Business in Hong Kong

Foreign Trade and Business in Hong Kong. Asian economic centre
- Introduction to the Special Administrative Region of Hong Kong
- Hong Kong: a gateway to China
- Economy of Hong Kong
- The Pearl River Delta
- Hongkongese international trade
- China-Hong Kong Agreement
- Agreement on Closer Economic Partnership between New Zealand, Hong Kong, and China
- Hong Kong China-New Zealand Agreement
- Investment in Hong Kong
- Incorporate a company in Hong Kong
- Case Study:
- Imaginarium in Hong Kong
- Mango in Hong Kong
- Access to the Hongkongese market
- Business Plan for Hong Kong
The objectives of the subject “International Trade and Business in the Special Administrative Region of Hong Kong” are the following:
- To analyze the Hongkongese Economy and Global Trade
- To know the business opportunities in Hong Kong
- To understand the importance of Hong Kong as a gateway to the Chinese market
- To explore the Hongkongese trade relations with the country of the student
- To examine the profile of Hongkongese companies
- To develop a business plan for the Hongkongese market
Global Trade and Business in Hong Kong: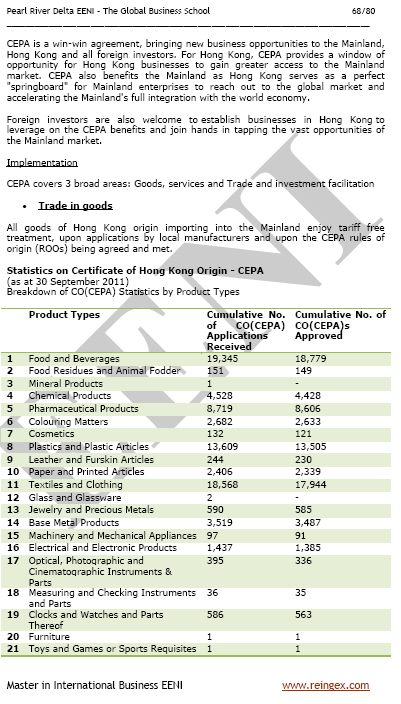

The Subject “Foreign Trade and Business in Hong Kong” belongs to the following Online Programs taught by EENI Global Business School:
Masters: International Business, Foreign Trade.
Course: Taoism, Confucianism & Business.

Languages:  or
or  Hong Kong
Hong Kong  Hong Kong
Hong Kong  Hong Kong.
Hong Kong.
- Credits of the subject “Doing Business in Hong Kong”: 3

- Duration: three weeks
Masters adapted to  Hongkongese Students.
Hongkongese Students.

International Trade and Business in Hong Kong
- Access to the East-West Corridor (Myanmar-Vietnam)
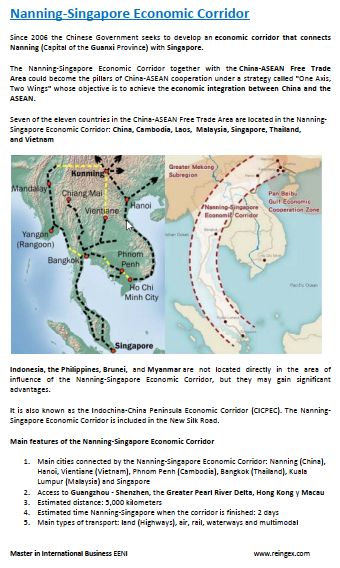
- Access to the Nanning-Singapore Economic Corridor

