Investments abroad (FDI). Portfolio Investment
Investments: allocation of capital into assets situated in foreign countries

Global Marketing -
Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) -
UNCTAD
Investments abroad refer to the allocation of capital by individuals, corporations, or governments into assets situated in foreign countries. These Cross-Border investments play a crucial role in driving Globalization and fostering international economic integration.
Types of Investments Abroad:
- Foreign Direct Investment (FDI):
- This involves acquiring a significant and lasting interest—typically defined as owning 10% or more of a foreign company—or establishing business operations overseas, such as factories, Subsidiaries, or Joint Venturess. FDI usually grants the investor control or substantial influence over the company’s management.
- Portfolio Investment:
- This type of investment consists of purchasing foreign financial assets, such as stocks, bonds, or other securities, without obtaining control over the issuing companies. Portfolio investments are generally more liquid than FDI and primarily aimed at generating financial returns.
- Other Investments:
- This category includes cross-border loans, trade credits, bank deposits, and other forms of financial claims or liabilities that do not fall under FDI or portfolio investment.
- Influence of religion on financial systems
The international expansion process can finalizes with creation of one or various sales delegations wherefrom, by area, the commissioned representatives are controlled.
Various legal ways exist for their establishment, all of which are destined to assure a steady presence with a rigorous tax control and parent company protection.
We will analyze the three most frequent cases for establishment from a commercial perspective:
- Foreign company branch
- Subsidiary
- Joint Ventures
In addition, the following case studies will be studied:
- Case Study: Mining Industry and Resource-Seeking FDI in Africa (The Case of Rio Tinto in Guinea)
- Case Study: Toyota’s Foreign Direct Investment in the United States

The Subject “Investments abroad” is included within the curriculum of the following academic programs at EENI Global Business School:
Postgraduate Certificate in Global Marketing.

Masters: International Business, Foreign Trade.

Languages:  or
or  Inversión extranjera directa
Inversión extranjera directa  Investissement direct à l’étranger.
Investissement direct à l’étranger.
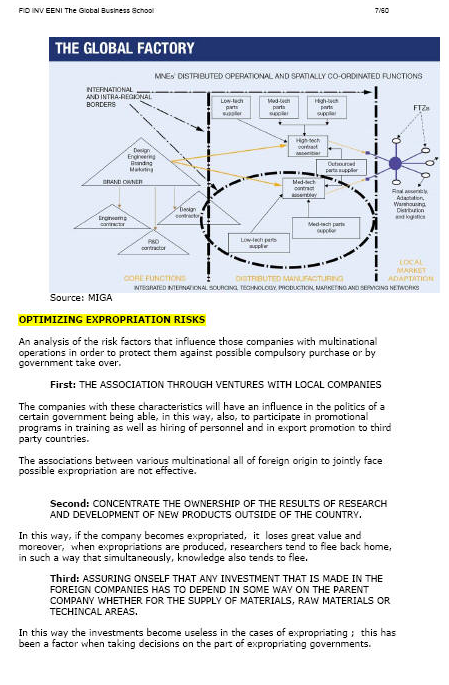
An analysis of Risk factors that influence those enterprises with multinational operations to protect them against the possible compulsory purchase or by a Government takes over.
Case study: Establishing a company in the United States. One company is made up of 150 full-time workers and manufacture bronze statues that are on a marble support. The designs are exclusive and using them; they make a substantial production of each one; even though it is a gift item with certain exclusive value; they are pieces whose originals were produced in large quantities. In this case; we will analyze eleven decisions taken by the Board of Directors.
We tend to associate Developing Countries with poverty and suffering. This image is reinforced by media because they inform us only about disasters in these countries and present their people as victims of circumstances beyond their control. The reality of developing world is a lot more varied and complex. In the first place, one has to be careful with generalizations.
Socio-cultural context of each developing country has prime importance in the sale of a Product. Religion, local traditions, history, superstitions, all these form part of a system of values that are called culture.
Sample - Investments abroad:
The obtaining permits or licences and establishing a business process in a developing country can be as long as it is costly. Much of the Government earnings come from such licences. The trouble of corruption can also present itself.
Increasingly, the social balance of a company, demands new management parameters of CORPORATE GOVERNANCE that can convert the enterprises into real engines of development and well-being in the place they are operating.
Multinational Organizations like the EU, the Inter-American Development Bank, the African Development Bank, and IMF, amongst others, direct significant quantities of economic resources towards social and Economic restructuring in Developing Countries, so that in this way they can speed up growth. Therefore, one is transferring “know-how” towards countries in need for this knowledge.
The considerations that should be taken into account before productive Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) surpass commercial decisions.

AI for Global Business -
Foreign Direct Investment (FDI)

(c) EENI Global Business School (1995-2025)
Top of this page










 WhatsApp
WhatsApp