Business in Bolivia. Bolivian Economy

Bolivian Foreign Trade, Business in La Paz (Bolivia)
- Introduction to the Plurinational State of Bolivia
- Bolivian Economy
- Business in La Paz
- International Trade of Bolivia
- Investment in Bolivia
- Case Study: Business Opportunities in Bolivia
- Petrol
- Gas
- Manufacturing
- Telecommunications
- Agriculture
- Services
- Case Study:
- Bolivian integration corridors
- ENTEL Telecommunications
- Access to the Bolivian Market
- Business Plan for Bolivia
The aims of the subject “Foreign Trade and Business in Bolivia” are the following:
- To analyze the Bolivian Economy and Global Trade
- To know the trade opportunities in Bolivia
- To explore the Bolivian trade relations with the country of the student
- To know the Bolivian Trade Agreements
- To examine the profile of the Bolivian Companies
- To develop a business plan for the Bolivian Market

The Subject “Foreign Trade and Business in Bolivia” belongs to the following Online Programs taught by EENI Global Business School:
Masters: International Business, Foreign Trade.
Doctorate: American Business, World Trade.

Languages:  (or
(or  Bolivia
Bolivia  Bolivia
Bolivia  Bolivie).
Bolivie).
- Credits of the subject “Doing Business in Bolivia”: 1

- Duration: one week

International Trade and Business in Bolivia

Bolivian Market Access and Agreements.
- Bolivia and the Latin American Economic Area
- Andean Community
- Andean Community Agreements: MERCOSUR, Mexico, the EU, Chile, Panama, India, China, Russia
- Bolivia-MERCOSUR (Associate). Protocol of accession to the MERCOSUR
- Latin American Integration Association (ALADI)
- Mexico-Bolivia Economic Complementation Agreement
- Latin American and Caribbean Economic System
- Union of South American Nations (UNASUR)
- Global System of Trade Preferences
- SICA (observer country)
- Bolivia retired from the Bolivarian Alliance for the Peoples of Our America (ALBA) in 2019

- WTO
- GATS
- Agreement on the Application of Sanitary Measures
- Agreement on Technical Barriers to Trade
- Agreement on Preshipment Inspection
- Agreement on Safeguards
- Trade Facilitation Agreement
- WCO

- Inter-American Development Bank
- OAS
- ECLAC
- CELAC
- East Asia-Latin America Cooperation
- Summit South American-Arab Countries
- Africa-South America Summit

- UN
- WB
- WTO
- IMF
Plurinational State of Bolivia (America).
- Bolivia has nine departments (Beni, Cochabamba, Chuquisaca, La Paz, Oruro, Pando, Potosi, Tarija, and Santa Cruz) and 112 provinces
- Borders of Bolivia: Brazil, Argentina, Peru, Paraguay, and Chile
- Bolivian population: 10 million people
- Bolivian Area: 1,098,581 km²
- Official languages of Bolivia: Spanish, Quechua, Aymara, Guarani, and thirty-three local languages
- According to the Bolivian Government: “Bolivia is a Social Unitary State of Plurinational Communitarian Law decentralized and autonomous”
- Abolition of Slavery in Bolivia: 1826
- African Diaspora in Bolivia: 0.5% of the Bolivian population
- Independence of Bolivia: 1825 (from Spain), recognized in 1847
Religion in Bolivia: Christianity (9.5 million).
- Catholicism (7 million)
- Protestants
Bolivia belongs to the Latin American Economic area of the Western Civilization.

Bolivian Economy.
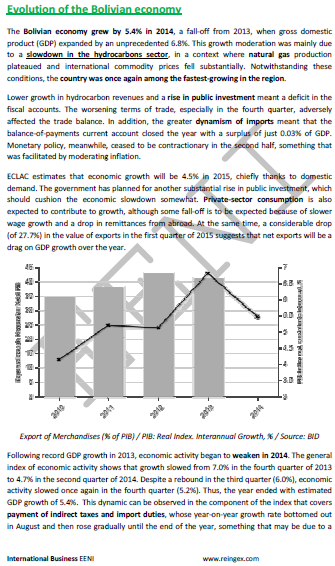
- According to the Central Bank of Bolivia, the balance of payments showed a surplus of 325 million dollars
- Bolivian GDP: 34,175 million dollars
- In 2009, the Bolivian Government signed a debt cancellation with the Government of Spain
- The Plurinational State of Bolivia has significant natural resources: mining and gas
- Through the Bioceanic Logistics Corridor, the Plurinational State of Bolivia has positioned itself as a regional distribution hub between the largest markets of the Pacific and the South Atlantic region of South America
- Nationalizations have taken place since 2006 in the hydrocarbons, mining, and telecommunications sectors; business opportunities in these areas for the foreign direct investment have become more limited
- FDI flows received in Bolivia were 687 million dollars, mainly in the hydrocarbons sector
- Currency: Bolivian (BOB)
- Entel holds a Leadership position in both fixed and mobile telephony, as in the various telecommunications value-added services
Global Trade and Business in Bolivia:


International Trade of Bolivia:
- Total Bolivian exports products reached 4.848 million dollars FOB (28% of the Bolivian GDP)
- Export flows were characterized by low levels (average of USD 1.919 million)
- Total petrol exports were lower
- Regarding the non-traditional exports, their value was higher by 1.4%
- Non-traditional export products that showed increases in value were: soybean meal (52%), sugar (41%), soybean oil (31%), soya beans (23%), flour soy (20%), and coffee (5%)
- Capital products imports stand for 28% of the total
- The balance of payments of Bolivia recorded an extra of 325 million dollars (Central Bank of Bolivia)
Foreign Trade flows of Bolivia with the rest of the World (data in dollars).
- Trade with the MERCOSUR fell to 708 million, mainly owing to lower natural gas exports to Brazil
- With the Andean Community, there was an increase of positive balance of 158 million due primarily to the higher exports to Colombia and Ecuador
- With the Central American Common Market - Central American Integration System (SICA), ran an international trade deficit of 0.2 million to an extra of 2.7 million
- With the U.S.-Mexico-Canada Agreement (USMCA/NAFTA 2.0), the deficit augmented to 131 million due both to the decline in exports as the largest imports
- With the EFTA augmented extra owing to augmented to 6 million dollars extra with Switzerland
- In Asia, the positive balance of 130 million mainly explained by the favorable balance with South Korea
(c) EENI Global Business School (1995-2024)
We do not use cookies
Top of this page


