Business in Rwanda. Kigali

Foreign Trade and Business in Rwanda: most densely populated African Country, Coffee, Tea
- Introduction to the Republic of Rwanda (Central Africa)
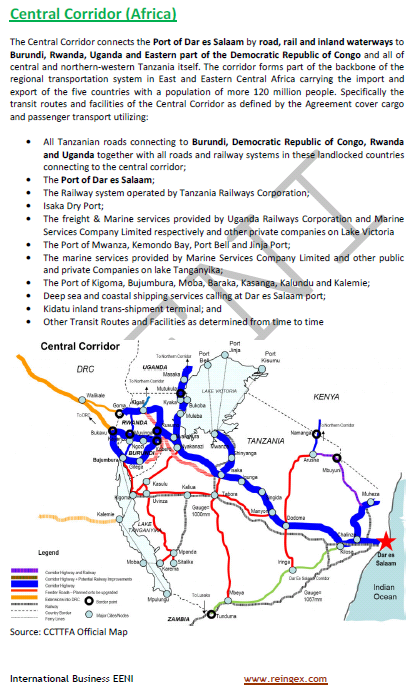
- Rwandan Economy
- International Trade of Rwanda
- Business and Investment Opportunities in Rwanda
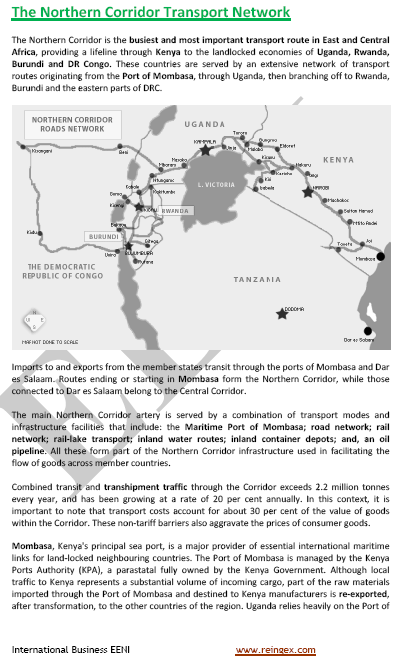
- Infrastructure
- Agriculture
- Energy
- Tourism
- Information and Communication Technology
- Mining
- Financial Services
- Property (real estate) and Construction
- Manufacturing
- Case Study: Bralirwa
- Rwanda Development Board (RDB)
- Access to the Rwandan Market
- Business Plan for Rwanda
The aims of the subject “Foreign Trade and Business in Rwanda” are the following:
- To analyze the Rwandan Economy and Global Trade
- To know the business opportunities in Rwanda
- To explore the Rwandan trade relations with the country of the student
- To know the Rwandan Trade Agreements
- To examine the profile of Rwandan Companies
- To develop a business plan for the Rwandan Market

The Subject “Foreign Trade and Business in Rwanda” belongs to the following Online Programs taught by EENI Global Business School:
Doctorate: African Business, World Trade.
Courses: Business in East Africa, Central Africa.

Masters: Business in Africa, Transport in Africa, International Business, Foreign Trade, International Transport.
Languages:  or
or  Rwanda
Rwanda  Ruanda
Ruanda  Ruanda.
Ruanda.

- Credits of the subject “Doing Business in Rwanda”: 1

- Duration: one week
Masters adapted to  Rwandese students.
Rwandese students.

International Trade and Business in Rwanda.
The Republic of Rwanda is the most densely populated African Country.



