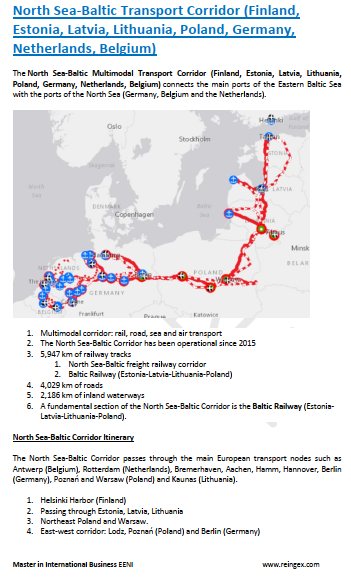
Business in the Netherlands, Amsterdam
Port of Rotterdam (Netherlands). Dutch Foreign Trade, Logistics. Gas

The Kingdom of the Netherlands is one of the most developed countries in the world, occupying the third place in human development (United Nations Human Development Index)
- According to the World Bank and IMF, the Netherlands is the 18th largest economy in the world
- 79% of the Dutch workforce works in services sector
- The Netherlands has significant natural gas resources
- The Netherlands is the eighth most competitive country in the world
- Introduction to the Kingdom of the Netherlands
- Dutch Economy
- Doing Business in Amsterdam
- Dutch International Trade
- Transport and Logistics
- Port of Rotterdam (the largest port in Europe)
- Investment in the Netherlands
- Access to the Dutch market
- Business Plan for the Netherlands

The educational aims of the Subject “Foreign Trade, Logistics and Business in the Netherlands (Holland)” are:
- To analyze the Dutch Economy, Logistics and Foreign Trade
- To conduct research on business opportunities in the Dutch market
- To research the trade relations of the Netherlands with the student's country
- To know Trade Agreements of the Netherlands as a member of the European Union
- To develop a business plan for the Dutch market

The Subject “Foreign Trade, Logistics and Business in the Netherlands” is included within the curriculum of the following academic programs at EENI Global Business School:

Masters: International Business, Foreign Trade.

Languages:  +
+  Paises Bajos
Paises Bajos  Pays-Bas
Pays-Bas  Países Baixos.
Países Baixos.
- Subject Credits “Doing Business in the Netherlands”: 1

International Trade, Logistics and Business in the Netherlands (Holland)

Transport and Logistics in the Netherlands:


Dutch Preferential Access and Trade Agreements:

- The Netherlands and the European Economic Area
- European Union
- Economic and Monetary Union
- European Customs Union
- European Single Market
- The European Union Services Directive
- European Digital Single Market
- As a member of EU, the Netherlands is a beneficiary of EU Trade Agreements
- Council of the Baltic Sea States (observer country)

- World Trade Organization (WTO)
- Agreement on Trade in Services (GATS)
- Agreement on the Application of Sanitary Measures
- Agreement on Technical Barriers to Trade
- Agreement on Preshipment Inspection
- Agreement on Safeguards
- Trade Facilitation Agreement
- World Customs Organization (WCO)
- Kyoto Convention
- International Convention on the Harmonization of Frontier Controls of Goods
- International Chamber of Commerce
- COTIF Convention (Rail)
- BIC
- Chicago Convention (ICAO)
- International Maritime Organization (IMO)
- Convention for Safe Containers
- Istanbul Convention
- Rotterdam Rules (Maritime Transport)
- CMR Convention
- CIM & CIT Rules (Rail Transport)
- International Road Transport Union (IRU)
- TIR Convention
- Guidelines on Safe Load Securing for Road Transport
- International Chamber of Shipping
- Customs Convention on Containers - not a member

- European Union
- European Central Bank
- European Investment Bank
- European Union-CELAC Summit
- European Bank for Reconstruction and Development (EBRD)
- Organization for Security and Cooperation in Europe (OSCE)
- Economic Commission for Europe (UNECE)

- Inter-American Development Bank
- African Development Bank
- Economic Commission for Latin America (ECLAC)
- Economic Commission for Asia (ESCAP)
- Asian Development Bank
- Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD)
- United Nations
- World Bank
- World Trade Organization (WTO)
- International Monetary Fund
- Asia-Europe Meeting
The Netherlands is an observer country to the Association of Caribbean States (ACS).
The Kingdom of the Netherlands (Europe).
- Capital of the Netherlands: Amsterdam and The Hague
- Official Language: Dutch
- Dutch Area: 41,543 km²
- Dutch Population: 17 million people (one of the most densely populated countries in the world)
- Type of Government of the Netherlands: Unitary parliamentary constitutional monarchy
- Borders of the Netherlands: Germany and Belgium
- Dutch Independence: 1581 (Spain)
- The three Caribbean islands of Bonaire, St. Eustatius and Saba belong to the Netherlands and are considered as overseas territories of EU, i.e., they are not part of the customs union or Schengen area
- Indonesia (Dutch East Indies, independence in 1949), Suriname and the Netherlands Antilles, belonged to the Dutch colonial empire
- Abolition of Slavery: 1814
- The headquarters of the International Court of Justice (United Nations) are in The Hague
Religion in the Netherlands: Christianity.
- Catholicism: 27%
- Protestantism: 17%
- The Baptist Church was founded by John Smyth in the Netherlands
The Netherlands belongs to the European Economic Area.
Economy of the Netherlands.
- The Netherlands has been a member of EU since 1958
- Currency of the Netherlands: Euro (1999)
- Main Dutch industrial activities are food processing, chemical industries, petroleum refining, electric machines
- Main Dutch enterprises are Royal Dutch Shell (oil), ABN AMRO Bank, Philips (consumer electronics), Heineken (Beers), Unilever (consumer products), KLM
- Many non-Dutch enterprises are based in the Netherlands, such as EADS, LyondellBasell and IKEA, due to low corporate taxes

Dutch Foreign Trade
- Dutch agri-food sector is crucial and highly export oriented (the third largest food product exporter in the world)
- Main Dutch Exports are natural gas, machinery, chemical products, fuels, food products
- Top Dutch exports destinations: Germany (24%), Belgium, France, the UK, Italy
- Main Dutch Imports are machinery, transport equipment, chemical products, fuels, foods, textiles
- Main suppliers of the Netherlands are Germany, China, Belgium, the UK, Norway
- As a member of EU, the Netherlands is the beneficiary of EU trade agreements with ASEAN, Egypt, Jordan, Lebanon, Ukraine, Moldova, Georgia...
The Port of Rotterdam is the seventh largest port of the world for container traffic and the largest European port. Distances from the Port of Rotterdam to:
- Port of Durban (South Africa): 8,156 Km / 34 days
- Port of Duala (Cameroon): 5,092 Km / 21 days
- Port of Dakar (Senegal): 2,558 Km / 8 days
- Port of Mombasa (Kenya): 7,120 Km / 29 days
- Port of Casablanca (Morocco): 1,681 Km / 7 days
(c) EENI Global Business School (1995-2025)
Top of this page









 WhatsApp
WhatsApp