Business in the UK

Foreign Trade and Business in the UK (Great Britain) - London
- Introduction to the UK
- British Economy
- Economic impact of the BREXIT
- British Manufacturing Industry
- British Services sector
- British International Trade
- Strategic importance of the Commonwealth
- Relations with the U.S.
- The new Free Trade and Economic Integration Agreements of the Kingdom after
BREXIT
- EU-United Kingdom Free Trade and Economic Integration Agreement
- Investment in the UK.
- British Investments Abroad
- Business in London
- Case Study:
- Business in Yorkshire and Humber
- Mohamed Ibrahim
- Access to the British Market
- Business Plan for the UK
The objectives of the subject “International Trade and Business in” the UK” are the following:
- To analyze the strengths of the British Economy and Global Trade
- To understand the causes of the BREXIT and its economic implications
- To know the trade opportunities in the British Market
- To analyze the trade relations of the UK with the country of the student
- To know the UK's new Free Trade and Economic Integration Agreements of the Kingdom after BREXIT
- To understand the political and economic importance of the Commonwealth
- To develop a business plan for the British Market

The Subject “Foreign Trade and Business in the UK” belongs to the following Online Programs taught by EENI Global Business School:
Doctorate: European Business, World Trade.
Masters: International Business, Foreign Trade.
Languages:  +
+  Reino Unido
Reino Unido  Royaume-Uni
Royaume-Uni  Reino Unido.
Reino Unido.
- Credits of the Subject “Doing Business in the UK”: 3

- Duration: three weeks
International Trade and Business in the United Kingdom

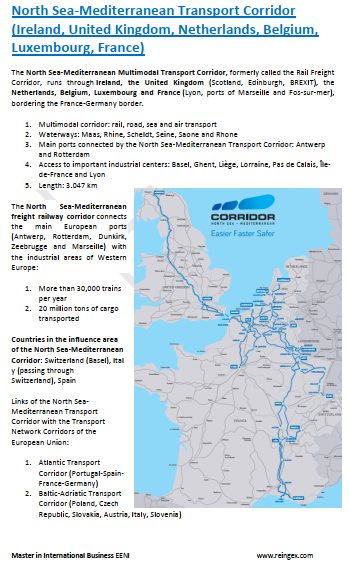
- North Sea-Mediterranean Corridor (Ireland, France)
- Access to the Atlantic Transport Corridor (Portugal-Spain-France-Germany)

British Preferential Access and Trade Agreements:
- The UK and the European Economic Area
- United Kingdom Trade Agreements: Cameroon, Canada, Egypt, Pacific States (Solomon Islands, Papua New Guinea, Samoa), Faroe Islands, Ghana, Israel, Kenya, Kosovo, Lebanon, Morocco, Mauritius-Seychelles-Zimbabwe, Norway-Iceland, Palestine, SACU and Mozambique, Switzerland-Liechtenstein, Tunisia, Turkey
- United Kingdom Free Trade and Economic Integration Agreements: Central America (Costa Rica, El Salvador, Guatemala, Honduras, Nicaragua, Panama), CARIFORUM, Chile, Colombia, the EU, South Korea, Ivory Coast, Ecuador-Peru, Georgia, Japan, Macedonia, Moldova, Singapore, Ukraine, Vietnam
- Regional Cooperation Council
The UK is no longer a member of the EU (until BREXIT).

- WTO
- Agreement on Sanitary and Phytosanitary Measures
- GATS
- Agreement on Technical Barriers to Trade
- Agreement on Preshipment Inspection
- Agreement on Safeguards
- Trade Facilitation Agreement
- WCO
- Convention Harmonization of Frontier Controls of Goods
- COTIF Convention
- CMR Convention
- BIC (Containers)
- Chicago Convention (ICAO)
- IMO
- Convention for Safe Containers
- Istanbul Convention
- IRU
- TIR Convention
- Guidelines on Safe Load Securing for Road Transport
- ICS
- CIM, CIT Rail Rules
- Customs Convention on Containers - not a member

European Economic Organizations
- OSCE
- UNECE
Global Organizations:
- WTO
- Inter-American Development Bank (The UK is a non-borrower member of the IDB)
- Asian Development Bank
- Asia-Europe Meeting
- UN
- UNCTAD
- ITC
- UNCITRAL
- WIPO
- ESCAP
- OECD
- OECD anti-corruption measures
- IMF
- Commonwealth
- African Development Bank
- WB
- ECLAC
- CPLP (observer country)
- ...
The UK is an observer member in:
- ACS
- Council of the Baltic Sea States
- IORA
- SICA
- Trans-Pacific Partnership (CPTPP) - Candidate Country
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland (Europe).
- The UK of Great Britain is constituted by Great Britain (England, Scotland and Wales) and Northern Ireland
- The UK was one of the member states of the EU - BREXIT
- Capital of the UK: London
- Area of the UK: 243,610 km²
- British Population: 64 million people
- The UK is a constitutional monarchy being a representative democracy, where Queen Elizabeth II is recognized as the Head of the State
- The UK is a unitary state comprised of four constituent nations: Scotland, Wales, England and Northern Ireland
- William Wilberforce
Dependencies of the British Crown: Guernsey, Isle of Man and Jersey.
The British Overseas Territories: Akrotiri, Anguilla, Bermuda, Gibraltar, Cayman Islands, South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands, Falkland Islands, Pitcairn Islands, Turks and Caicos Islands, British Virgin Islands, Montserrat, Santa Elena, Ascension and Tristan de Acuña, British Antarctic Territory, British Indian Ocean Territory.
Main religion in the UK: Anglican Church - Justin Welby (Archbishop of Canterbury).- Quakerism was founded by George Fox in the UK. The Quaker William Wilberforce was one of the most important figures in the abolition of Slavery (1807)
- Abolition of Slavery in the UK: 1807
- Methodism was created by the British John Wesley

The UK belongs to the European Economic Area.
UK Economy
- The UK of Great Britain is a commercial powerhouse and a global financial centre
- The UK is one of the most developed countries in the world
- The UK represents the fifth world Economy and the second largest in Europe (after Germany and followed by France)
- British GDP (nominal): 2,231 mil million dollars
- GDP by sector:
- Agriculture (0.9%)
- Industry (22.8%)
- Services (76.2%)
- UK GDP per capita: 36,600 dollars
- Its capital, London (along with New York) is one of the two largest financial centers in the world
- Currency of the UK: Pound Sterling
- The UK economy is one of the most important in Europe, increasingly based on the services sector, although it maintains a significant presence in the high-technology sector
- The UK of Great Britain is ranked 13th in the competitiveness ranking of the World Economic Forum

Many leading companies and businesspeople from around the world are based in London:
- The Russian businessman Alexander Lebedev is the owner of four UK newspapers
- The Sudanese businessman Mohamed Ibrahim
- The Zimbabwean businessman Strive Masiyiwa
- The Chaldean Christian businessman of Iraqi origin Nadhmi Shakir Auchi
- The Saudi businessman Sheik Mohamed Bin Issa Al Jaber
- The head office of Hinduja, an Indian business group

- Top export markets of the UK of Great Britain: The U.S., Germany, France, the Republic of Ireland, the Netherlands, Belgium, Spain, Italy..
- The main British Exports: manufactured products, fuels, chemical products, tobacco, beverages, foods
- Top Trading Partners of the UK of Great Britain: Germany, the U.S., the Republic Popular of the China, the Netherlands, France, Belgium, Norway, Italy.
- Main British Imports: manufactured products, fuels, machines, foods
(c) EENI Global Business School (1995-2024)
We do not use cookies
Top of this page