Rwandan Preferential Access and Trade Agreements:
- Rwanda and the Central African Economic Area / East African Economic Area
- Common Market for Eastern and Southern Africa (COMESA)
- East African Community (EAC)
- COMESA-EAC-SADC Agreement
- African Continental Free-Trade Area
- Economic Community of Central African States (ECCAS)
- Rwanda-EU
- Trade Agreement with India
- Rwanda-U.S.
- AGOA United States-Rwanda
- East African Community-US Agreement
- Conference on the Great Lakes
- Economic Community of the Great Lakes Region
- Nile Basin Initiative
- Global System of Trade Preferences among Developing Countries (GSTP) - accession process

- WTO
- GATS
- Agreement on Sanitary Measures
- Agreement on Technical Barriers to Trade
- Agreement on Preshipment Inspection
- Agreement on Safeguards
- Trade Facilitation Agreement
- WCO
- Single African Air Transport Market (SAATM / IATA)
- BIC (Containers)
- Chicago Convention (ICAO)
- IMO - not a member
- Istanbul Convention - not a member
- Customs Convention on Containers - not a member

- Economic Commission for Africa
- African Union
- AU Convention on Preventing and Combating Corruption
- AUDA-NEPAD
- Africa Agriculture Development Programme
- African Development Bank
- Africa-South America Summit
- China-Africa Cooperation
- Africa-India Cooperation
- Africa-BRICS
- Africa-Turkey Partnership
- BADEA
- Africa-Korea Partnership
- Africa-Japan Cooperation

- WB
- WTO
- IMF
- UN
- The Republic of Rwanda (landlocked country) is a poor rural African nation with 90% of the population working in the agriculture sector
- Rwanda is the most densely populated nation in Africa
- Few natural resources, small industry
- The Genocide (1994) shocked the economy of Rwanda and his population
- Capital of Rwanda: Kigali (1 Million people): one of the African safest cities
- The largest Rwandan cities are Kigali, Butare and Gisenyi
- Rwanda is landlocked country
- The official languages of Rwanda: Kinyarwanda, French, English, and Kiswahili
- Independence of Rwanda: 1962 (Belgium)
- Rwandan population: 12 million people
- Area of Rwanda: 26,338 km²
- Borders or the Republic of Rwanda: Uganda, Burundi, the DR Congo, and Tanzania
More information about Rwanda (EENI African Business Portal).
Religions in Rwanda.
- African Traditional Religions
- Christianity:
- Catholicism (4.7 million)
- Protestants (4 million, 43% of Rwandan population)

Rwanda belongs to the Central African Economic Area and the East African Economic Area.
Rwanda: a landlocked poor rural country.
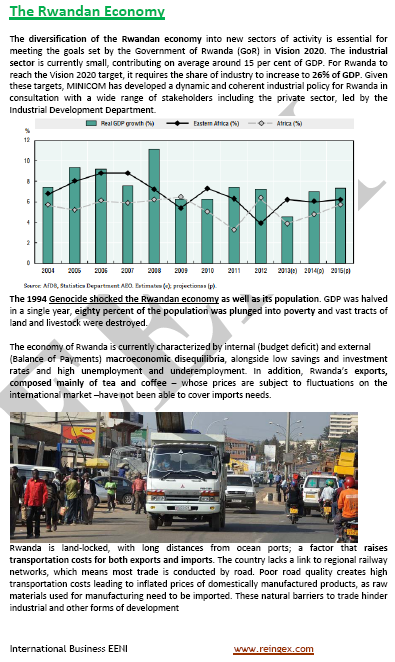
- Rwandan GDP growth: 7%
- GDP per capita of Rwanda: USD 644
- Rwandan Agriculture sector: 90% of the labour force
- Services sector in Rwanda: 45% of the GDP
- Rwandan Industry: 15% of the GDP
- The most Rwandan dynamic sector are construction and property (real estate)
- Inflation in Rwanda: 4.4%
- Top Rwandan export products: tea and coffee, minerals
- Trade with the East African Community (EAC) countries: 35% of the total exports
- Currency of Rwanda: Rwandan Franc (RWF)
- The favorable terms of international trade, Foreign direct investment and aid inflows have aided and stimulated the Rwandan economy considerably over the last decade
- The substantial growth was from an increase in cereal products production (maize and wheat)
Global Trade and Business in Rwanda:

Foreign Trade of Rwanda
Exports of Rwanda continue to remain small compared to the average of Central Africa and mainly stand for the two largest cash crops, tea, and coffee and, recently, mineral products.