Financial Integration in Africa
Regional Financial Integration in Africa. Mobile banking services. Cross-border banking

Regional Integration in Africa
In general, financial systems in Africa are limited (both in capacity and size) and not fully regional integrated, this cause high transactions cost and elevated levels of Risk

- Introduction to Regional Financial Integration in Africa
- Trends in African regional financial integration
- Case Study: The four largest African banking groups
- ECOBANK (Togo)
- United Bank for Africa (Nigeria)
- Standard Bank Group (South Africa)
- BMCE BANK Group (Morocco)
- Cross-border banking
- Mobile banking services
- Payment systems in Africa
- Risks from cross-border banking in Africa
- Case Study: Vodafone Money Transfer (M-PESA) in Africa
- Capital markets development in Africa
- Regional Financial infrastructure
- History of monetary cooperation in Africa
- Challenges of the CFA zone
- Case Study: Monetary Cooperation Arrangements of Regional Economic Communities (REC)
Sample - Financial Integration in Africa:

The Subject “Regional financial integration in Africa” is included within the curriculum of the following academic programs at EENI Global Business School:
Doctorate in African Business.

Master in Business in Africa, Transport and Logistics in Africa.

Languages:  or
or  Intégration financière en Afrique
Intégration financière en Afrique  Integración Financiera Africana
Integración Financiera Africana  Integração financeira africana.
Integração financeira africana.
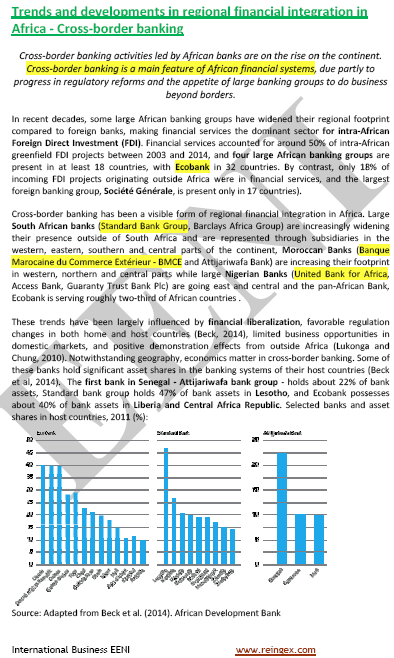
- A right financial infrastructure (legal framework, payment systems, credit registries...) can contribute to boost intra-African trade and economic growth
- One of the pillars of the African financial system is Cross-border banking
- The four largest Banks in Africa are ECOBANK (Togo), United Bank for Africa (Nigeria), Standard Bank Group (South Africa) and BMCE BANK Group (Morocco)
- M-PESA is a money transfer system launched by Vodafone; PESA means MONEY in Swahili
- In Africa, M-PESA is operative in Kenya, Tanzania, South Africa, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Mozambique, Egypt and Lesotho
- The JSE (Johannesburg Stock Exchange) represents 65 percent of total market capitalization in Africa
- Southern African Development Community (SADC), Common Market for Eastern and Southern Africa (COMESA), West African Economic and Monetary Union (WAEMU), and Central African Economic and Monetary Community (CEMAC) are trying to harmonize their regional payment systems
(c) EENI Global Business School (1995-2025)
Top of this page









 WhatsApp
WhatsApp