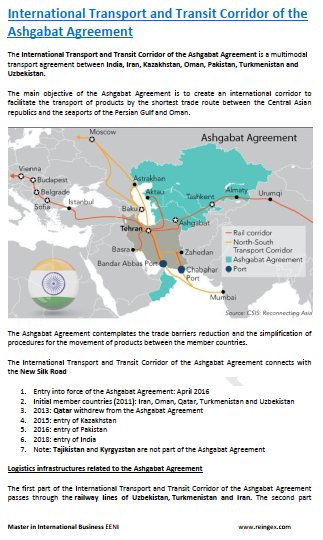
- Corridor of the Ashgabat Agreement
- Silk Road
- Access to:
- Transport Corridor Europe-Caucasus-Asia (TRACECA)
- Trans-Caspian Corridor
- China-Central-West Asia Economic Corridor
- India-Chabahar (Iran)-Afghanistan Economic Corridor
- International North-South Transport Corridor (India-Russia)
- Kyrgyzstan-Iran Corridor

Pakistani Preferential Access and Trade Agreements:
- Pakistan and the Central Eurasian Economic Area
- Economic Cooperation Organization (ECO)
- South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation
- Asian Clearing Union
- Central Asia Cooperation (CAREC)
- Shanghai Cooperation Organization
- Islamic Trade Preferential System
- Pakistan-China Free Trade Agreement
- Mauritius-Pakistan Preferential Trade Area
- ASEAN-Pakistan Free-Trade Area
- Pakistan-Sri Lanka Agreement
- Trade Agreements with India, MERCOSUR
- Global System of Trade Preferences
- Trade Negotiations Among Developing Countries
- Iran-Pakistan-Turkey Transit Transport Framework Agreement (TTFA)
- Indonesia-Pakistan Agreement
- Pakistan-Malaysia Agreement
- EU-Pakistan
- EU-Pakistan Cooperation Agreement
- The EU's Generalized System of Preferences (GSP)
- ALADI (observer)


- WTO
- GATS
- Agreement on Sanitary Measures
- Agreement on Technical Barriers to Trade
- Agreement on Preshipment Inspection
- Agreement on Safeguards
- Trade Facilitation Agreement
- WCO
- CIM, CIT Rail Rules
- IRU
- TIR Convention
- Guidelines on Safe Load Securing for Road Transport
- Hamburg Rules (Sea)
- COTIF Convention
- BIC
- Chicago Convention (ICAO)
- IMO
- Convention for Safe Containers
- Istanbul Convention
- Customs Convention on Containers - not a member

- Islamic Development Bank
- OIC
- Asia-Middle East Dialogue

- Asian Development Bank
- Colombo Plan
- Africa-Asia Strategic Partnership
- Boao Forum for Asia
- Asia Cooperation Dialogue
- ESCAP

- UN
- WB
- WTO
- IMF
The Islamic Republic of Pakistan.
- Borders of Pakistan: Afghanistan, Iran, India, and China
- Pakistani Population: 199 million people
- Area of Pakistan: 881,913 km²
- Capital of Pakistan: Islamabad
- The largest city of Pakistan is Karachi
- Pakistani official languages are Urdu (official) and English (co-official)
- Other languages: Punjabi, Pashto, and Sindhi
- Currency of Pakistan: Pakistani Rupee (PKR)
- Independence of Pakistan from the UK: 1940
- Abolition of Slavery in Pakistan: 1992 (the last country in the World to abolish slavery)
Religion in Pakistan.
Islam is the state religion of the Islamic Republic of Pakistan, most of 199 million Pakistani (95-97%) are Sunni Muslims, and Shiites represent 5% of the population, the second country after Iran.
- Most Muslims in Pakistan follows the Madhhab Hanafi school of Islamic Jurisprudence
- Pakistan is a democratic Parliamentary Federal Republic with Islam as the state religion
- In 1979 the new penal measures based on the Islamic principles of law (Sharia) entered into force (establishing a social welfare system based on the Zakat)
- Only Muslims have the right to act as judges in the Federal Court of the Sharia
- The Headquarters of the Islamic Chamber of Commerce and Industry are in Pakistan
- Hinduism: 1% of the population (3.6 million)

Pakistan belongs to the Central Eurasian Economic Area (Islamic Civilization).


Economy of Pakistan.
- Pakistan is a Frontier Market
- The Islamic Republic of Pakistan is advantageously situated in Central-South Asia
- Pakistan is a Next Eleven Economy with major economic and political challenges
- Pakistan has made significant economic reforms mainly in the manufacturing sector and financial services, but the outlook for economic growth in the Islamic Republic of Pakistan is not optimistic
- The Automotive sector of Pakistan (32 automotive manufacturing units) is one of the largest contributors to the manufacturing sector in Pakistan (growth of 30% annually)
- The Textile industry of the Islamic Republic of Pakistan is the largest driver of export growth
- The International Trade Development Authority of Pakistan is the agency of the Government of Pakistan working for foreign trade promotion of Pakistan
- Access to the Eurasian Land Transport Initiative (Silk Road)
Shahid “Shad” Khan (Pakistan, 1952) is a prominent billionaire Businessman living in the U.S.. He is the owner of the Jacksonville Jaguars and Flex-N-Gate (auto components manufacturer).
The Saigol Family (from India) established the first textile unit “Kohinoor Textile Mills” under the umbrella of Kohinoor Industries Limited.
Global Trade and Business in Pakistan:





