Globalization and International Business
Economic, cultural and political dimensions of Globalization. Regionalism

This module explores the complex, multi-dimensional nature of globalization and its impact on international business operations. Students will critically examine economic, political, technological, cultural, and environmental forces driving globalization and analyze their implications for business strategy, governance, and ethics. The module fosters an advanced understanding of how firms navigate globalization challenges and opportunities in diverse markets.
Syllabous
1- Introduction to Globalization. Global Economic Institutions
- Definitions and phases. Globalization
Regionalization,
and Deglobalization
- Case Study: Poland and EU Cohesion Policy (Regionalization)
- Case Study: Deglobalization in the U.S. Semiconductor Industry (2018-2025)
- Positive and adverse effects of Globalization
- Case Study: Ghana's Economic System Transition
- Case Study: Vietnam’s Economic System Transition
- AI and Global Trade
- Theories of Globalization
- World-Systems Theory, Hyperglobalism, Scepticism, Transformationalism
- Case Study: Huawei and U.S.–China Trade & Tech Tensions
- Global Economic Institutions
- World Trade Organization (WTO)
- Liberalization. The role of WTO
- Trends to Regionalization
- World Trade Agreements
- Case Study: WTO vs. United States on Steel Tariffs
- International Trade Centre (ITC)
- World Customs Organization (WCO)
- International
Monetary Fund (IMF)
- Case Study: IMF and Argentina – Sovereign Debt Restructuring and Economic Crisis
- World Bank (WB) Group
- World Bank’s Role in Global Trade
- Case Study: World Bank’s Role in African Global Trade
- United Nations
- Specialized Agencies
- UN Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD)
- Global System of Trade Preferences (GSTP)
- Case Study: UNCTAD and the Aid for Trade Initiative
- International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO)
- International Maritime Organization
- World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO)
- Arab Gulf Programme
- UN Commission on International Trade Law (UNCITRAL)
- Regional Blocs: EU, ASEAN, NAFTA/USMCA, African Continental
Free Trade Area (AfCFTA)...
- Case Study: The European Union’s Handling of Brexit
- Case Study: African Continental Free Trade Area (AfCFTA)

- World Trade Organization (WTO)
2- Political Dimensions of Globalization
- Global Governance, State Sovereignty, Populism, and Trade Wars
- Case Study: The U.S.–China Trade Conflict
3- Technology, AI and Globalization
- Globalization and tech development
- Case Study: The Rise of Zoom (Technology and Globalization)
- Digital Globalization
- Case Study: Spotify’s Global Expansion
- Global Innovation Networks (GINs)
- Case Study: Apple Inc. and Its Global Innovation Network
- AI and Globalization
- Case Study: Google – AI Powering Globalization
- Case Study: DeepL’s Translation Revolution
4- Cultural Globalization
- Case Study: McDonald’s and Cultural Globalization
- Cultural Homogenization Vs Hybridization
- Case Study: K-pop as an Example of Cultural Hybridization
- Cross-Cultural Management
and Globalization
- Case Study: McDonald’s in India – A Cross-Cultural Management Success Story
- AI and Cross-Cultural Management
- Spiritual Globalization
- Cultural influence of religion in global business
5- Global Value Chains (GVCs) and Globalization
- Offshoring, Reshoring, Supply Chain Disruptions, Logistics
- Case Study: Apple and the Global Value Chain
- Case Study: Toyota – Managing a Global Value Chain in the Automotive Industry
- International Transport and Logistics
- AI in Global Supply Chain Management

6- Globalization, Labor and Migration
- How Globalization Affects Labor Markets
- Policy Challenges and Responses to Labor Migration under Globalization
- Environmental Globalization
- Climate Change, Sustainability, ESG In Global Strategy
7- Globalization, Ethics and Inequality
- Global Justice, Emerging Markets, Inequality and Globalization
- Case Study: The Rana Plaza Factory Collapse in Bangladesh
- Multinational corporations (MNCs) in emerging markets
- Case Study: Unilever in India (Hindustan Unilever Limited)
- Ethical and Regulatory Considerations in Global AI
- Principles of Global Ethics



8- Business Strategy in a Globalized World
“The essence of globalization is localization” Zhang Ruimin, Managing Director (CEO) of Haier.
- Internationalization Strategies
- Global-Local Tension and Glocalization
- Standardization vs. Adaptation. Glocalization Strategies
- Glocal Strategies: Balancing Global Efficiency with Local
Responsiveness
- Case Study: Unilever’s Glocal Strategy
- Case Study: Nestlé’s Glocal Strategy
- Case Study: Danone’s Glocal Strategy
- Glocal Strategies: Balancing Global Efficiency with Local
Responsiveness
- Global Strategy Frameworks
- CAGE Framework (Cultural, Administrative, Geographic, Economic Distance)
- Global Integration vs. Local Responsiveness (IR Framework)
- Porter’s Five Forces
- AAA Framework (Adaptation, Aggregation, Arbitrage)
- PESTEL Analysis (Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Environmental, and Legal)
- Ansoff Matrix
- Case Studies related to the application of Porter’s Diamond Model
- AI in Global Strategy and Decision-Making
By the end of the module, students will be able to:
- Define and critically assess key theories and dimensions of globalization.
- Evaluate the impact of globalization on international business strategy and operations.
- Analyze globalization’s effects on culture, labor markets, supply chains, and innovation.
- Identify global risks and ethical considerations in business expansion.
- Apply globalization insights to real-world business cases across sectors and regions
Transatlantic slave trade is considered a crime against humanity and the first system of Globalization.

