Business in Luxembourg. Luxembourger Economy
Luxembourger Foreign Trade, Logistics. Luxembourg: the European financial centre

The Grand Duchy of Luxembourg is one of the most important financial centers in Europe (28% of the Luxembourger GDP): investment funds and high-risk, private banking, capital management
The Luxembourger steel industry is crucial
Luxembourg offers significant tax advantages for enterprises (it is one of the European Countries with least taxes)
- Introduction to the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg (EU)
- Luxembourger Economy: one of the most important financial centers of Europe
- Doing Business in Luxembourg
- Luxembourger Foreign Trade
- Transport and Logistics
- Investment in Luxembourg
- Access to the Luxembourger Market
- Business Plan for Luxembourg
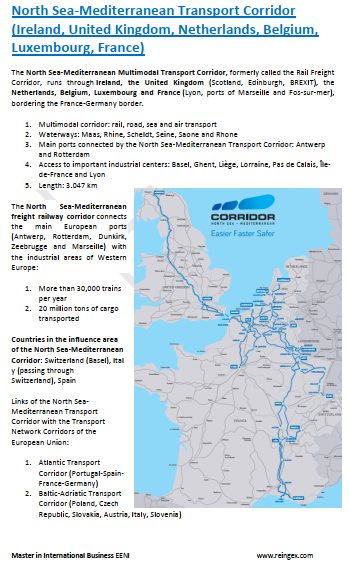

The educational aims of the Subject “Foreign Trade, Logistics and Business in Luxembourg” are:
- To analyze the Luxembourger Economy, Logistics and Foreign Trade
- To conduct research on business opportunities in the Luxembourger Market
- To analyze the Luxembourger trade relations with the student's country
- To learn about Luxembourger free trade agreements as a member of the European Union
- To develop a business plan for the Luxembourger Market

The Subject “Foreign Trade, Logistics and Business in Luxembourg” is included within the curriculum of the following academic programs at EENI Global Business School:

Masters: International Business, Foreign Trade.

Languages:  +
+  Luxemburgo
Luxemburgo  Luxembourg
Luxembourg  Luxemburgo.
Luxemburgo.
- Subject Credits “Doing Business in Luxembourg”: 1

International Trade, Logistics and Business in Luxembourg


Luxembourger Preferential Access and Trade Agreements:
- Luxembourg and the European Economic Area
- European Union
- Economic and Monetary Union
- European Customs Union
- European Single Market
- The European Union Services Directive
- European Digital Single Market
- As a member of EU, Luxembourg is a beneficiary of EU Trade Agreements


- World Trade Organization (WTO)
- Agreement on Trade in Services (GATS)
- Agreement on Sanitary Measures
- Agreement on Technical Barriers to Trade
- Agreement on Preshipment Inspection
- Agreement on Safeguards
- Trade Facilitation Agreement
- World Customs Organization (WCO)
- Kyoto Convention
- Convention on the Harmonization of Frontier Controls of Goods
- Rotterdam Rules
- CMR Convention
- International Chamber of Commerce
- COTIF Convention
- BIC
- Chicago Convention (ICAO)
- International Maritime Organization (IMO)
- Convention for Safe Containers
- Istanbul Convention
- International Road Transport Union (IRU)
- TIR Convention
- Guidelines on Safe Load Securing for Road Transport
- CIM & CIT Rules (Rail Transport)
- Customs Convention on Containers - not a member

European Trade and Economic Organizations
- European Union
- European Central Bank
- European Investment Bank
- European Bank for Reconstruction and Development (EBRD)
- Organization for Security and Cooperation in Europe (OSCE)
- Economic Commission for Europe (UNECE)

- United Nations
- World Bank
- World Trade Organization (WTO)
- International Monetary Fund
- Asian Development Bank
- African Development Bank
- OECD
- OECD anti-corruption measures
- Asia-Europe Meeting
- CPLP (observer country)
The Grand Duchy of Luxembourg (Europe).
- Luxembourger Capital: Luxembourg
- Official Language of Luxembourg: French, Luxembourger, German
- Luxembourger Area: 2,586 km²
- Luxembourger Population: 543,202 of people
- Type of Government: Parliamentary Monarchy
- Borders of Luxembourg: France, Germany and Belgium
- Luxembourg is a landlocked country
- Independence of Luxembourg: 1867 (Netherlands)
Religion in Luxembourg: Catholicism (Christianity).
Luxembourg belongs to the European Economic Area.
Economy of Luxembourg.
- Luxembourger Currency: Euro (1999)
- Luxembourg is a member of EU since 1958
- Luxembourg has an outstanding logistics platform thanks to its strategic position between France, Belgium and Germany
- There have been several scandals related to the tax evasion that has hit enterprises like Pepsi Cola, Ikea, Procter & Gamble, FedEx, Accenture, Burberry, JP Morgan, Deutsche Bank or Amazon
- OECD does not consider Luxembourg as a tax haven
- Arcelor Mittal, the world steel leader, has its headquarters in Luxembourg
- 60% of the workforce is foreigner
- The Headquarters of the Court of Justice of EU are in Luxembourg

Luxembourger Foreign Trade.
- Main Luxembourger Exports are machinery, steel products, chemical products and rubber
- Top export markets of Luxembourg: Germany (23%), France, Belgium, Italy
- Main Luxembourger Imports are minerals, metals, airplanes, chemical products, luxury products
- Main suppliers of Luxembourg are Belgium (31%), Germany, France, the United States
(c) EENI Global Business School (1995-2025)
Top of this page









 WhatsApp
WhatsApp