Business in Ecuador, Guayaquil, Quito
Ecuador: leading exporter of bananas. Ecuadorian Foreign Trade, Logistics, fruits, flowers

Thanks to its geographical location, Ecuador has an appropriate climate for growth of many agricultural export products
- Ecuador is the largest bananas, palm of hearts, balsa wood, passion fruit juice, and roses exporter in the World
- Ecuador is renowned for its high-quality food products, including cocoa, coffee, aromatic, and medicinal plants
- Introduction to the Republic of Ecuador (Andean Community)
- Doing Business in Guayaquil and Quito
- Ecuadorian Economy
- International Trade of Ecuador
- Customs of Ecuador
- Import and export formalities
- Investment in Ecuador
- Transport and Logistics
- Case Study: Business Opportunities in Ecuador
- Industrial sector
- Fashion and accessories
- Services
- Agribusiness sector. Case Study:
- UBESA
- Holding Favorite Fruit Company
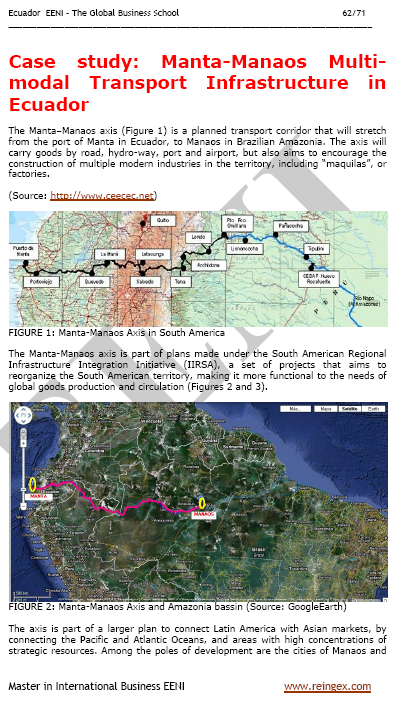
- Case Study: Manta-Manaus Multimodal Transport Infrastructure in Ecuador
- Access to the Ecuadorian Market
- Business Plan for Ecuador

The educational aims of the Subject “Foreign Trade, Logistics and Business in Ecuador” are:
- To analyze the Ecuadorian Economy, Logistics and Global Trade
- To conduct research on business opportunities in Ecuador
- To explore the Ecuadorian trade relations with the student's country
- To learn about Ecuadorian Trade Agreements
- To examine the profile of Ecuadorian companies
- To develop a business plan for the Ecuadorian Market

The Subject “Foreign Trade, Logistics and Business in Ecuador” is included within the curriculum of the following academic programs at EENI Global Business School:
Masters: International Business, Foreign Trade.


Languages:  or
or  Ecuador
Ecuador  Equateur
Equateur  Equador.
Equador.
- Credits: 1

International Trade, Logistics and Business in Ecuador

- Ecuador and the Hispanic American Economic Area
- Andean Community
- Union of South American Nations (UNASUR)
- Latin American Integration Association (ALADI)
- Latin American and Caribbean Economic System
- Mexico-Ecuador Economic Complementation Agreement
- El Salvador-Ecuador Agreement
- UK-Ecuador-Peru Free Trade and Economic Integration Agreement
- Global System of Trade Preferences
- MERCOSUR (Associate)
- SICA (observer country)
The Republic of Ecuador retired from the Bolivarian Alliance for the Peoples of Our America (ALBA) in 2018.
- Ecuador seeks to join the Pacific Alliance after its departure from ALBA

- World Trade Organization (WTO)
- Agreement on Trade in Services (GATS)
- Agreement on Sanitary Measures
- Agreement on Technical Barriers to Trade
- Agreement on Preshipment Inspection
- Agreement on Safeguards
- Trade Facilitation Agreement
- World Customs Organization (WCO)
- Kyoto Convention
- Hamburg Rules (Sea)

- Inter-American Development Bank
- Organization of American States (OAS)
- Economic Commission for Latin America (ECLAC)
- Summit South American-Arab Countries
- Africa-South America Summit
- East Asia-Latin America Cooperation
- Community of Latin American and Caribbean States (CELAC)
- European Union-CELAC Summit

- United Nations
- Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD)
- International Trade Centre
- Commission on International Trade Law (UNCITRAL)
- World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO)
- OPEC Fund for International Development (OFID)
- World Bank
- World Trade Organization (WTO)
- International Monetary Fund
- Pacific Economic Cooperation Council
- Borders of Ecuador: Colombia and Peru
- Ecuadorian Capital: Quito
- Guayaquil is the second-largest Ecuadorian city
- Official language of Ecuador: Spanish
- Ecuadorian population: 15.7 million people
- Ecuadorian Area: 283,561 km²
- Ecuadorian currency: Dollar USD
- Abolition of Slavery in Ecuador: 1851
- African Diaspora in Ecuador: 1.1 million people (7.2% of Ecuadorian population)
- Independence of Ecuador from Spain: 1809, recognized in 1830
Main religion in Ecuador: Christianity (Catholicism: 13 million).
Ecuador belongs to the Hispanic American Economic Area (Western Civilization).
Ecuadorian Economy.
- Ecuador benefits from his strategic position that provides the direct access to the East Asian markets and the Western Coast of the United States
- Its proximity to the Panama Canal permits safe access to Europe, the United States, Africa, the Middle East, and Asia
- The Ecuadorian economy is the eighth largest economy in Latin America after Brazil, Mexico, Argentina, Chile, Colombia, Venezuela, and Peru
- The Dollarization of Ecuador creates an advantage negotiating with a strong currency (since January 2000, the United States Dollar is the official currency)
- Petrol, manufacturing, commerce, and agricultural production are the pillars of the Ecuadorian economy
- Petrol accounts for 40% of the Ecuadorian exports, petroleum exports allow having a positive trade balance
- Tax reform in Ecuador in 2014. Tax amnesty in 2015
- The Union of South American Nations (UNASUR) is in Quito
- Ecuador is a leader in bananas, shrimp, fresh tilapia, tuna, fine cocoa, passion fruit concentrate, palm, pond, leaf snuff, and broccoli production

The main activity of the Holding Favorite Fruit Company is production and export of first-class green bananas, Cavendish variety. The Favorite Fruit Company has a 4.5% share of the worldwide market; exports have shown a continuous growth.

International Trade of Ecuador.
- Ecuador has an international reputation as a reliable seafood and aquaculture products supplier, the manufacturing industry is known for its strengths in design, quality, and reliability
- The largest import partners of Ecuador are Latin America excluding the Andean Community 37%, the United States 25%, the Andean Community 22% Asia 19%, and EU 10%
- The Port of Guayaquil handles a majority of International Trade of Ecuador; it is the economic capital of Ecuador
- Other important ports of Ecuador are Esmeraldas, Manta and Puerto Bolívar (banana). A larger bulk of International Trade takes advantage of ocean routes. Every year, there are over 2,500 vessels that leave from Ecuadorian ports
Ecuador is:
- World's leading bananas exporter
- The first palm hearts exporter
- The first roses exporter
- The third largest flower exporter
Ecuador is a member of the Andean Community and associated to MERCOSUR

(c) EENI Global Business School (1995-2025)
Top of this page









 WhatsApp
WhatsApp