International Contracts. Vienna Convention
Contracts and International Trade, Distributor, Guarantees, Arbitration
A contract is a single document, in which the rights and obligations of the exporter and importer are stipulated. International Trade practice shows that majority of transactions are carried out without signing a contract.
- Introduction to International Contracts
- Risks related to International Trade
- Instruments of Risk minimization
- Guarantees in Foreign Trade
- UN Commission on International Trade Law (UNCITRAL)
- Clauses of an international contract
- Anti-corruption clause of the International Chamber of Commerce
- Arbitration
- Analysis of International Sales Contracts
- Examples of contracts:
- International Distributor
- Importer
- Agent
- Religion and international contracts
- Introduction to Sharia (Islamic law)
- Examples of contracts: distributor, importer, and broker
- Case Study: Dispute over Late Delivery in an International Sales Contract
- Case Study: Financing Contract between a Saudi company and a European company
Legislative texts related to International sale of goods (UNCITRAL)
- United Nations Convention on Contracts for the International Sale of Goods (1980) [CISG]
- Vienna Convention on Law of Treaties
- Hague Conference on Private International Law
- Convention on the Limitation Period in international Sale of Goods
- UNCITRAL Model Law on International Commercial Arbitration
- UNCITRAL Model Law on International Commercial Conciliation
Rules and conventions related to International Transport.

This Subject objectives at familiarizing the student with International Contracts as they are used in International Trade transactions.
- To learn how to implement the main clauses of an international sales contract and how to minimise the risks
- To know main international institutions and conferences related to International Contracts
- To know how to manage an international arbitration process
- To know functioning of an arbitration process

The Subject “International Contracts” is included within the curriculum of the following academic programs at EENI Global Business School:
Masters: International Business, Foreign Trade, International Transport.

Postgraduate Certificate in International Trade.


Languages:  or
or  Contrat international
Contrat international  Contratos internacionales
Contratos internacionales  contratos.
contratos.
- Subject Credits “International Contracts”: 3 ECTS
- Duration: 3 weeks
- However, it is strongly recommended establishing an international contract of sale for all international transactions
- One can avoid doubts and misunderstandings concerning what has been agreed during the negotiation of terms if they are set down in writing
- In certain cases, a verbal agreement is legally binding, for example, when an exporter makes a sale at an international fair
- Most Foreign Trade transactions do not use a formal contract in practice. However, the clauses in the commercial invoice and the incorporation of an appropriate Incoterm in the export price as well as national legislation will nevertheless imply certain obligations of the parties
- In any case; we recommend using a formal contract
- A standard model contract for international sales has been drafted by the International Chamber of Commerce
Anti-corruption Clause of the International Chamber of Commerce.

CLAUSES.
An international contract is drafted based on the following:
- Regulations and practice of International Trade (for example, Incoterms)
- Arbitration in International Trade (for example, possible Dispute Resolution)
Here are the usual clauses of an international contract. However, one should call upon the services of a legal advisor to produce a well-prepared contract.
- Preamble
- Definitions
- Duties and obligations
- Communication and documentation
- Prices
- Terms of payment
- Penalties
- Force majeure
- Official authorizations and permits
- Dispute resolution
- Language
- Other condition
Arbitration is a method of dispute resolution relating to International Contracts of sale. A well-prepared clause on arbitration provides a basis to conduct arbitration duty in the case of litigation.
The Vienna Convention on International Sales Contracts of Goods regulates the formation of international contracts of sales. The Convention was signed in Austria on 11 April 1980. Forty countries have adopted it, the majority of which are developed.
The layout of a contract is left entirely up to enterprises; it can also be accepted in a verbal form; although there are signatories countries to the Vienna Convention who do not accept verbal agreements and only recognise a written form of a contract. For a contract to be considered accepted the consignee's consent must be obtained. Silence cannot be interpreted as consent.
The delivery of products must be performed according to what has been stipulated in the contract of sale, and products must be of the agreed quality, quantity, and type. The products must be inspected as soon as possible and, if the products are non-compliant; it must be communicated to the exporter within a reasonable period.

Religions and Global Business -
Religious diversity
Religion plays a significant role in international contracts by influencing the ethical values, cultural practices, and legal norms of the parties involved. To ensure the success of these contracts, it is essential that negotiators be culturally competent, respect religious differences, and adopt an ethical approach that fosters mutual trust. Although religion can create challenges, it also offers opportunities for intercultural cooperation and dialogue, particularly through cultural diplomacy and corporate social responsibility.

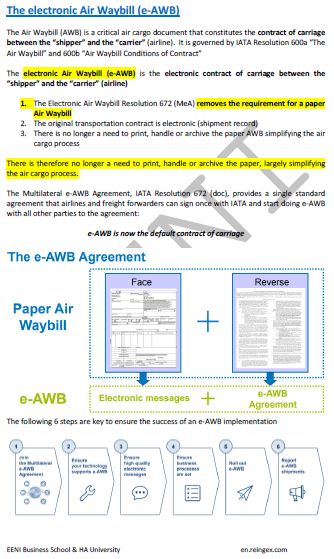
FIATA Transport Documents and International Contracts:
- FIATA FBL: FBL is a transportation contract
- FIATA FWB: FWB is a transportation contract
- e-Bill of Lading
- FIATA FCR: it is not accepted as a transport document according to the rules of letters of credit
- FIATA FCT: FCT is a transportation contract
- Warehouse Receipt
(c) EENI Global Business School (1995-2025)
Top of this page










 WhatsApp
WhatsApp