Business in Nepal, Kathmandu

Nepalese Economy and Foreign Trade. Hinduism. Ties Nepal-India
- Introduction to the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal
- Nepalese Economy
- The main sectors of the Nepalese Economy
- Business in Kathmandu
- Foreign Trade of Nepal
- Investment in Nepal
- Case Study:
- Jyoti Group
- Kedia Organization
- Access to the Nepalese market
- Business Plan for Nepal
The objectives of the subject “International Trade and Business in the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal” are the following:
- To analyze the Nepalese Economy and Global Trade
- To know the trade opportunities in the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal
- To explore the Nepalese trade relations with the country of the student
- To know the Nepalese Trade Agreements
- To examine the profile of Nepalese companies
- To develop a business plan for the Nepalese market

The Subject “Foreign Trade and Business in Nepal” belongs to the following Online Programs taught by EENI Global Business School:
Courses: Hinduism and Business, Buddhism and Business.
Bhagavad Gita Courses: Karma Yoga, Bhakti Yoga, Jnana Yoga, Dhyana Yoga, Realization of the Gita
Masters: Ethics, Religions & Business, International Business
Masters adapted to 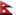 Nepalese students.
Nepalese students.
- Credits of the subject “Doing Business in Nepal”: 1

- Duration: one week

International Trade and Business in Nepal.

Nepalese Market Access and Trade Agreements.
- Nepal and the Hindu Economic Area
- Bay of Bengal Initiative
- South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation
- South Asian Free-Trade Area (SAFTA)
- Asian Clearing Union
- South Asia Economic Cooperation (SASEC)
- India-Nepal Free Trade Agreement
- Double Taxation Avoidance Agreement and FDI agreement between India and Nepal
- Bangladesh-Nepal Trade, Payments, and Transit Agreement
- SCO (Dialogue Partner)
- Generalized System of Preferences (EU)

- WTO
- GATS
- Agreement on the Application of Sanitary Measures
- Agreement on Technical Barriers to Trade
- Agreement on Preshipment Inspection
- Agreement on Safeguards
- Trade Facilitation Agreement
- WCO
- International Road Transport Union (IRU)
- International Maritime Organization
- Istanbul Convention - not a member
- Customs Convention on Containers - not a member

- Asia-Middle East Dialogue
- Asian Development Bank
- Boao Forum for Asia
- ESCAP
- Colombo Plan
- Asia Cooperation Dialogue (in the process of accession)

- UN
- WB
- WTO
- IMF
- WCO
- Nepal is eligible for the European Investment Bank
The Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal.
- Borders of Nepal: India and China
- Nepal is a Landlocked country
- Nepalese Capital: Kathmandu
- Area of Nepal: 147,181 km²
- Nepalese Population: 26.49 million people (74% works in the agriculture sector)
- The official language of Nepal is Nepali
- English is used in business
- Abolition of Slavery in Nepal: 1926
Jyoti Group (Nepal)

The main religion of Nepal is Hinduism, the second-largest is Buddhism (Mahayana).
- Lord Buddha was born in Nepal


Nepal belongs to Hindu Civilization/Buddhist civilization.

Nepalese Economy
- Nepal has deep economic and cultural ties with India
- Strong economic reforms and liberalization: financial system, FDI
- The main business opportunities in Nepal are tourism, agriculture, hydro-power, infrastructure, mining, and IT
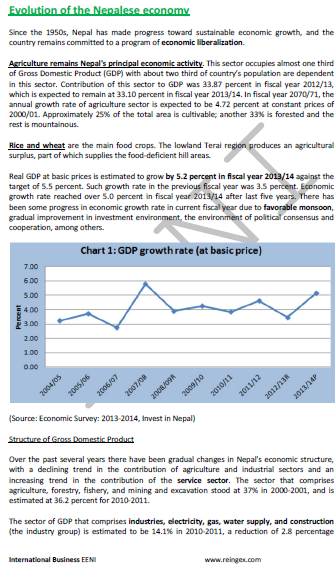
- The main Nepalese economic activity is agriculture (33% of the GDP)
- The main Nepalese crops are rice and wheat
- Open to FDI in near all the sectors of the Nepalese economy
- Nepal Investment Board is the official body
- Special Economic Zone
- Top Nepalese sectors attracting FDI are energy, services, manufacturing, tourism, construction agriculture, and minerals
- The main investors in Nepal are China, India, the U.S., South Korea, and Japan
- Nearest Port of Nepal: Calcutta (India), Chittagong, and Mangola (Bangladesh)
- Top Nepalese export products: Hand Knotted Woolen Carpet of Nepal, Readymade garments, Pashmina Products, Handicraft, and Leather Goods

(c) EENI Global Business School (1995-2024)
We do not use cookies
Top of this page




 or
or 
