European Economic and Monetary Union (EU)

Eurozone. Economic and Monetary Union. European Central Bank
- Introduction to the Economic and Monetary Union (EMU) of the EU
- Historical evolution of the Economic and Monetary Union
- Institutions related to the Economic and Monetary Union
- European Central Bank (ECB)
- European System of Central Banks (SEBC)
- Economic and Financial Committee (CEF)
- Eurogroup
- Economic and Financial Affairs Council (ECOFIN)
- European Monetary Policy
- Price Stability
- Open Market Operations
- Asset Acquisition Programs
- Economic Governance in the Eurozone
- Coordination and Monitoring of the economic policies;
- Stability and Growth Pact
- Budget Pact
- Macroeconomic Surveillance
- Macroeconomics disequilibrium procedure
- Financial Assistance Mechanisms of the EU
- European Financial Stabilization Mechanism: Ireland, Portugal and Greece
- European Financial Stabilization Facility (EFSF)
- European Stability Mechanism (ESM): Spain, Cyprus and Greece
- Banking Union
- Single Supervision Mechanism
- Single Resolution Mechanism
The objectives of the subject “Economic and Monetary Union (EMU) of the EU” are the following:
- To understand the fundamentals of the European Economic and Monetary Union
- To analyze the roles of the five key institutions related to the Economic and Monetary Union
- To understand the principles of the European Monetary Policy
- To know the behavior of the Eurozone's supervision
- To evaluate the EU's financial assistance mechanisms

The Subject “European Economic and Monetary Union (EU)” belongs to the following Online Programs taught by EENI Global Business School:
Doctorate: European Business, World Trade.
Masters: International Business, Foreign Trade.

Languages:  or
or  Unión Económica (UE)
Unión Económica (UE)  Union économique UE
Union économique UE  União Económica UE.
União Económica UE.
Masters adapted for  EU Students.
EU Students.
Sample - European Economic and Monetary Union (EU):
The Economic and Monetary Union is one of the pillars of the European Single Market (EU). Since 1 January 1999, when the Euro was introduced, the entire monetary policy of the EU is managed by the European Central Bank (ECB).
Each member state of the EU Economic and Monetary Union must comply with the so-called “Stability and Growth Pact”, which avoids, among other things, that a country has a high deficit.
Five key institutions are related to the EU Economic and Monetary Union (EMU):
- European Central Bank (ECB)
- European System of Central Banks (ESCB). It consists of the European Central Bank and Central Banks of the EU member states. The main objective is to achieve price stability
- Economic and Financial Committee (EFC)
- The Eurogroup, formed by the Ministers of Economy and Finance of the Eurozone. It is an advisory body
- Council of Ministers of Economy and Finance (ECOFIN)
These institutions have the following objectives:
- Define the monetary policy of the EU
- Set the rules for Euro issue
- Design price stabilization strategies in the Economic Union market
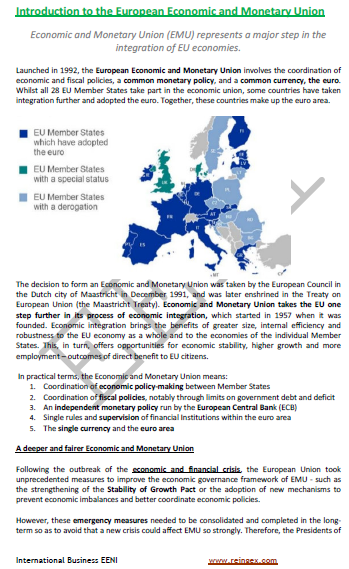
Nineteen EU countries have adopted the euro and are therefore part of the Eurozone: Austria, Belgium, Cyprus, Estonia, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Ireland, Italy, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Malta, Slovakia, Slovenia, Spain, the Netherlands and Portugal.
- The following countries are not yet part of the Eurozone: Bulgaria, Croatia, Hungary, Poland, the Czech Republic, Romania and Sweden
- Denmark opted out of the Eurozone
- After the BREXIT, the UK will no longer belong to the EU (Europe)

European Economic Area (Western Civilization).
(c) EENI Global Business School (1995-2024)
We do not use cookies
Top of this page



