International Maritime Trade. Analysis
Increase in international maritime freights (shipping costs), Logistics

Main Pavilions of Convenience: Panama, Liberia and the Marshall Island
70% of Maritime Transport is controlled by 15 enterprises
- Evolution of International Maritime Trade
- Global economic situation of maritime trade
- World maritime traffic
- Structure, ownership and registration of the world maritime fleet
- Global trends in international maritime transport
- Freight and international shipping costs
- Container freight charges, dry bulk and tankers
- Container ports
- Maritime transport connectivity
- Trade Facilitation and international shipping
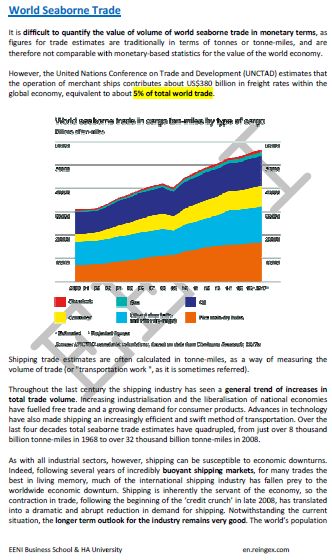
Sample - Analysis of International Maritime Trade (Source UNCTAD):

The Subject “Analysis of International Maritime Trade” is included within the curriculum of the following academic programs at EENI Global Business School:
Logistics Courses: Maritime transport, Multimodal, Transport and Logistics in Africa.
Certificate in International Transport

Masters: International Transport, Transport and Logistics in Africa.


Languages: 
 Comercio Marítimo
Comercio Marítimo
 Commerce maritime
Commerce maritime  Comércio maritime.
Comércio maritime.
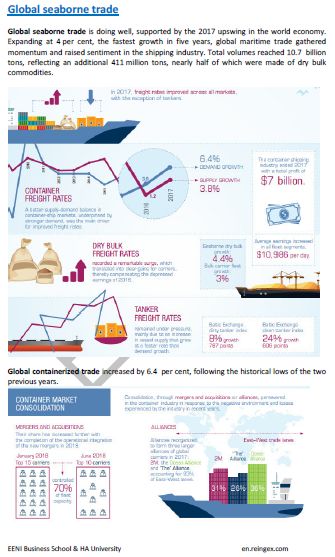
International Maritime Trade is characterized by:
- Increase in international maritime freights, except on tankers
- Strong growth in containers and dry bulk cargo
- Total world tonnage increased by 42 million gross tons
- Strong tendency to Strategic Alliances
- Germany controls 20% of the world's container ships, followed by Greece, China and Canada
- nds
- China, Korea and Japan control 90% of shipping construction
- India, Bangladesh and Pakistan are the main ship dismantling centers
- Asia-Africa Logistics Corridor

(c) EENI Global Business School (1995-2025)
Top of this page









 WhatsApp
WhatsApp