Business in Cameroon

Foreign Trade and Business in Cameroon. Cameroonian Economy (40% of the CEMAC GDP). Douala and Yaoundé
- Introduction to the Republic of Cameroon (Central Africa)
- Cameroonian Economy
- International Trade of Cameroon
- Business and Investment Opportunities in Cameroon
- Agriculture and agribusiness sector
- Housing and construction sector
- Business services in Cameroon
- Mining sector
- Tourism
- Cameroon Investment Promotion Agency (CIPA)
- Case Study:
- Cameroon Telecommunications
- How to invest in Cameroon
- Cameroon Breweries
- Fadil Group
- Access to the Cameroonian Market
- Business Plan for Cameroon
- To analyze the Cameroonian Economy and Global Trade
- To know the business opportunities in Cameroon
- To explore the Cameroonian trade relations with the country of the student
- To know the Cameroonian Trade Agreements
- To examine the profile of the Cameroonian Companies
- To develop a business plan for the Cameroonian Market
Global Trade and Business in Cameroon:

The Subject “Foreign Trade and Business in Cameroon” belongs to the following Online Programs taught by EENI Global Business School:
Doctorate: African Business, World Trade.

Masters: Business in Africa, International Business, Foreign Trade.
Languages:  or
or  Cameroun
Cameroun  Camarões
Camarões  Camerún.
Camerún.
- Credits of the subject “Doing Business in Cameroon”: 2

- Duration: two weeks
Masters adapted to  Cameroonian Students.
Cameroonian Students.

International Trade and Business in Cameroon.
Cameroon: 40% of the CEMAC GDP



Cameroonian Preferential Access and Trade Agreements:
- Cameroon and the Central African Economic Area
- Central African Economic and Monetary Community (CEMAC)
- Economic Community of Central African States (ECCAS)
- African Continental Free-Trade Area
- AGOA (U.S.)
- Trade Agreements with Egypt, South Africa, Switzerland, China, Russia, India
- Africa-EU Partnership
- Niger Basin Authority
- OHADA
- Global System of Trade Preferences
- UK-Cameroon Agreement


- WTO
- GATS
- Agreement on the Application of Sanitary Measures
- Agreement on Technical Barriers to Trade
- Agreement on Preshipment Inspection
- Agreement on Safeguards
- Trade Facilitation Agreement
- WCO
- BIC (Containers)
- Chicago Convention (ICAO)
- International Maritime Organization
- Hamburg Rules (Sea)
- Rotterdam Rules


- Economic Commission for Africa
- African Union
- AU Convention on Preventing and Combating Corruption (not signed)
- AUDA-NEPAD
- African Development Bank
- Africa-Asia Partnership
- China-Africa Cooperation
- Africa-India Cooperation
- Africa-BRICS
- Africa-Turkey Partnership
- Africa-South America Summit

- Islamic Development Bank
- OIC
- Afro-Arab Cooperation
- BADEA

- Commonwealth (since November 1995)
- UN
- WB
- WTO
- IMF

The Republic of Cameroon is situated in Central Africa, sharing borders with Chad, the Central African Republic, Congo, Gabon, Equatorial Guinea, and Nigeria.
- The Republic of Cameroon has an area of 475,440 km² and a population of 24 million people
- Cameroonian Languages: French (80% of the Cameroonian population) and English (20%)
- Cameroonian Independence: 1960 (France)
- Cameroonian Capital: Yaoundé (2.5 million people)
- Douala is the largest city: 3 million people, Port of Douala
- Largest cities: Bafoussam, Garoua, Ngaoundéré, Bamenda, and Marua
More information about Cameroon (EENI African Business Portal).
Main religion in Cameroon.
- African Traditional Religions
- Christianity
- Catholicism (4 million)
- Protestants (3 million, 27% of the Cameroonian population)
- Islam (mainly in Northern regions)



Cameroonian Economy:
- The Cameroonian economy is based on the primary sector (42% of the GDP)
- Main revenue sources of Cameroon: agriculture, livestock, fisheries, forestry, mining, and industry
- Fighting against corruption and poverty is a preference for the Government of the Republic of Cameroon
- The Cameroonian agriculture is the main sector of the Republic of Cameroon, employs 70% of the workforce and contributes 42% to the GDP formation of Cameroon
- Main cash crops of Cameroon: cocoa, coffee, cotton, bananas, rubber, potato, and pepper
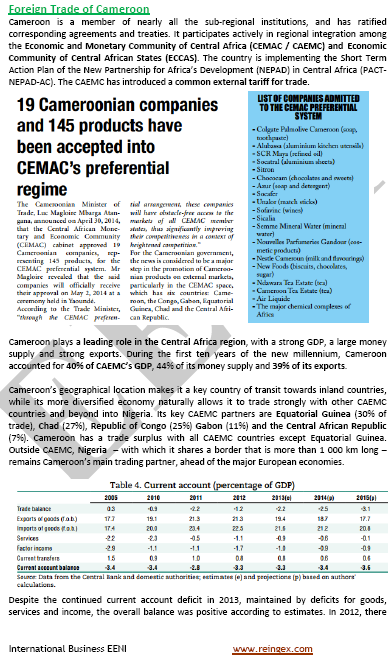
- Cameroonian GDP growth: 5%
- Tertiary sector (47.8% of the GDP)
- Primary sector (22.5%)
- Secondary sector (29.7%) - Cameroon represents 40% of the CEMAC GDP and 39% of the total CEMAC exports
- Cameroonian Inflation: 2,3%
- Most dynamic economic sectors in Cameroon: trade, construction, agriculture, manufacturing, and extractive industries (petrol and gas)
- Cameroonian currency: CFA FRANC
- The objective of the National Investment Corporation of Cameroon is to mobilise and focus on national savings
The Republic of Cameroon has four independent ports. The Autonomous Port of Douala represents 95% of Shipping freight and international trade of Cameroon.
The telecommunications sector develops very quickly in Cameroon. The Cameroon Telecommunications is a public company owned 100% by the State of Cameroon. Created in 1998, Cameroon Telecommunications (CAMTEL) is strongly implicated in the development and modernization of telecommunications markets in Cameroon. CAMTEL just signed an agreement with a Chinese company.
Brasseries du Cameroon (Cameroon breweries) is a food processing company specialising in soft drinks manufacture and distribution. The company is the leading industry in Cameroon. Created in Douala (Cameroon) in 1948, became an affiliated company of the Castel Group in 1990.