Business in France, Paris. French Economy
France: third European economy. Trade Relations with Africa, Logistics

The French Republic is a highly developed market being the:
- Fifth largest economy in the world by nominal GDP
- Eighth largest economy in purchasing power
France is the most visited country in the world (82 million tourists per year)
The economy of the French Republic is heavily based on services (76% of GDP, 75% of the population)
- Introduction to the French Republic (EU)
- French Economy
- France: one of the political and economic leaders of the European Union
- Information and communication technologies in France
- Doing Business in Paris
- French International Trade
- Political, economic and cultural relations with the African Francophone countries
- Strategic Partnership between Africa and France
- Strategic importance of the Francophonie
- French Foreign Direct Investment
- Transport and Logistics
- Main French companies
- Case Studies:
- The Hijab in France
- Michelin
- Alstom
- Essilor
- L’Oréal
- Danone
- Carrefour
- Access to the French Market
- Business Plan for France
Sample: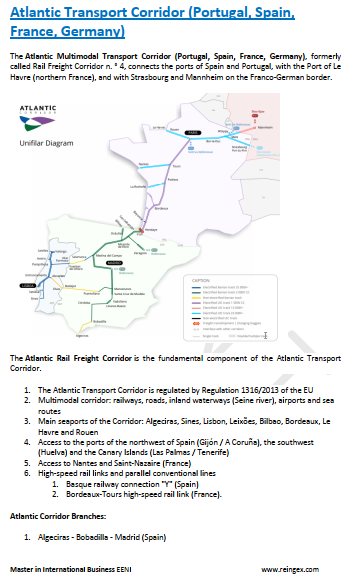

The educational aims of the Subject “Foreign Trade, Logistics and Business in the French Republic” are:
- To analyze the strengths of the French Economy, Logistics and Foreign Trade
- To conduct research on business opportunities in the French Market
- To research the trade relations of France with the student's country
- To learn about French Free Trade Agreements as a member of the European Union
- To understand the political and economic importance of France in the European Union
- To analyze the Africa-France Strategic Partnership
- To develop a business plan for the French Market

The Subject “Foreign Trade, Logistics and Business in France” is included within the curriculum of the following academic programs at EENI Global Business School:

Masters: International Business, Foreign Trade.

Languages:  Francia
Francia  France
France  França.
França.
- Subject Credits “Doing Business in France”: 3

International Trade, Logistics and Business in France:

- Atlantic Corridor (Portugal-Germany)
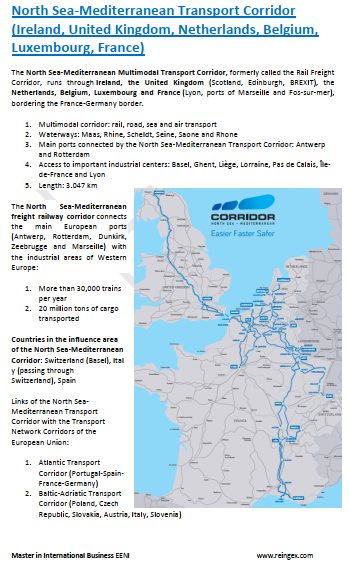
- North Sea-Mediterranean Corridor (Ireland, France)
- Access to the North Sea-Baltic Transport Corridor


French Preferential Access and Trade Agreements:
- France and the European Economic Area
- European Union
- As a member of EU, France is a beneficiary of EU Trade Agreements
- European Single Market
- The European Union Services Directive
- European Digital Single Market
- Economic and Monetary Union
- European Customs Union
- Indian Ocean Commission (Reunion Islands)
- Regional Cooperation Council
- SICA (observer country)


- World Trade Organization (WTO)
- Agreement on Trade in Services (GATS)
- Agreement on Sanitary Measures
- Agreement on Technical Barriers to Trade
- Agreement on Preshipment Inspection
- Agreement on Safeguards
- Trade Facilitation Agreement
- World Customs Organization (WCO)
- Kyoto Convention
- International Chamber of Commerce
- COTIF Convention
- BIC (Containers)
- Chicago Convention (ICAO)
- International Maritime Organization (IMO)
- Convention for Safe Containers
- Istanbul Convention
- Rotterdam Rules
- Hamburg Rules
- CMR Convention
- International Road Transport Union (IRU)
- TIR Convention
- Guidelines on Safe Load Securing for Road Transport
- International Union of Railways (UIC)
- International Chamber of Shipping
- CIM & CIT Rules (Rail Transport)
- Customs Convention on Containers - not a member

European Trade and Economic Organizations of France
- The European Union
- Economic Commission for Europe (UNECE)
- Organization for Security and Cooperation in Europe (OSCE)
- Group of States of the European Council Convention against Corruption
- OECD
- OECD anti-corruption measures

- United Nations
- African Union
- Inter-American Development Bank (non-borrower)
- Asia-Europe Meeting
- World Bank
- Economic Commission for Latin America (ECLAC)
- International Organisation of La Francophonie (OIF)
- World Trade Organization (WTO)
- Economic Commission for Asia (ESCAP)
- Asian Development Bank
- African Development Bank
- International Monetary Fund
- International Chamber of Commerce
- ...
France is an associate / observer country:
- Association of Caribbean States (ACS)
- Organization of the Black Sea Economic Cooperation
- Council of the Baltic Sea States
- PECC
- CPLP
- Capital of France: Paris
- Official Language: French
- Area of France: 643,801 km²
- Population of France: 67 million people
- Borders of France: Monaco, Italy, Spain, Andorra, Belgium, Luxembourg, Germany and Switzerland
- France has a Maritime border with the UK (submarine tunnel)
- Abolition of Slavery in France: 1848 (Victor Schoelcher)
- Pierre Teilhard of Chardin
Type of Government of France: Semi‑presidential Republic
The main religion in France: Catholicism (Christianity).
France is known for its principle of “laïcité”, a model of secularism that promotes religious neutrality in public spaces. This principle has sparked debates about religious dress, especially the hijab (an Islamic veil that covers the hair and neck), worn by some Muslim women as an expression of faith, identity, or modesty. France has a significant Muslim population (approximately 8–10% of the population, according to recent estimates), making the issue relevant.
France belongs to the European Economic Area.
Economy of France.
- Decentralized EU Agency in France:
- Community Plant Variety Office (CPVO): Angers


French Foreign Trade.
- France ranks second in the world regarding the service exports and agricultural products
- The French Republic makes 70% of his Foreign Trade with its European Union partners
- French Foreign Trade has a surplus in export products trade balance
- Germany imports 14% of the French exports, followed by Italy, Spain, the UK, Belgium, the United States, the Netherlands, Switzerland and China
- Of the total of the imported products of France, 16% are originated in Germany followed by Belgium, Italy, China, Spain, the United States, the UK, the Netherlands, Russia, Switzerland and Japan
- Main French Exports are machinery, mechanical appliances, vehicles, Air navigation and pharmaceutical products
- The French Republic is the second most attractive European country for Foreign Direct Investment
- The largest French Port is Le Havre
- Headquarters of the International Union of Railways (UIC) and the International Bureau of Containers and Intermodal Transport (BIC)
(c) EENI Global Business School (1995-2025)
Top of this page









 WhatsApp
WhatsApp