Business in Germany. German Foreign Trade
Germany: EU political leader, largest European economy, Logistics, Berlin
Germany: The leading European economy and political leader of the European Union.
The Federal Republic of Germany is:
- The Largest European Economy
- The Third largest economy in the world
- The Fifth largest economy (Purchasing Power Parity)
- One of the largest industrialized nations
- Introduction to the Federal Republic of Germany (EU)
- Germany: the most important political player of the European Union
- Federated States of Germany
- Economy of Germany
- Germany as the European Economic Engine
- Economic Profile of the main cities of Germany
- German Industry
- German services sector
- German Foreign Trade
- Transport and Logistics
- Investment in Germany. German's Investments Abroad
- Case Studies:
- Allianz Group
- VOLKSWAGEN Group
- Bayer
- Henkel
- Access to the German Market
- Business Plan for Germany
Sample: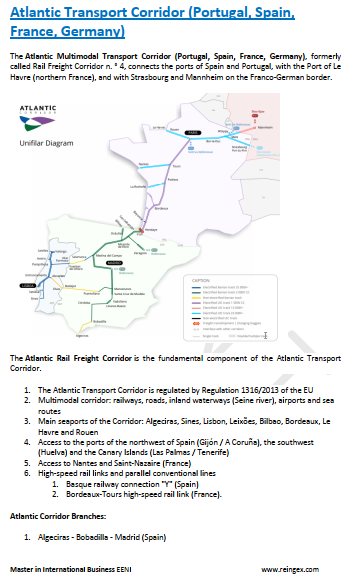

The educational aims of the Subject “Foreign Trade, Logistics and Business in the Federal Republic of Germany” are:
- To analyze the strengths of the German Economy, Logistics and Global Trade
- To conduct research on business opportunities in the German Market
- To research the trade relations of Germany with the student's country
- To learn about German Free trade agreements as a member of the European Union
- To understand the importance of Germany as the first European economy and the political leader of the European Union
- To develop a business plan for the German Market

The Subject “Foreign Trade, Logistics and Business in Germany” is included within the curriculum of the following academic programs at EENI Global Business School:

Masters: International Business, Foreign Trade.

Languages:  +
+  Alemania
Alemania  Allemagne
Allemagne  Alemanha.
Alemanha.
- Subject Credits “Doing Business in Germany”: 3

EENI Global Business School in German: Master in International Business.
International Trade, Logistics and Business in Germany:

- Atlantic Corridor (Portugal-Germany)
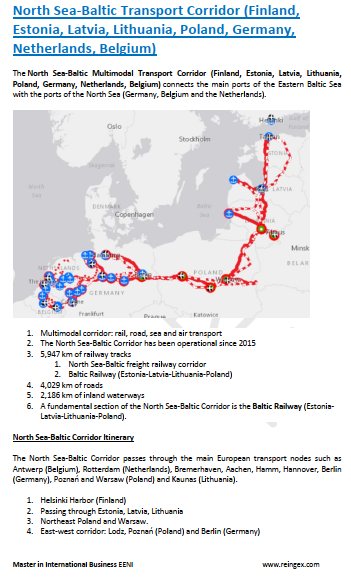
- North Sea-Baltic Corridor (Finland, Belgium)
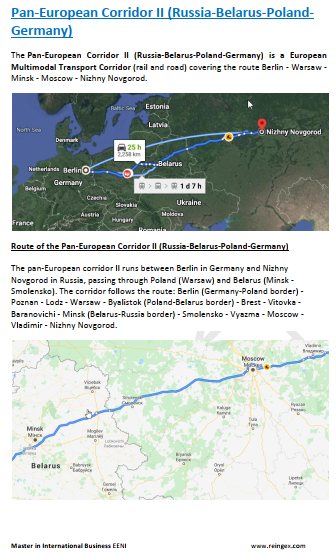
- Pan-European Transport Corridor II (Russia-Germany)
- Access to the
- China-Mongolia-Russia Corridor
- Trans-Siberian Railway (Russia, North Korea)
- Baltic-Adriatic Corridor (Poland, Slovenia)


