Business in Belgium, Brussels, Port of Antwerp
Belgian Foreign Trade, Logistics. Brussels (Belgium) EU headquarters

The headquarters of EU are in Brussels, one of the largest lobbies in the world
Industry is mainly located in Flanders (northern Belgium)
- Introduction to the Kingdom of Belgium (EU)
- Economy of Belgium
- Doing Business in Brussels: The political capital of the European Union
- Belgian Foreign Trade
- Transport and Logistics
- Investment in Belgium
- Access to the Belgian Market
- Business Plan for Belgium

The educational aims of the Subject “Foreign Trade, Logistics and Business in Belgium” are:
- To analyze the Belgian Economy, Logistics and Global Trade
- To conduct research on business opportunities in the Belgian Market
- To analyze the Belgian trade relations with the student's country
- To learn about Belgian Trade Agreements as a member of the European Union
- To develop a business plan for the Belgian Market

The Subject “Foreign Trade, Logistics and Business in Belgium” is included within the curriculum of the following academic programs at EENI Global Business School:

Masters: International Business, Foreign Trade.

 Masters adapted to Belgian Students.
Masters adapted to Belgian Students.
Languages:  +
+  Bélgica
Bélgica  Belgique
Belgique  Bélgica.
Bélgica.
- Subject Credits “Doing Business in Belgium”: 1

International Trade, Logistics and Business in Belgium

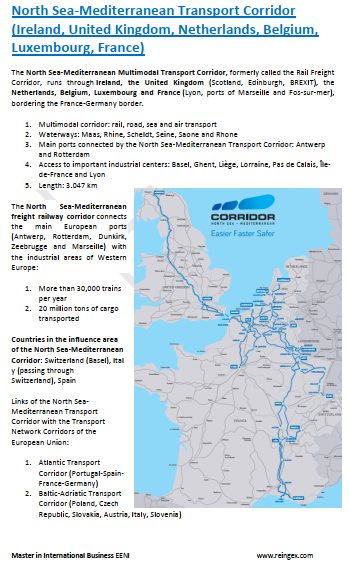
- North Sea-Mediterranean Corridor (Ireland, France)
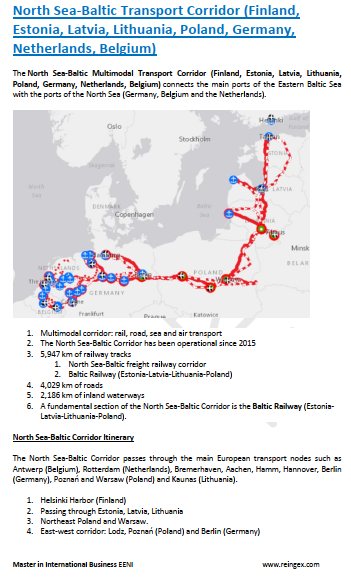
- North Sea-Baltic Corridor (Finland, Belgium)
- Access to the Atlantic Transport Corridor (Portugal-Spain-France-Germany)
Doing Business in Belgium:


Preferential Access and Trade Agreements of Belgium
- Belgium and the European Economic Area
- European Union
- European Single Market
- The European Union Services Directive
- European Digital Single Market
- Economic and Monetary Union
- European Customs Union
- As a member of EU, Belgium is a beneficiary of EU Trade Agreements with Chile, South Africa, South Korea, India, Ukraine, Moldova, Georgia etc
- Group of States of the European Council Convention against Corruption


- World Trade Organization (WTO)
- Agreement on Trade in Services (GATS)
- Agreement on Sanitary Measures
- Agreement on Technical Barriers to Trade
- Agreement on Preshipment Inspection
- Trade Facilitation Agreement
- World Customs Organization (WCO)
- Kyoto Convention
- COTIF Convention (Rail)
- BIC
- Chicago Convention (ICAO)
- International Maritime Organization (IMO)
- Convention for Safe Containers
- Istanbul Convention
- International Chamber of Shipping
- CMR Convention
- International Road Transport Union (IRU)
- TIR Convention
- Guidelines on Safe Load Securing for Road Transport
- CIM & CIT Rules (Rail Transport)
- Customs Convention on Containers - not a member
- International Chamber of Commerce

European Trade and Economic Organizations of Belgium
- European Union
- European Bank for Reconstruction and Development (EBRD)
- European Investment Bank
- European Central Bank
- European Union-CELAC Summit
- Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD)
- Economic Commission for Europe (UNECE)
- Asia-Europe Meeting
- Organization for Security and Cooperation in Europe (OSCE)

- United Nations
- World Bank
- World Trade Organization (WTO)
- International Monetary Fund
- Inter-American Development Bank
- Asian Development Bank
- African Development Bank
The Kingdom of Belgium (Europe).
- Capital of Belgium: Brussels
- Belgian Official Languages: French, Dutch and German
- Area of Belgium: 30,528 km²
- Belgian Population: 11.2 million people
- Type of Government: Federal parliamentary monarchy
- Borders of Belgium: Germany, France, Luxembourg and the Netherlands
- Belgium became independent of the Netherlands (Spain in the past) in 1830
- The Democratic Republic of the Congo became independent from Belgium in 1960
- The Republic of Burundi and Rwanda became independent from Belgium in 1962
Religion: Catholicism.
Belgium belongs to the European Economic Area.
Economy of Belgium.
- Belgian Currency: Euro (1999)
- Belgium joined the EU in 1958
- The company "Unitel International Holdings BV" of the Angolan businesswoman Isabel dos Santos is in Brussels

Belgian Foreign Trade.
- 75% of the Belgian Foreign Trade is made with the countries of the European Union
- Main suppliers of Belgium are Germany, the Netherlands and France (and also the main export destination)
- Main export products are diamonds, machinery, chemical products, food products
- The Port of Antwerp is the second largest in Europe
- Headquarters of the International Road Transport Union (IRU) and the International Union for Road-Rail Combined Transport (UIRR): Brussels
(c) EENI Global Business School (1995-2025)
Top of this page









 WhatsApp
WhatsApp