Business in Ireland, Dublin, Foreign Trade

Economy of Ireland (Celtic Tiger) Distribution and Sales. Ryanair. Facebook
- Introduction to the Republic of Ireland (EU): the Celtic Tiger
- Business in Dublin
- Irish Economy
- Main sectors of the Irish economy
- Tax advantages offered by Ireland
- Irish International Trade
- Case Study
- Ryanair
- Facebook in Ireland
- Global companies located in Ireland
- Access to the Irish Market
- Business Plan for Ireland
The objectives of the subject “International Trade and Business in” Ireland” are the following:
- To analyze the Irish Economy and Foreign Trade
- To know the trade opportunities in the Irish Market
- To analyze the trade relations of Ireland with the country of the student
- To know the Irish Free trade agreements as a member of the EU
- To develop a business plan for the Irish Market

The Subject “Foreign Trade and Business in Ireland” belongs to the following Online Programs taught by EENI Global Business School:
Doctorate: European Business, World Trade.
Masters: International Business, Foreign Trade.

 Masters adapted to Irish Students.
Masters adapted to Irish Students.

Languages:  +
+  Irlanda
Irlanda  Irlande
Irlande  Irlanda.
Irlanda.
- Credits of the Subject “Doing Business in Ireland”: 1

- Duration: one week
International Trade and Business in Ireland

- North Sea-Mediterranean Corridor (Ireland, France)
- Access to the Pan-European Corridor II
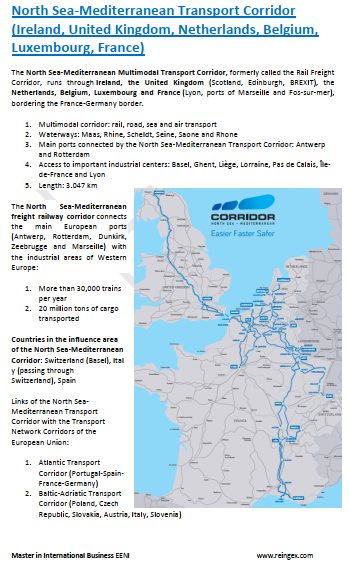


Irish Preferential Access and Trade Agreements:

- Ireland and the European Economic Area
- The EU
- Economic and Monetary Union
- European Customs Union
- European Single Market
- The EU Services Directive
- European Digital Single Market
- As a member of the EU, Ireland is a beneficiary of the EU Trade Agreements with Algeria, Ivory Coast, South Africa, South Korea, India, Mexico, MERCOSUR, Chile, Egypt, Georgia etc. besides the Customs Union with Turkey
- Regional Cooperation Council

- WTO
- GATS
- Agreement on Sanitary Measures
- Agreement on Technical Barriers to Trade
- Agreement on Preshipment Inspection
- Agreement on Safeguards
- Trade Facilitation Agreement
- WCO
- Convention Harmonization of Frontier Controls of Goods
- CMR Convention
- COTIF Convention (Rail)
- BIC
- Chicago Convention (ICAO)
- IMO
- Convention for Safe Containers
- Istanbul Convention
- IRU
- TIR Convention
- Guidelines on Safe Load Securing for Road Transport
- ICS
- CIM, CIT Rail Rules
- Customs Convention on Containers - not a member

European Trade and Economic Organizations of Ireland
- The EU
- ECB
- EIB
- EU-CELAC Summit
- Group of States of the European Council Convention against Corruption
- UNECE
- OSCE

- OECD
- OECD anti-corruption measures
- Asia-Europe Meeting
- Asian Development Bank
- African Development Bank
- IMF
- UN
- UNCTAD
- ITC
- WIPO
- WB
- WTO
The Republic of Ireland (Europe).
- Capital of Ireland: Dublin
- Official languages: Irish and English
- Area of Ireland: 70,273 km²
- Irish Population: 4.5 million people
- Government of Ireland: Parliamentary Republic
- Independence of Ireland from the UK: 1916
Religion in Ireland: Christianity (Catholicism).

Ireland belongs to the European Economic Area.
Irish Economy
- Ireland experienced a major economic growth between 1980 and 2000, from a developing country to one of the countries with the highest GDP per capita in the world
- Irish GDP (nominal): 307,917 million EUR
- Services: 75% of Irish GDP
- GDP per capita (nominal): 65,870 EUR
- Ireland is a small market, open, and very dependent on international trade
- The opening of the Irish economy is reflected on the international mobility of its workers, capital and foreign direct investment
- The Republic of Ireland is a leader in information and communication technologies (IT), pharmaceutical and medical sector
- Ireland is the digital communication centre in the EU, with the largest number of multinational companies based in Dublin
- The main sectors of the Irish economy are food export products, bees, textiles, telecommunications, chemical products and pharmaceutical, machinery, transport equipment and software

Irish Foreign Trade
- More than 80% of Irish manufactured products are exported to the international markets
- Top Irish Exports markets: the UK, the U.S., Belgium, Germany, France
- Top Irish import partners: the UK, the U.S., Germany, the Netherlands, France
(c) EENI Global Business School (1995-2024)
We do not use cookies
Top of this page


