Business in Lebanon. Lebanese Foreign Trade
Lebanese Economy, Logistics. Doing Business in Lebanon (Beirut) Nayla Hayek

The Lebanese agricultural sector accounts for about 7% of GDP
The Lebanese industrial sector represents 22% of GDP and services sector 71% of GDP, highlighting financial and commercial sector

Religions and Global Business -
Religious diversity
- Introduction to the Lebanese Republic (Middle East)
- Doing Business in Beirut
- Lebanese economy
- Lebanese International Trade
- Lebanese Customs Administration
- Business Opportunities in Lebanon:
- Agro-industry
- Industry
- Information Technology
- Business process outsourcing
- Telecommunication
- Tourism
- Media and film industry
- Investment in Lebanon
- Investment Development Authority of Lebanon (IDAL)
- Case Study:
- Nayla Hayek
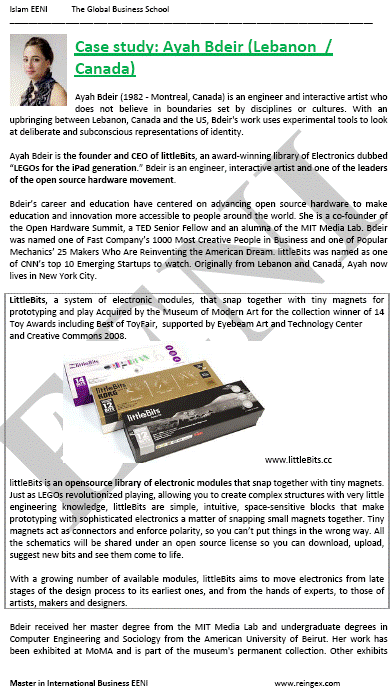
- Ayah Bdeir
- Lebanese largest companies
- INDEVCO
- Access to the Lebanese market
- Transport and Logistics
- Business Plan for Lebanon
International Trade and Business in Lebanon


The educational aims of the Subject “Foreign Trade, Logistics and Business in the Lebanese Republic” are:
- To analyze the Lebanese Economy, Logistics and Global Trade
- To conduct research on business opportunities in the Lebanese Republic
- To explore the Lebanese trade relations with the student's country
- To learn about Lebanese Trade Agreements
- To examine the profile of Lebanese companies
- To develop a business plan for the Lebanese market

The Subject “Foreign Trade, Logistics and Business in Lebanon” is included within the curriculum of the following academic programs at EENI Global Business School:
Masters: International Business, Foreign Trade.


 Master in International Business for Lebanese Students.
Master in International Business for Lebanese Students.
- Subject Credits “Doing Business in Lebanon”: 2


Lebanese Preferential Access and Trade Agreements:
- Lebanon and the Arab Economic Area
- Greater Arab Free Trade Area (GAFTA)
- European Union-Lebanon Agreement
- Trade Agreements with Turkey, Syria, Kuwait, Egypt...
- UK-Lebanon Agreement
- EFTA-Lebanon Agreement
- Islamic Trade Preferential System
Sample:

- WTO (in process of accession)
- Customs Convention on Containers
- International Maritime Organization
- Istanbul Convention - not a member
- Hamburg Rules (Maritime Transport)
- CIM & CIT Rules (Rail Transport)
- COTIF Convention (Rail)
- BIC
- Chicago Convention (ICAO)
- International Road Transport Union (IRU)
- TIR Convention
- Guidelines on Safe Load Securing for Road Transport
- Is not a member of WCO
- Kyoto Convention

- Arab League
- Summit of South American-Arab Countries
- Asia-Middle East Dialogue
- Islamic Development Bank
- Economic Commission for Western Asia (ESCWA)
- Organization of Islamic Cooperation (OIC)
- Committee for Economic Cooperation
- Islamic Chamber of Commerce
- Islamic Centre for Development of Trade
- Afro-Arab Cooperation
- Arab Bank for Africa (BADEA)
- Arab Development Funds
- Arab Trade Financing Programme

- United Nations
- World Bank
- World Trade Organization (WTO)
- International Monetary Fund
- With 5.8 million people, Lebanon has 75% of Muslim population and 25% of Christians
- The Lebanese Republic shares borders with Syria and Israel
- Arab and French are the official languages in Lebanon
- The capital of the Lebanese Republic is Beirut (1.8 million people), an important regional Foreign Trade Port
- Main Lebanese cities are Beirut, Baabda, Saida, Baalbek, Zahle, Tripoli, and Nabatiyeh
- The headquarters of the Economic and Social Commission for Western Asia (ESCWA) are in Beirut (Lebanon)
- Independence of Lebanon: 1946 (from France)
- Lebanese Government: Parliamentary Democracy
- Area of Lebanon: 10,452 km²
- Human Development Index of Lebanon: 0.765
Religion in Lebanon.
- Islam Sunni is the main religion in Lebanon (75% population), the largest school of Islamic Jurisprudence is the Hanafi
- In Lebanon, there are about 1 million Maronites (Christians Catholics)
- Beirut is divided between Christian and Muslim areas


Lebanon belongs to the Arab Economic Area.
Lebanese Economy.
- Top Lebanese public enterprises: Middle East Airlines, Electricity of Lebanon, Water Company, TV Lebanon Tobacco Company, and the National Wheat and Beet
- Currency of Lebanon: Lebanese Pound (LBP)
- Labour Force in Lebanon: 1.6 million people


International Trade of Lebanon.
- Major supplier of the Lebanese Republic: the United States (11%), China (9%), France (8%), Italy (7%), and Germany (6.3%)
- Major export destinations of the Republic of Lebanon: Switzerland, Iraq, Syria, and Saudi Arabia
- Machinery and electrical equipment accounted for 21% of the Lebanese exports, jewellery (13%), chemicals (11%), and food (7%)
- Top Lebanese imports: Mineral fuels (27%), machinery (12%), transport equipment (12%), and pharmaceutical products (4%)
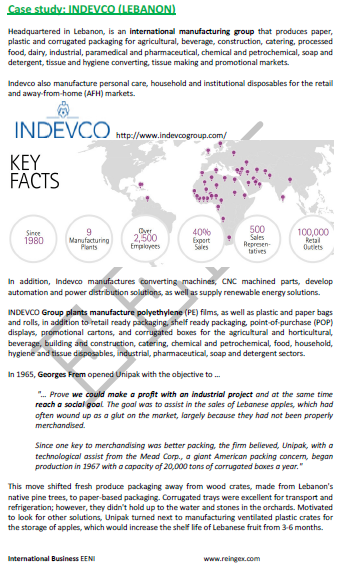
Sample - Ayah Bdeir:
Sample: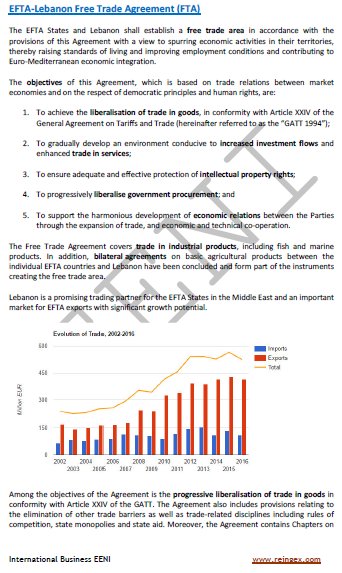
(c) EENI Global Business School (1995-2025)
Top of this page









 WhatsApp
WhatsApp or
or 