Preferential Access and Trade Agreements of Hong Kong
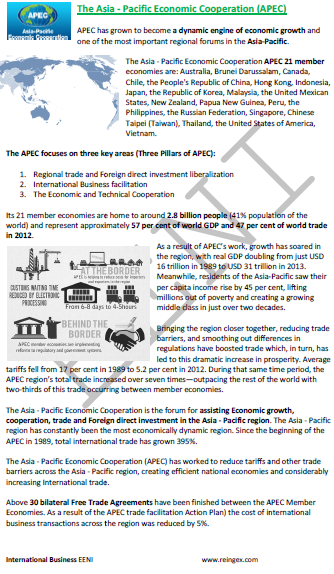
- APEC
- Closer Economic Partnership Arrangement (CEPA)
- New Zealand-Hong Kong China Closer Economic Partnership
- ASEAN-Hong Kong China Agreement
- Georgia-Hong Kong China Agreement
- Australia-Hong Kong China Agreement
- Macao-Hong Kong Agreement
- Chile-Hong Kong China Agreement
- EFTA-Hong Kong Agreement

- WTO
- Agreement on Sanitary and Phytosanitary Measures
- Agreement on Trade in Services (GATS)
- Agreement on Technical Barriers to Trade
- Agreement on Preshipment Inspection
- Agreement on Safeguards
- Trade Facilitation Agreement
- World Customs Organization
- Revised Kyoto Convention
- BIC (Containers)
- Chicago Convention (ICAO)
- International Maritime Organization
- Istanbul Convention
- Customs Convention on Containers
- ICS

- ESCAP
- Asian Development Bank
- PEEC
- Colombo Plan

- UN
- UNCTAD
- ITC
- UNCITRAL
- WIPO
- WB
- WTO
- IMF

Hong Kong has a prime location at the geographical, financial, and economic centre of Asia.
- Business Executives in Hong Kong have fast and easy access to all the largest markets in the Asia-Pacific region
- This strategic position is one of the main reasons for the popularity of Hong Kong as a location for regional operations
- Executives can travel back and forth to Beijing, Shanghai, and other major Chinese cities in a single day while making their home in Hong Kong
- Situated on the South-east coast of Mainland China, Hong Kong has a huge hinterland, which with 1.3 billion people is the largest single market in the world
- Hong Kong is the largest source of the Foreign direct investment in Mainland China
- 100 mainland companies are listed on the Hong Kong Stock Exchange
- At least 1,800 Mainland-backed companies are incorporated in Hong Kong
- There are twenty-six Chinese banks and seven representative offices operating in Hong Kong
- Free trade is the vision of Hong Kong
- HK is one of the most open, externally orientated economies in the World
- The Heritage Foundation has consistently rated it as the freest economy in the World
Special Administrative Region of Hong Kong
- The official languages of Hong Kong are English and Cantonese
- Area of Hong Kong: 1,108 km²
- Hongkongese population: 7.1 million people
- Independence of Hong Kong from the UK in 1997
- Currency: Hong Kong Dollar
- Hongkongese GDP (nominal): 215,354 billion dollars;
- Agriculture: 0.1%
- Industry: 9%
- Services: 90.9%
- GDP (PPP) of Hong Kong: 350 billion dollars
- Inflation in Hong Kong: 2%
- The main export destinations are China, the U.S., and Japan
The Greater Pearl River Delta region, which consists of the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region, Macau Special Administrative Region, and the Pearl River Delta Economic development Zone part of Guangdong Province, has emerged as one of the most dynamic economic regions in the World.
The Closer Economic Partnership Arrangement (CEPA), which took effect in the beginning of 2004, provides to Hong Kong with additional and exclusive Mainland market access benefits. Thousands of international companies implicated in international trade with China have chosen to set up their headquarters in Hong Kong.
Requisites for establishing a business in Hong Kong are famous for being simple and straight forward. You can set up a new company in six days, and it will cost you only a few hundred dollars.
The type of structure that is most appropriate will depend on tax issues, strategic plans, financial aspects, willingness to take on ongoing obligations and much more. Because of the complex and long-term impact of this decision; it is advisable to seek professional advice.
Most common forms of business for the foreign investors are:
- Private limited companies
- Branch offices of foreign companies
- Representative offices
- Partnerships/sole proprietorships
- Joint Ventures

New Zealand-Hong Kong Agreement



