Global Brand Positioning, unique value proposition
Core Brand Identity, Cultural Sensitivity, Emotional Connection (Positioning)

Global Marketing -
Segmentation -
Targeting
Global brand positioning involves creating a consistent and compelling brand identity that resonates across diverse markets while adapting to local nuances. It defines what the brand stands for—its values, personality, and unique value proposition—and ensures it connects with global audiences both emotionally and functionally.
- Introduction to international Market positioning
- International positioning stages
- Strategies of Global Positioning
- Global Branding
- Case Study: Coca-Cola – A Masterclass in Global Branding
- Case Study: Nike’s Global Brand Positioning
- Case Study: MTN Group’s Brand Positioning in Africa
- Case Study: Starbucks in China – Brewing Global Brand Success Locally
- Case Study: Chick-fil-A's Faith-Based Branding Strategy
- Case Study: PureHarvest Ramadan Campaign
- Case Study: “24/7 Prayer” – Digital Prayer and Meditation App
- Global Brand Strategy
- Brand importance in strategy of Internationalization
- Brand value
- Brand strategies in foreign markets
- Global, regional, and local brands
- Building an international brand
- Religious influencers and business
- Case Study:
- Top global brands
- Unilever
- Wrigley Company
- ACER
- Gucci Group
- Nutrexpa
- Mitsubishi
- Intellectual Property Rights (TRIPS)
- Religion and international promotion
- The Twenty-two Immutable Laws of Marketing
- Case Study:
- United Biscuits
- Ford Motor Company
- Erste Bank
- Positioning a new product in the Australian Market
- Cultural influence of religion in global business
- Faith-based Marketing

The Subject “Global Brand Positioning, unique value proposition” belongs to the following Programs offered by EENI Global Business School:
Masters: Foreign Trade, International Business.

Postgraduate Certificate in Global Marketing.


Languages:  or
or  Positionnement mondial de la marque
Positionnement mondial de la marque  posicionamiento global de marca
posicionamiento global de marca  Posicionamento global da marca.
Posicionamento global da marca.
Positioning is the process of designing an offer and enterprise image so that it occupies a distinct and valued place in the mind of the consumer.
Key Elements of Global Brand Positioning:
- Core Brand Identity
- Unique Value Proposition (UVP)
- Cultural Sensitivity and Adaptation
- Emotional Connection
- Market Segmentation
Strategies for Effective Global Positioning
- Standardization vs. Localization
- Digital and Social Media Presence
- Sustainability and Ethics
- Competitor Analysis
- Consistency in Visual and Verbal Identity
The objective of positioning a product or a service is to make sure that it occupies a certain place in the mind of the consumer, differentiating it from the competition.
Positioning a Product or service consists gaining a proper meaning in the mind of the customer as to where the product or service sits in the market segment to which it belongs.
This may be achieved by product attributes (or service) or through International Promotion Policy.
Global branding is the process of developing and maintaining a brand that is consistently positioned, perceived, and communicated across multiple international markets. It emphasizes building a unified brand identity that resonates with global audiences while allowing for cultural adaptation to meet local market needs.
Best Practices for Global Branding
- Develop a unified global brand strategy that aligns with the company’s long-term vision and objectives
- Define core brand values that are universal and resonate across cultural boundaries
- Create a flexible framework that allows for localized adaptation without compromising brand consistency
- Invest in Cultural intelligence and local partnerships to ensure relevance and authenticity in each market
- Monitor brand perception in real time to respond proactively to regional challenges and opportunities
- Continuously evolve the brand based on emerging global trends and local consumer insights
Nike, a global leader in athletic footwear, apparel, and equipment, has built a strong brand identity around its iconic tagline, “Just Do It,” which embodies empowerment, performance, and self-expression. Operating in over 190 countries, Nike’s global brand positioning blends a consistent message of inspiration with localized strategies to connect with diverse audiences—from urban youth to professional athletes.
Sample - International Segmentation, Brand and Positioning:
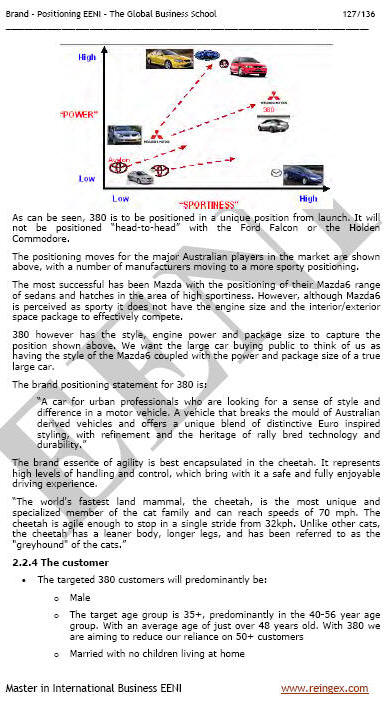
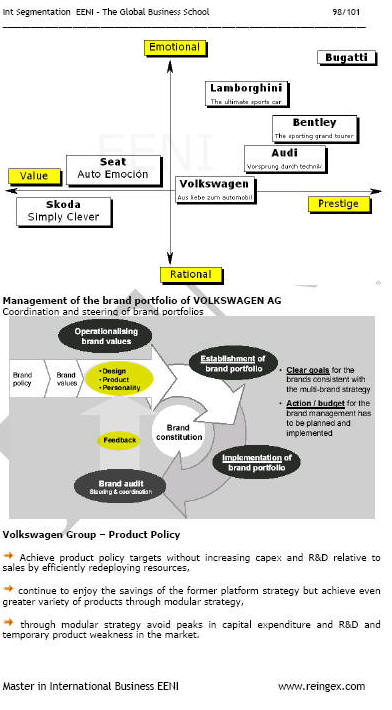
(c) EENI Global Business School (1995-2025)
Top of this page










 WhatsApp
WhatsApp