Business in Argentina, Buenos Aires

Argentinian Economy. Exporter, cereals, wine (International Trade), Mendoza
- Introduction to the Argentine Republic (South America)
- Argentinian Economy
- Economic Profile of the Argentinian provinces
- International Trade of Argentina
- Investment in Argentina
- Case Study:
- Argentinian Automotive Industry
- Biotechnology
- Software and information technology services
- Creative industries
- Business in Buenos Aires
- Case Study:
- Audiovisual industry in Buenos Aires
- Arcor Group
- Access to the Argentinian Market
- Business Plan for Argentina
The objectives of the subject “International Trade and Business in Argentina” are the following:
- To analyze the Argentinian Economy and Global Trade
- To know the trade opportunities in Argentina
- To explore the Argentinian trade relations with the country of the student
- To know the Argentinian Trade Agreements
- To examine the profile of the Argentinian Companies
- To develop a business plan for the Argentinian Market

The Subject “Foreign Trade and Business in Argentina” belongs to the following Online Programs taught by EENI Global Business School:
Masters: International Business, Foreign Trade.
Doctorate: American Business, World Trade.

Languages:  or
or  Argentina
Argentina  Argentina
Argentina  Argentine.
Argentine.
- Credits of the subject “Doing Business in Argentina”: 2

- Duration: two weeks

International Trade and Business in Argentina.

Preferential Access and Trade Agreements of Argentina.
- Argentina and the Latin American Economic Area
- MERCOSUR
- MERCOSUR Trade Agreements: Andean Community, Mexico, Peru, Chile, India, Egypt, Israel, the EU, SACU
- Latin American Integration Association (ALADI)
- Union of South American Nations (UNASUR)
- Latin American and Caribbean Economic System
- Argentina-Mexico Economic Complementation Agreement
- Global System of Trade Preferences
- Andean Community (associate member)
- SICA (observer country)

- WTO
- GATS
- Agreement on Sanitary Measures
- Agreement on Technical Barriers to Trade
- Agreement on Preshipment Inspection
- Agreement on Safeguards
- Trade Facilitation Agreement
- WCO
- Kyoto Convention
- IRU
- TIR Convention
- Guidelines on Safe Load Securing for Road Transport

- Inter-American Development Bank
- OAS
- ECLAC
- East Asia-Latin America Cooperation
- Summit South American-Arab Countries
- Africa-South America Summit
- CELAC

Global Economic Organizations (Argentina)
- UN
- WB
- IMF
- OECD
- African Development Bank
- CPLP (observer country)
- Borders of the Argentine Republic: Bolivia, Paraguay, Brazil, Chile, and Uruguay
- Argentinian capital: Buenos Aires
- Argentinian official language: Spanish
- Argentina has a population of 42 million people
- Argentina is the eighth largest country in the World
- Currency of Argentina: Argentinian Peso
- Abolition of Slavery in Argentina 1853
- African Diaspora in Argentina: 0.1% of the Argentinian population
- Independence of Argentina from Spain: 1816, recognized in 1857
Main religion in Argentina: Christianity (Catholicism: 38 million, Maronites: 750,000).
Argentina belongs to the Latin American Economic area of the Western Civilization.
Buenos Aires is one of the largest cities in Latin America.
- Including its metropolitan area (Greater Buenos Aires), Buenos Aires has 13 million people, one of the ninth most populated urban conglomerates in the World
- Buenos Aires is the thirteenth urban centre with the largest revenue in USD in the World, ahead of Hong Kong, Miami or São Paulo, and its growth forecasts are excellent
- Buenos Aires is home to big Argentinian companies
The main economic sectors of Buenos Aires are:
- Creative industries
- Software
- Pharmaceutical industry

Argentinian Economy.
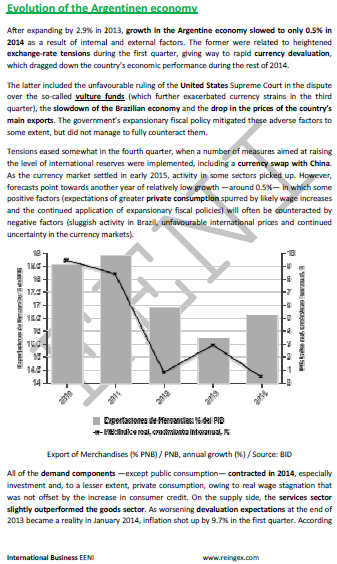
- Argentina is a Frontier Market
- The compound annual growth rate was 8%, below China (10.7%) and India (8.4%)
- 1,000 foreign corporations are in Argentina, including 50% of the Fortune 100 firms
- The Argentinian Automotive Industry is a key contributor to the manufacturing production and exports;
- The Automotive sector represented 2.5% of the Argentinian GDP (including the automotive parts manufacturing), 8.5% of the industrial output and 10% of the total exports
- Ten car makers in Argentina: Fiat, Ford, General Motors, Iveco, Mercedes-Benz, PSA Peugeot-Citroën, Renault, Scania, Toyota, and Volkswagen
- The Argentine Republic counts with an extensive competitive food and beverage industry, with total sales of USD 53 billion (31% of total manufacturing sales production) and exports USD 21 billion (30% of the total manufacturing export production)
- Software and computer services industry in Argentina has 40,000 workers in near 1,000 companies
- Creative industries are principally concentrated in Buenos Aires (7.5% of the district's GDP and 8% of the total employment)
- Other big cities in Argentina, Cordoba, Mendoza or Rosario, are also developing the creative industries sector
- Significant accumulation of reserves
- A fixed monetary policy
- A competitive exchange rate
- Argentina has significant natural resources
- Argentina is a member of the MERCOSUR
Global Trade and Business in Argentina

Argentinian Emerging Sectors:
- Biofuel
- Software
- TV
- New technologies

International Trade of Argentina.
- Argentinian exports decreased by 12% (cereals, fuel, energy, industrial manufacturing, slowdown in Brazil) and imports decreased by 11.4%
- The Services export sector registered a record-high volume of 12 billion dollars (one of the highest levels in Latin America)
- The largest Argentinian trading partners are Brazil, China, Chile, the U.S., and Germany
- Records of the foreign direct investment in twenty-five years
Argentina is a member of the MERCOSUR (Argentina, Brazil, Paraguay, and Uruguay), having access to a widespread market with 295 million people and the chance of exporting to and importing from the MERCOSUR economies without having to pay customs duties. Since the creation of the MERCOSUR, foreign trade between Argentina and the other members of the MERCOSUR went up by 500%
(c) EENI Global Business School (1995-2024)
We do not use cookies
Top of this page