German Preferential Access and Trade Agreements:
- Germany and the European Economic Area
- European Union
- European Single Market
- The European Union Services Directive
- European Digital Single Market
- Economic and Monetary Union
- European Customs Union
- As a member of EU, Germany is a beneficiary of EU Trade Agreements
- Council of the Baltic Sea States
- Regional Cooperation Council
Germany is an observer country at the.
- Black Sea Economic Cooperation
- Central American Integration System (SICA)
- IORA (dialogue partner)


- World Trade Organization (WTO)
- Agreement on Sanitary and Phytosanitary Measures
- Agreement on Trade in Services (GATS)
- Agreement on Technical Barriers to Trade
- Agreement on Preshipment Inspection
- Agreement on Safeguards
- Trade Facilitation Agreement
- World Customs Organization (WCO)
- Kyoto Convention
- Convention Harmonization of Frontier Controls of Goods
- Hamburg Rules
- CMR Convention (UN)
- International Road Transport Union (IRU)
- TIR Convention
- Guidelines on Safe Load Securing for Road Transport
- COTIF Convention
- BIC (Containers)
- Chicago Convention (ICAO)
- International Maritime Organization (IMO)
- Convention for Safe Containers
- Istanbul Convention
- Customs Convention on Containers - not a member
- International Chamber of Commerce
- International Rail Transport Committee (CIT)
- International Chamber of Shipping
- CIM / CIT Rules

European Trade and Economic Organizations of Germany
- The European Union
- International Bank for Reconstruction and Development
- Organization for Security and Cooperation in Europe (OSCE)
- Economic Commission for Europe (UNECE)

Global Organizations
Germany is a member, among others, of...
- Germany belongs to WTO since 1 January 1995
- Inter-American Development Bank
- Economic Commission for Latin America (ECLAC)
- Asia-Europe Meeting
- OECD
- OECD anti-corruption measures
- Asian Development Bank
- African Development Bank
- Islamic Development Bank
- United Nations
- World Bank
- International Monetary Fund
At a regional level Germany is a founding member of EU and the European Council. As a member of EU, Germany is beneficiary of EU Free trade agreements.
The Federal Republic of Germany (Europe).
- Borders of Germany: France, Belgium, Luxembourg, the Netherlands, Denmark, Poland, the Czech Republic, Austria, and Switzerland
- Capital of Germany: Berlin
- Language of Germany: German
- Area of Germany: 357,022 km²
- German Population: 82 million people
Religion in Germany: Christianity.
- Catholicism (50%)
- Protestants
Germany belongs to the European Economic Area.
- The Nobel Peace Prize Albert Schweitzer was born in Germany

German Economy
- Frankfurt is the financial centre of the Federal Republic of Germany (the largest stock exchange in Europe)
- The industry is the largest pillar of the German economy (25% of GDP, 8 million workers)
- Secondary sector: 30% of GDP of Germany, 25% of the workforce of the Federal Republic of Germany (10 million people)
- The services sector is the largest of the German economy (70% of theGDP)
- Main German enterprises are Volkswagen, Daimler, Porsche, Siemens, Continental, BMW, Basf, Bayer, Beiersdorf, DHL, Bosch, Infineon, Deutsche Telekom, ThyssenKrupp, Bertelsmann, Lufthansa, SAP, Adidas, Hugo Boss
- The European Central Bank (ECB) is in Frankfurt
- Decentralized EU Agency in Germany: the European Aviation Safety Agency (EASA): Cologne

German Foreign Trade.
- Germany is the second largest exporting country in the world (total imports from Germany correspond to those of France and Italy together)
- Main German exports: machinery, vehicles, metals, chemical products, textiles, manufactures and food products
- Main German imports: machinery, foods, chemical products, textiles, vehicles and metals
- The largest German port is the Port of Hamburg
- With a total of 995 Billions Euros in export products, Germany obtained a surplus in its trade balance of 176 Billions Euros
- Germany controls 20% of the world's container ships (international maritime trade)
(c) EENI Global Business School (1995-2025)
Top of this page









 WhatsApp
WhatsApp