The module “Globalization” is included within the curriculum of the following academic programs at EENI Global Business School:
Masters: International Business, Foreign Trade.

Doctorate: Global Trade, Ethics, Religion & Business.
Languages:  or
or  Mondialization
Mondialization  Globalización
Globalización  Globalização.
Globalização.
- Credits of the module “Globalization”: 2

Area of Knowledge: Globalization.

Globalization is the process of increasing interconnectedness and interdependence among countries through trade, investment, technology, information, people, and culture.
Regionalization refers to the process by which regions become the central focus of economic or political integration, typically through trade agreements, common markets, or coordinated policies.
Deglobalization is the decline or reversal of global interdependence, characterized by reduced international flows of trade, investment, capital, and people—often in response to crises or protectionist policies.
Phases of Globalization:
- Proto-globalization (pre-1800): early trade routes, colonial empires.
- First Wave (1800–1914): rise of industrial capitalism, imperialism.
- Interwar Retreat (1914–1945): protectionism, Great Depression, world wars.
- Second Wave (1945–1980): Bretton Woods, post-WWII reconstruction, Cold War dynamics.
- Third Wave (1980s–2008): neoliberalism, WTO, emerging markets.
- Post-2008 Phase: financial crisis, multipolarity, rise of China.
- Deglobalization and Fragmentation (2016–present?): Brexit, US-China trade war, COVID-19, reshoring, AI nationalism.
In the last few years, the world economy has gone through some major changes, the result of which has been the creation of a global market. With the establishment of the World Trade Organization (WTO), almost all the economies of the World are likely to establish more and more interdependent relationships with each other.
In 1980s, the world economy was characterized by an International Trade between large economic blocs, since the mid-90s, International Trade has tended to develop towards globalization to a stage where it is feasible to conceive a trade without frontiers.
Domestic trade has become a global trade, where the entire world is a global market. You are now probably working on a computer, which was produced in China, using Japanese chips, and an American operating system. You may be wearing a pair of trousers made in Taiwan, an Italian sunglass, and a Swiss watch. Perhaps tonight you will have a French glass, a Chilean wine, or a cup of Kenyan coffee with your dinner. You may drive a Korean or German car, or use a Finnish phone. This is our reality today, which has become possible due to Globalization.
Today we witness the emergence of a new economy: The world as a Global market!

A core element of globalization is to achieve an open International Trade through trade barriers elimination or reduction (import Tariffs).
Globalization refers to increasing integration of economies around the world, movement of people (labour) and knowledge (technology) across international borders.
Today more than 400 Regional Free Trade Agreements are in force: Free Trade Agreements and partial scope agreements account for 90%, while customs unions account for less than 10%.
Sample: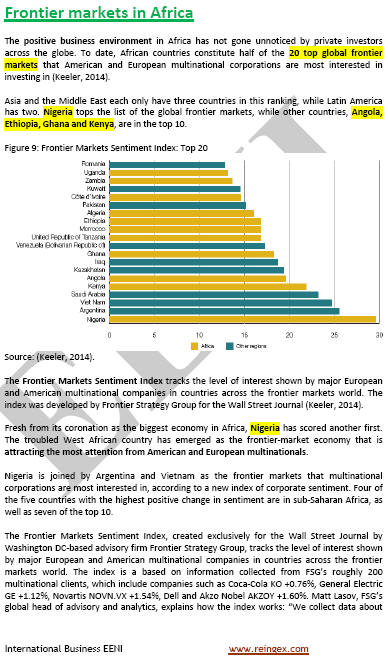
Sample: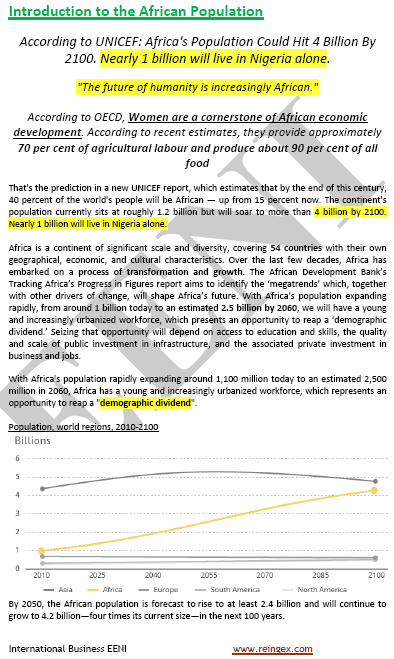
(c) EENI Global Business School (1995-2025)
Top of this page









 WhatsApp
WhatsApp