International Product/Service Policy. Brand
Global Product Strategies: Standardization, adaptation, diversification
A Global Product Policy is a strategic framework that defines the principles, guidelines, and standards a company follows in developing, marketing, and managing its products or services across international markets. It serves to ensure consistency in brand identity and product quality, while allowing for necessary local adaptations based on market needs, regulatory environments, and cultural preferences.
The objective of a global product policy is to balance global brand integrity with local responsiveness, thereby enhancing customer trust, ensuring legal compliance, and increasing the likelihood of commercial success in diverse markets.
The Subject “International Product Policy” consists of two parts:
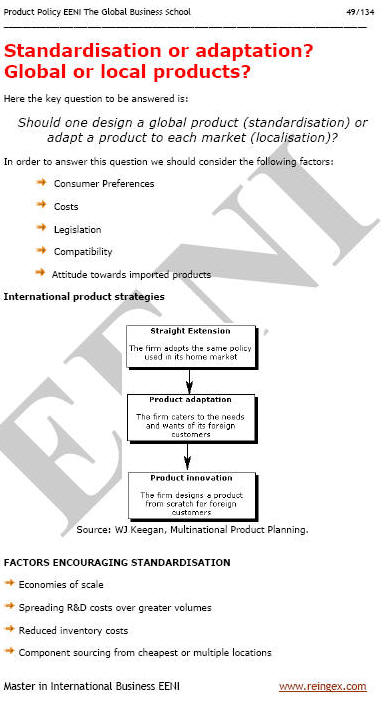
1- International Product Strategies.
- Introduction to international product/service strategies
- Case Study: McDonald’s Global Product Policy
- Case Study: Apple Inc.'s Global Product Policy for the iPhone
- Standardization, adaptation, and diversification of products and services
- Globally standardized products and services
- Product Adaptation to Different Markets
- Case Study: Nestlé’s Product Policy for Halal Products in Islamic Markets
- Case Study: Toyota – Product Adaptation in Global Markets
- Case study: Product Adaptation for Islamic Markets. The Case of Unilever.
- Brand and product/service policy
- Business portfolio
- BCG Growth-Share Matrix
- McKinsey matrix
- Experience curve
- Case Study: The Global Smartphone Industry
- E-Product. Digital value. Pervasive computing
- Case Study:
- Silicon Graphics
- Comfort (Unilever)
- AESSEAL
- Johnson and Johnson
- General Motors Corporation
- Tantrix
- Linux
- Nintendo
2- Quality and International Marketing
- Quality and International Marketing
- Standards and certifications
- Case Study: CE Mark

Objectives: the Subject “International Product Policy” sets out to analyze the key areas of international product / service policy.
- To know how to design product/services strategies for international markets
- To learn the importance of adapting an export product or service to local or regional requirements when entering new export markets
- To know how to add value to a traditional product with value digital services
This will be achieved by:
- Examining product/service adaptation options available to the exporter
- Analyzing product/service characteristics that typically need to be modified for different international markets

The Subject “International Product Policy” is included within the curriculum of the following academic programs at EENI Global Business School:
Postgraduate Certificate in Global Marketing.

Masters: Foreign Trade, International Business.


Languages:  or
or  Politiques du produit d’exportation
Politiques du produit d’exportation  Producto de exportación
Producto de exportación  Políticas de produto.
Políticas de produto.
Credits of the Subject “International Product Policy”: 2

