Business in the Dominican Republic, Santo Domingo
Dominican Economy and Foreign Trade. Tourism, Logistics, agreements, free zones

services sector is the pillar of the Dominican economy (55% of GDP, the largest employment generator)
- Other significant Dominican economic sectors are free trade zones, tourism, telecommunications, and construction
- tourism sector represents more than 1,000 million dollars annually
African Diaspora in the Dominican Republic: 8.7 million people (84% of the Dominican population)
- Introduction to the Dominican Republic
- Doing Business in Santo Domingo
- Dominican Economy
- International Trade of the Dominican Republic
- Transport and Logistics
- Case Study:
- Trade Relations with Chile and Canada
- Brugal
- Access to the Dominican Market
- Business Plan for the Dominican Republic

The educational aims of the Subject “Foreign Trade, Logistics and Business in the Dominican Republic” are:
- To analyze the Dominican Economy, Logistics and Global Trade
- To conduct research on business opportunities in the Dominican Republic
- To explore the Dominican trade relations with the student's country
- To learn about Dominican Trade Agreements
- To examine the profile of Dominican companies
- To develop a business plan for the Dominican Market

The Subject “Foreign Trade, Logistics and Business in the Dominican Republic” is included within the curriculum of the following academic programs at EENI Global Business School:
Masters: International Business, Foreign Trade.


Masters adapted for Caribbean students.
Languages:  or
or  Repúbliba Dominicana
Repúbliba Dominicana  Repúblique Dominicaine.
Repúblique Dominicaine.
- Subject Credits “Doing Business in the Dominican Republic”: 1


International Trade, Logistics and Business in the Dominican Republic.

The Dominican Republic Trade Agreements and Market Access.
- The Dominican Republic and the Hispanic American Economic Area
- Central American Integration System
- Association of Caribbean States
- Latin American and Caribbean Economic System
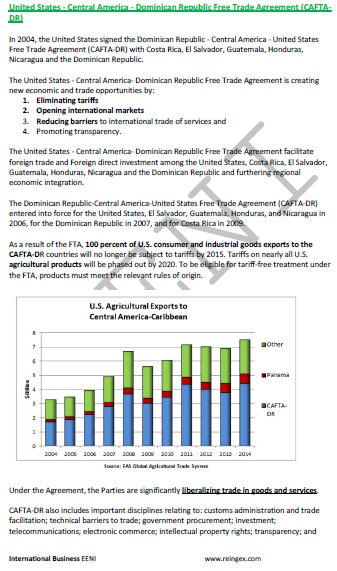
- Trade Agreement with the United States
- Dominican Republic-Central America Agreement
- Mesoamerica Project
- UK-CARIFORUM Free Trade and Economic Integration Agreement
- CARICOM (Observer State)
- Trade Agreement with CARICOM
- ALADI (observer)

- World Trade Organization (WTO)
- Agreement on Trade in Services (GATS)
- Agreement on the Application of Sanitary Measures
- Agreement on Technical Barriers to Trade
- Agreement on Preshipment Inspection
- Agreement on Safeguards
- Trade Facilitation Agreement
- Hamburg Rules (Sea)

- Inter-American Development Bank
- Organization of American States (OAS)
- Economic Commission for Latin America (ECLAC)
- East Asia-Latin America Cooperation
- Community of Latin American and Caribbean States (CELAC)

- United Nations
- World Bank
- World Trade Organization (WTO)
- International Monetary Fund
- The capital of the Dominican Republic is Santo Domingo
- The Dominican population is 9.9 million people
- Area of the Dominican Republic: 48,311 km²
- The official language of the Dominican Republic is Spanish
- The Dominican Republic gained the independence from Spain in 1821
- Abolition of Slavery in the Dominican Republic: (1804)
Religion in the Dominican Republic: Catholicism.

The Dominican Republic belongs to Western Civilization (Hispanic American Economic Area).

The Dominican Economy and Foreign Trade.
- The Dominican economy is closely related to Foreign Direct Investment from the United States
- The economic slowdown due to the impact of the international financial crisis
- The economy of Santo Domingo (capital) is based on services and industry
- The Dominican financial sector is strong and is one of the largest in the Caribbean region
- In the Dominican Republic, Exports were reduced by 231 million dollars mainly due to the fall in exports of ferro-nickel, as a result of international nickel prices reduction. All this led to the temporary closure of the company Falconbridge
- The Dominican Republic has one of the most advanced telecommunications infrastructures in Central America, open to Foreign Direct Investment
Brugal is one of the largest enterprises in the Dominican Republic. In recent years, Brugal has begun a process of strengthening its presence in international markets, to increase exports and guarantee its continued growth process.
(c) EENI Global Business School (1995-2025)
Top of this page









 WhatsApp
WhatsApp