Cultural intelligence and Religious diversity
Ability to adapt to diverse cultural contexts (Cultural intelligence)

Religions and Global Business -
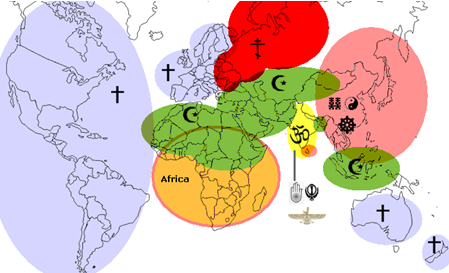
Religious diversity
Cultural intelligence (CQ) is the ability to adapt and function effectively in diverse cultural-religious contexts.
Companies like Procter & Gamble train their executives in religious nuances, reducing cultural misunderstandings by 25% (HBR, 2023). KFC's vegetarian menu in India and its Halal menu in Malaysia show how adapting products to religious norms boosts market share.
- Cross-Cultural Management
- Standardization vs. adaptation: Glocalization strategies
- Religious differences and ethical conflicts
It is composed of four main dimensions:
- Cognitive CQ: Knowledge about the norms, values, practices, and traditions of different cultures. For example, understanding how religious holidays are celebrated or how communication norms vary.
- Metacognitive CQ: Awareness and reflection on one's own cultural assumptions and the ability to adjust thinking in intercultural interactions.
- Motivational CQ: Interest and motivation to learn about other cultures and participate in diverse environments.
- Behavioral CQ: Ability to adapt behavior (verbal and nonverbal) to different cultural contexts, such as adjusting tone or gestures according to the situation.
Cultural intelligence is key in globalized environments, as it fosters empathy, reduces misunderstandings, and improves collaboration in multicultural teams.
Cultural intelligence is essential for managing religious diversity. For example:
- A person with high cognitive QC can understand that Ramadan involves fasting for Muslims and adjust gatherings or events to respect this practice.
- Behavioral CQ allows you to adapt your language or actions to avoid offending religious beliefs, such as avoiding certain topics in sensitive conversations.
- Cultural motivation drives interest in learning about holidays such as the Hindu Diwali or the Jewish Passover, promoting inclusion.
Companies should encourage learning about different religions and cultures to create synergies and avoid potential conflicts..




The subject «Cultural intelligence and Religious diversity» is included within the curriculum of the following academic programs at EENI Global Business School:
Masters: Religions & Business, Master: International Business

Doctorate: Ethics, Religions & Business, World Trade

Languages:  or
or  Inteligencia cultural y diversidad religiosa
Inteligencia cultural y diversidad religiosa  Intelligence culturelle
Intelligence culturelle  Religions.
Religions.
(c) EENI Global Business School (1995-2025)
Top of this page










 WhatsApp
WhatsApp
