Business in Haiti. Haitian Economy
Textiles sector in Haiti. Port-au-Prince (Foreign Trade). Food, beverages

Haiti was the first black Republic and the second to become independent.
Top Haitian economic sectors: tourism (1 million tourist/year), apparel industry (36,000 workers, 10% of GDP), agribusiness, electronics manufacturing (Android-based tablets), free zones, Business Process Outsourcing (BPO), and IT Industry
80% of the Haitian population is living under the poverty line
African Diaspora in Haiti: 10.2 million people (95% of the Haitian population)
- Introduction to the Republic of Haiti (Caribbean)
- Haitian Economy
- Haitian advantages
- Doing Business in Port-au-Prince
- Foreign Trade of Haiti
- Hemispheric Opportunity through Partnership Encouragement (HOPE) Act
- Investment in Haiti
- Business Opportunities in Haiti
- Apparel
- Agribusiness
- Tourism
- Transport and Logistics
- BPO and IT
- Case Study:
- Apparel and textiles sector in Haiti
- Sûrtab (Android-based tablet)
- Access to the Haitian Market
- Business Plan for Haiti

The educational aims of the Subject “Foreign Trade, Logistics and Business in Haiti” are:
- To analyze Haitian Economy, Logistics and Global Trade
- To conduct research on business opportunities in Haiti
- To explore the Haitian trade relations with the student's country
- To learn about Haitian Trade Agreements
- To examine the profile of Haitian companies
- To develop a business plan for the Haitian Market

The Subject “Foreign Trade, Logistics and Business in Haiti” is included within the curriculum of the following academic programs at EENI Global Business School:
Masters: International Business, Foreign Trade.


Languages:  or
or  Haiti
Haiti  Haïti
Haïti  Haiti.
Haiti.
Doctorate and Masters in International Business for the Caribbean students (CARICOM).
Credits of the Subject “Doing Business in Haiti”: 1 
International Trade, Logistics and Business in Haiti

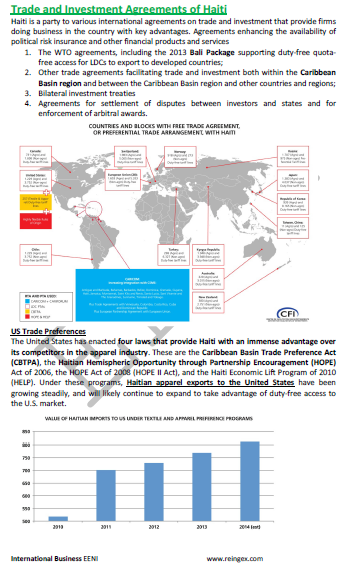
Haitian Preferential Access and Trade Agreements with
- Haiti and the Caribbean Economic Area
- CARICOM
- Colombia-Haiti (CARICOM) Agreement
- Costa Rica-CARICOM (Haiti)
- CARICOM-Dominican Republic Agreement
- UK-CARIFORUM Free Trade and Economic Integration Agreement
- The Caribbean Single Market Economy (CSME)
- Association of Caribbean States
- Latin American and Caribbean Economic System
- The United States-Haiti
- Hemispheric Opportunity through Partnership Encouragement (HOPE) Act - United States
- The United States-Caribbean Basin Trade Partnership Act (CBTPA)
- European Union-Haiti
- Beneficiary of Everything but Arms (EBA)
- CARIFORUM-EU Agreement
- Caribbean Basin Initiative
- The United States-Caribbean Basin Trade Partnership Act (CBTPA)
- Caribbean-Canada Trade Agreement
- Caribbean Development Bank
- Global System of Trade Preferences among Developing Countries (GSTP) - accession process
- Bolivarian Alliance for the Peoples of Our America (ALBA) - observer country

- World Trade Organization (WTO)
- Agreement on Trade in Services (GATS)
- Agreement on Sanitary Measures
- Agreement on Technical Barriers to Trade
- Agreement on Preshipment Inspection
- Agreement on Safeguards
- Trade Facilitation Agreement
- World Customs Organization (WCO)
- Kyoto Convention

American Trade and Economic Organizations. Haiti is a member of:
- Organization of American States (OAS)
- Economic Commission for Latin America (ECLAC)
- Inter-American Development Bank
- Community of Latin American and Caribbean States (CELAC)
Global Organizations:
- Commonwealth
- United Nations
- World Bank
- World Trade Organization (WTO)
- International Monetary Fund
- World Customs Organization (WCO)
- Population of Haiti: 10 million (65% under the age of 30, black 95%)
- Haitian Capital: Port-au-Prince
- 2010 earthquake
- Official languages of Haiti: French and Creole (official)
- Haitian Area: 27,750 km²
- Haiti is the second-largest island the Caribbean
- Haitian frontier: The Dominican Republic
- Near countries: Cuba (77 kilometers), Puerto Rico, Jamaica, and the United States
- Independence of Haiti from France: 1825
- Abolition of Slavery in Haiti: (1804)
Religions in Haiti:
- Catholicism (official) 55%
- Protestants 28%
- Voodoo (official) 2.1%
Haiti belongs to the Caribbean Economic Area.

Haitian Economy.
- Post-earthquake Action Plan for National Recovery and Development of Haiti
- Government support to the free trade zones, and industrial parks
- Global Brands in Haiti: Heineken, Unilever, Coca-Cola, Marriot
- Haiti is one of the most corrupt countries in the World
International Trade and Business in Haiti


Haitian Foreign Trade.
- Top Haitian export sector: Apparel
- Largest ports of Haiti: Port-au-Prince and Cap-Haïtien
- Transit time Port-au-Prince to Port Everglades (Florida, US): three days
- Main Haitian agribusiness exports: bananas, cocoa, coffee, mangos, and sisal
(c) EENI Global Business School (1995-2025)
Top of this page









 WhatsApp
WhatsApp