Business in Estonia, Tallinn. Baltic Tiger
Estonia: the most digital country of EU. Estonian Foreign Trade, Logistics

- The Republic of Estonia is the European leader in Internet penetration and mobile telephony
- Concept of e-Residency: towards the Digital Nomades
- Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania are the so-called Baltic Tigers
- Introduction to the Republic of Estonia (EU)
- Economy of Estonia: The most digital country of EU
- The Estonian E-Resident Concept
- Doing Business in Tallinn
- Estonian Foreign Trade
- Transport and Logistics
- Investment in Estonia
- Main Estonian companies
- Access to the Estonian Market
- Business Plan for Estonia

The educational aims of the Subject “Foreign Trade, Logistics and Business in Estonia” are:
- To analyze the Estonian Economy, Logistics and Global Trade
- To conduct research on business opportunities in the Estonian Market
- To research the trade relations of Estonia with the student's country
- To learn about Estonian free trade agreements as a member of the European Union
- To develop a business plan for the Estonian Market

The Subject “Foreign Trade, Logistics and Business in Estonia” is included within the curriculum of the following academic programs at EENI Global Business School:

Masters: International Business, Foreign Trade.

Languages:  +
+  Estonia
Estonia  Estonie
Estonie  Estónia.
Estónia.
- Subject Credits “Doing Business in Estonia”: 1

International Trade, Logistics and Business in Estonia

Transport Corridors related to Estonia:
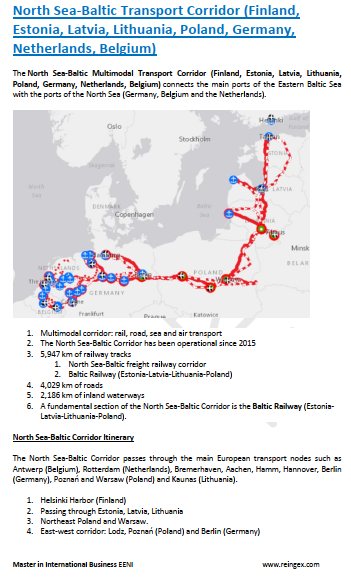
- North Sea-Baltic Corridor (Finland, Belgium)
- Access to the:
- Trans-Siberian Railway (Russia, North Korea)
- Pan-European Corridor II
- Pan-European Corridor IX



Estonian Preferential Access and Trade Agreements:
- Estonia and the European Economic Area
- European Union
- As a member of EU, Estonia is a beneficiary of EU Trade Agreements
- European Single Market
- The European Union Services Directive
- European Digital Single Market
- European Customs Union
- Council of the Baltic Sea States

- World Trade Organization (WTO)
- Agreement on Sanitary and Phytosanitary Measures
- Agreement on Trade in Services (GATS)
- Agreement on Technical Barriers to Trade
- Agreement on Preshipment Inspection
- Agreement on Safeguards
- Trade Facilitation Agreement
- World Customs Organization (WCO)
- Kyoto Convention
- COTIF Convention (Rail)
- BIC
- Chicago Convention (ICAO)
- International Maritime Organization (IMO)
- Convention for Safe Containers
- Istanbul Convention
- Customs Convention on Containers - not a member
- Convention Harmonization of Frontier Controls of Goods
- CMR Convention
- International Chamber of Commerce
- CIM & CIT Rules (Rail Transport)
- International Road Transport Union (IRU)
- TIR Convention
- Guidelines on Safe Load Securing for Road Transport
- Organization for Cooperation between Railways (OSJD)

- The European Union
- Organization for Security and Cooperation in Europe (OSCE)
- Group of States of the European Council Convention against Corruption

- Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD)
- Asia-Europe Meeting
- International Monetary Fund
- United Nations
- World Bank
- Estonian Capital: Tallinn
- Official Language of Estonia: Estonian
- Estonian Area: 45,228 km²
- Estonian population: 1.3 million people (one of the less populated countries in the EU)
- About 25% of the population of Estonia has a Russian origin, which generates tensions
- Type of Government of Estonia: Parliamentary Republic
- Borders of Estonia: Latvia and Finland
- Independence of Estonia from the Soviet Union: 1991
Main religion in Estonia: Lutheran Protestantism (Christianity).
Estonia belongs to the European Economic Area.
Economy of Estonia.
- The information technology and the electronic sector are the pillars of the Estonian economy
- Estonian Currency: Euro (2011)
- Estonia is a member of EU since 2004
- The Headquarters of the European Agency for the operational management of large-scale IT systems in the area of freedom, security and justice (eu-LISA) are in Tallinn (Estonia)
- Virtually all sectors of the Estonian economy have been privatized (except power plants)
- Top Estonian Industries are engineering, electronics, wood products, textiles, information technology, telecommunications
- Top Estonian enterprises are Hansapank, Eesti Energia, SEB Eesti Ühispank, Eesti Telekom, Tallinnk Grupp, Olympic Entertainment Group, Tallinnna Sadam, Tele2 Eesti, Sampo Pank, Tallinnna Kaubamaja, Merko Group, BLRT Grupp, Elisa, Tallinnna Vesi, Transgroup Invest, Eesti Raudtee, Kunda Nordic Tsement, Viru Keemia Grupp, Falck Baltics

Estonian Foreign Trade.
- 50% of the Estonian Foreign Trade is made with the countries of the European Union
- Main Estonian Exports are wood houses, machinery, electronics and textiles
- Top Estonian trading partners are Germany, Finland and Sweden
(c) EENI Global Business School (1995-2025)
Top of this page









 WhatsApp
WhatsApp