Duration: 2 weeks.
Area of Knowledge: International Marketing.
A well-crafted global product policy is a critical driver of international business success. It ensures that product strategies are aligned with the realities of diverse global markets—such as customer preferences, competitive landscapes, and regulatory requirements—while maintaining brand consistency, quality standards, and legal compliance.
By striking the right balance between global standardization and local adaptation, companies can enhance market responsiveness, streamline product management, and strengthen their global brand presence.
Perhaps, the most important question for the exporter is:
Is it a global (regional) product or service or shall I localize it to every market or region?
The exporter should ask himself if the product or service is exportable. A product (or service) which is successful in the local market will not always be as successful in international markets. Although the exporter works in the Globalization age, each market is different (culture, perceptions, or the way of doing business).
Therefore, only through international market research, the exporter can find out if the product or service has potential or not in each target market.
Furthermore, exporter should look at what types of modifications and/or adaptations should carry out on the product or service in his International Marketing strategy.
Product adaptation is the process of modifying a product to better suit the specific needs, preferences, and conditions of a target market in a different country or region. The objective is to enhance appeal, usability, compliance, and ultimately, market success in diverse international environments.
Why Product Adaptation Is Necessary
- Cultural Differences
- Language and Communication
- Legal and Regulatory Requirements
- Economic Environment
- Technological and Infrastructure Differences
- Environmental and Climatic Conditions
Two common mistakes related to product (or service) and exporting.
- The first, and main one, is to believe that what is right for home market will also be suitable for international markets
- The other is that they do not keep in mind different channels available for their product distribution (importers, Subsidiaries)
When an exporting firm makes a Market Research, one of the most important tasks it will face will be the analysis of goods or services of the competition in each target market. Especially when entering new markets, familiarity with the products or services of the competitors is vital. Many exporters ignore this key point.
Two questions are fundamental:
- How competitive is our product or service?
- What advantages, unique to our product or service, are granted on customer/Importer?
Case Example: Apple Inc. – Global Product Policy in Action
Apple, a leading global technology company, exemplifies the effective use of a global product policy through its flagship product—the iPhone, sold in over 150 countries.
The iPhone’s global success is built on a policy that ensures uniform quality, design, and user experience across markets, reinforcing Apple’s strong brand identity. At the same time, Apple tailors elements such as network compatibility, regulatory compliance (e.g., data privacy and local certifications), language settings, and marketing content to meet the specific needs and preferences of regional markets.
This strategic balance of standardization and localization allows Apple to maintain brand integrity while effectively navigating international market dynamics.
Case Example: Nestlé – Leveraging Global Product Policy in Islamic Markets
Nestlé operates in over 190 countries, including key Islamic markets such as Malaysia, Indonesia, Saudi Arabia, and the United Arab Emirates. These countries are part of a broader global Muslim population of 1.9 billion. The global halal market is projected to grow to $30 trillion by 2030, driven largely by a young, tech-savvy demographic, with 60% of the population under 30 in many Muslim-majority countries.
Nestlé’s continued success in these markets is underpinned by a robust global product policy that ensures:
- Halal compliance in product formulation and manufacturing processes, supported by certification and transparent supply chains.
- Cultural alignment, including sensitivity to local dietary norms, religious values, and consumer expectations.
- Ethical and localized marketing, tailored to resonate with Islamic values while maintaining global brand consistency.
By aligning its global standards with regional expectations, Nestlé not only builds consumer trust but also strengthens its competitive Positioning in one of the world’s fastest-growing consumer segments.
Nestlé's strategy not only addressed religious restrictions but also capitalized on the commercial opportunities of the Halal market, which is expected to reach a value of $2.8 trillion by 2030. This approach can be applied to other religions, such as the development of kosher products for Jewish communities or vegetarian foods for Hindu and Buddhist markets.
Case Example: McDonald’s – “Glocal” Strategy through Global Product Policy
To maintain its global brand identity while effectively appealing to local tastes and cultural preferences, McDonald’s has developed a comprehensive global product policy rooted in a “think global, act local” (glocal) strategy.
This policy guides critical aspects of the company’s operations, including:
- Product development, with standardized core menu items like the Big Mac alongside localized offerings such as the McAloo Tikki in India or the Teriyaki Burger in Japan.
- Marketing, balancing global brand messaging with region-specific campaigns tailored to local languages, values, and traditions.
- Supply chain management, ensuring consistent quality and safety standards while sourcing locally to meet regional regulatory and sustainability requirements.
- Regulatory compliance, adapting to health, food safety, and labeling standards across diverse legal environments.
Through this globally coordinated yet locally responsive approach, McDonald’s achieves brand consistency, operational efficiency, and high levels of customer satisfaction in over 100 countries.
E-Product.
In many cases; we will add value to our products (atoms) with digital services (bits). We will also see industries in transition, which are no longer selling atoms to sell bits. In almost every case enterprises are re-inventing in some way, their products (their atoms) to add digital value to them through bits.
(c) EENI Global Business School (1995-2025)
Top of this page










 WhatsApp
WhatsApp