Business in France, Paris. French Economy

France: third European economy, Paris. Trade Relations with Africa
- Introduction to the French Republic (EU)
- French Economy
- France: one of the political and economic leaders of the EU
- Information and communication technologies in France
- Business in Paris
- French International Trade
- Political, economic and cultural relations with the African Francophone countries
- Strategic Partnership between Africa and France
- Strategic importance of the Francophonie
- French foreign direct investment
- Main French Companies
- Case Studies:
- Michelin
- Alstom
- Essilor
- L’Oréal
- Danone
- Carrefour
- Access to the French Market
- Business Plan for France
The objectives of the subject “International Trade and Business in” the French Republic” are the following:
- To analyze the strengths of the French Economy and Foreign Trade
- To know the trade opportunities in the French Market
- To analyze the trade relations of France with the country of the student
- To know the French Free Trade Agreements as a member of the EU
- To understand the political and economic importance of France in the EU
- To analyze the Africa-France Strategic Partnership
- To develop a business plan for the French Market

The Subject “Foreign Trade and Business in France” belongs to the following Online Programs taught by EENI Global Business School:
Doctorate: European Business, World Trade.
Masters: International Business, Foreign Trade.
Languages:  Francia
Francia  France
France  França.
França.
- Credits of the Subject “Doing Business in France”: 3

- Duration: three weeks

 Masters adapted to French Students.
Masters adapted to French Students.
International Trade and Business in France:

- Atlantic Corridor (Portugal-Germany)
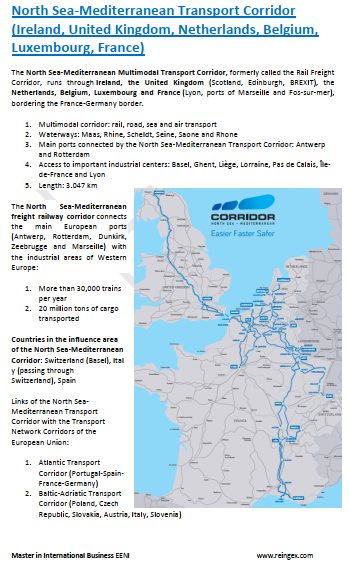
- North Sea-Mediterranean Corridor (Ireland, France)
- Access to the North Sea-Baltic Transport Corridor
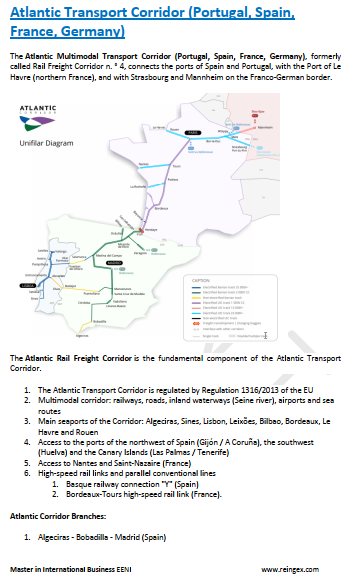


French Preferential Access and Trade Agreements:
- France and the European Economic Area
- The EU
- As a member of the EU, France is a beneficiary of the EU Trade Agreements
- European Single Market
- The EU Services Directive
- European Digital Single Market
- Economic and Monetary Union
- European Customs Union
- Indian Ocean Commission (Reunion Islands)
- Regional Cooperation Council
- SICA (observer country)


- WTO
- GATS
- Agreement on Sanitary Measures
- Agreement on Technical Barriers to Trade
- Agreement on Preshipment Inspection
- Agreement on Safeguards
- Trade Facilitation Agreement
- WCO
- ICC
- COTIF Convention
- BIC (Containers)
- Chicago Convention (ICAO)
- IMO
- Convention for Safe Containers
- Istanbul Convention
- Rotterdam Rules
- Hamburg Rules
- CMR Convention
- IRU
- TIR Convention
- Guidelines on Safe Load Securing for Road Transport
- International Union of Railways (UIC)
- ICS
- CIM & CIT Rules (Rail)
- Customs Convention on Containers - not a member

European Trade and Economic Organizations of France
- The EU
- UNECE
- OSCE
- Group of States of the European Council Convention against Corruption
- OECD
- OECD anti-corruption measures

- UN
- African Union
- Inter-American Development Bank (non-borrower)
- Asia-Europe Meeting
- WB
- ECLAC
- OIF
- WTO
- ESCAP
- Asian Development Bank
- African Development Bank
- IMF
- ICC
- ...
France is an associate / observer country:
- AEC
- Organization of the Black Sea Economic Cooperation
- Council of the Baltic Sea States
- PECC
- CPLP
The French Republic (Europe).
- Capital of France: Paris
- Official Language: French
- Area of France: 643,801 km²
- Population of France: 67 million people
- Borders of France: Monaco, Italy, Spain, Andorra, Belgium, Luxembourg, Germany and Switzerland
- France has a Maritime border with the UK (submarine tunnel)
- Abolition of Slavery in France: 1848 (Victor Schoelcher)
- Pierre Teilhard of Chardin
Type of Government of France: Semi‑presidential Republic
The main religion in France: Catholicism (Christianity).

France belongs to the European Economic Area.
Economy of France.
- The French Republic is a highly developed market being the:
- Fifth largest economy in the world by nominal GDP
- Eighth largest economy in purchasing power
- France is the third largest economy in the EU (behind Germany and the UK - BREXIT-)
- GDP (nominal) of France: 1,944 Billions Euros
- GDP per capita: 27,100 Euros
- France is the most visited country in the world (82 million tourists per year)
- The economy of the French Republic is heavily based on services (76% of the GDP, 75% of the population)
- Decentralized EU Agency in France:
- Community Plant Variety Office (CPVO): Angers


French Foreign Trade.
- France ranks second in the world regarding the service exports and agricultural products
- The French Republic makes 70% of his foreign trade with its European Union partners
- French foreign trade has a surplus in export products trade balance
- Germany imports 14% of the French exports, followed by Italy, Spain, the UK, Belgium, the U.S., the Netherlands, Switzerland and China
- Of the total of the imported products of France, 16% are originated in Germany followed by Belgium, Italy, China, Spain, the U.S., the UK, the Netherlands, Russia, Switzerland and Japan
- The main French Exports are machinery, mechanical appliances, vehicles, Air navigation and pharmaceutical products
- The French Republic is the second most attractive European country for foreign direct investment
- The largest French Port is Le Havre
- Headquarters of the International Union of Railways (UIC) and the International Bureau of Containers and Intermodal Transport (BIC)
(c) EENI Global Business School (1995-2024)
We do not use cookies
Top of this page



