International Trade Finance. Financing Exports
Finance of export/ import transactions. International risks: foreign exchange

There are two basic forms for Financing Foreign Trade transactions:
- Import finance
- Export finance
Both can be performed in the currency of the exporter (for example, Euros) or any other fully convertible currency agreed by both parties.
- Introduction to International Trade finance
- Export/import financing
- Pre-shipment finance
- International risks: payment, foreign exchange, counterparty, and delivery
- Case Study: The Impact of Currency Risk on Volkswagen AG (2015)
- Country
Risk
- Sovereign risk
- Credit ratings
- Evaluation and classification of Country Risk
- Corruption perceptions index
- Export credits (OECD)
- Bank-guaranteed trade finance (documentary trade)
- Not-bank-guaranteed trade finance
- Supply chain finance
- Purchase order finance (pre-shipment finance)
- Inventory finance (warehouse)
- Factoring and Forfaiting
- Case Study: Using Factoring and Forfaiting for Export Financing
- Case Studies:
- The case of Thailand and South Africa
- Introduction to Islamic Banking
- Financing Contract between a Saudi company and a European company
- FOREX
- International Bonds and Guarantees
- Influence of religion on financial systems
- Religion and International Trade Finance
- Case Study: Ayurvedic Product Trade and Ethical Financing in India
- AI and Global Trade
- Digital Trade and Cross-Border E-Commerce
- AI in Global Strategy and Decision-Making
- AI in Global Finance and Risk Management

The objectives of the subject “Foreign Trade Finance” are the following:
- To familiarise the student with the various methods of finance both for exports and imports
- To understand the risks associated with Foreign Trade operations
- To know how to manage pre-financing and export financing

The Subject “International Trade Finance” is included within the curriculum of the following academic programs at EENI Global Business School:
Masters: International Business, Foreign Trade.


Postgraduate Certificate in International Trade.

Languages:  or
or  Financement
Financement
 Financiación
Financiación  Financiamento.
Financiamento.
Credits of the subject “Foreign Trade Finance”: 4 ECTS.
In the second case, the company assumes certain risks as the exchange rates difference. However, it can also profit from trading in another currency if there is a rise in the foreign currency value.
Financial transactions in Foreign Trade can be performed in the currency of the exporter/importer or a third currency.
In many cases, export enterprises must facilitate financing for their clients mainly due to market requirements. In the Foreign Exchange Market, dealers trade in currencies.
Product and service exports, Foreign Direct Investment and foreign loans forms currency supply whereas currency demand consists of imports, Foreign Direct Investment and other factors.
These operations stimulate the buying and selling of currencies in a market governed by the supply and demand. If a payment for a service provided or for a product delivered to a foreign client is in a currency other than in which the exporter usually operates, the exporter is exposed to the risk of exchange rate fluctuation.
In any exporting or importing transaction there is a range of risks to be considered including:
- Payment Risk
- Performance Risk
- Foreign Exchange Risk
- Interest Rate Risk
- Counterparty/Bank Risk
- Country Risk
- Delivery Risk
The underlying commercial contract should clearly state the.
- Description of the products
- Delivery terms, when and by what means the payment is to be made
- Required documents, which will allow the Importer to obtain the delivery of goods and to arrange clearance through the customs
- Currency in which the settlement is to be effected and
- Any specific requirements attaching to shipment
Sample - International Trade Finance:
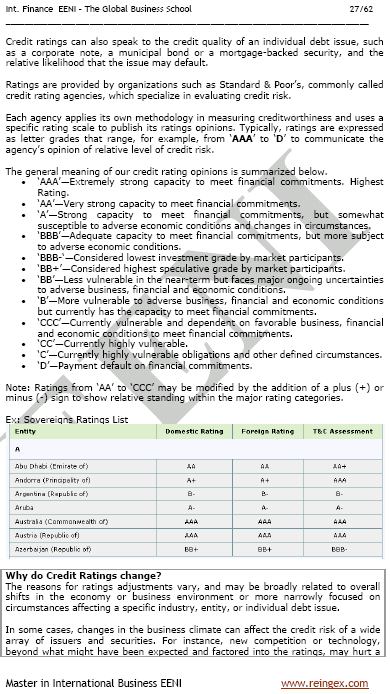
Country risk is caused by political (unwillingness to repay) or economic (inability to repay) events in a particular country. Normally, country risk is measured as transfer risk or cross-border risk, which is another terminology used to describe the country risk.
Sovereign risk is the risk of the Government, or Government-related entity, making the payment. Country risk embodies both govern and commercial risk.
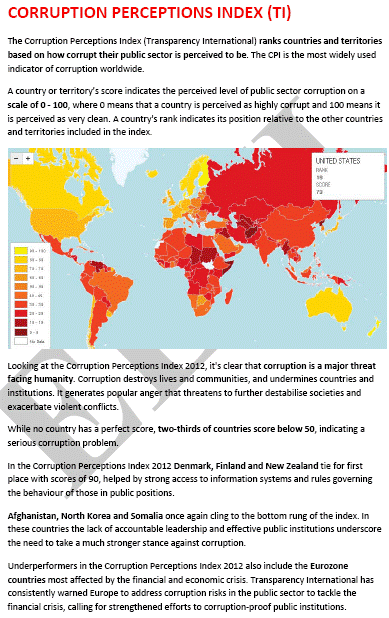
The Corruption perceptions index measures the perceived level of the public-sector corruption in 180 countries economies.

Religions and Global Business -
Religious diversity
The relationship between religion and international trade finance is a complex issue encompassing ethical, cultural, and practical aspects. Religious beliefs influence commercial and financial practices, shaping investment decisions, financing structures, and negotiation strategies in global trade.
Many religions promote values such as fairness, transparency, and justice, which impact business transactions. For example, in Islamic finance, the prohibition of usury (riba) leads to structures such as murabaha (cost-plus financing) or sukuk (Islamic bonds), which avoid interest and align with Sharia law.
eligion influences corporate ethics and financial systems. For example:
- Islamic Finance: The prohibition of interest (riba) and speculative investments has boosted a $4 trillion Islamic finance industry (Reuters, 2025).
- Banks such as HSBC and Standard Chartered offer Sharia-compliant products, such as sukuk (Islamic bonds), which grew 12% globally in 2024.
(c) EENI Global Business School (1995-2025)
Top of this page










 WhatsApp
WhatsApp