Business in Italy, Roma, Milan
Italian Economy and Foreign Trade. Transport and Logistics
The largest sectors of the Italian economy (61 million people) are fashion, mechanical construction, tourism (the fifth country in the world that receives more tourists), chemical export products, automotive sector and food products
- The Northern regions are among the richest in the European Union
- Milan is the financial and industrial centre of the Italian Republic, Milan is one of the world fashion capitals
- Rome is the third most visited city in the European Union
- Turin is the Italian automotive industry centre
- Introduction to the Italian Republic (EU)
- Doing Business in Roma and Milan
- Italian Economy
- Italian Foreign Trade
- Transport and Logistics
- Case Studies: Italian enterprises
- Ferrero
- Benetton
- Fiat
- Access to the Italian market
- Business Plan for Italy

The educational aims of the Subject “Foreign Trade, Logistics and Business in Italy” are:
- To analyze the Italian Economy, Logistics and Global Trade
- To conduct research on business opportunities in the Italian market
- To research the trade relations of Italy with the student's country
- To learn about Italian trade agreements as a member of the European Union
- To develop a business plan for the Italian market
Sample: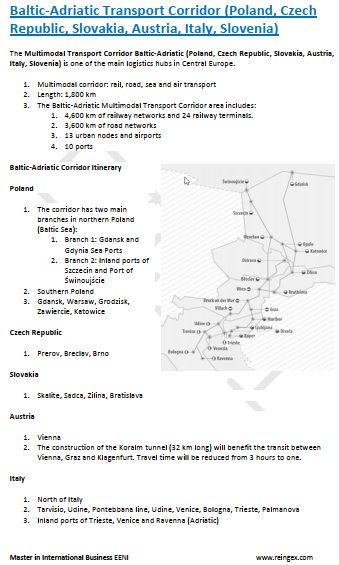

The Subject “Foreign Trade, Logistics and Business in Italy” is included within the curriculum of the following academic programs at EENI Global Business School:

Masters: International Business, Foreign Trade.

Languages:  +
+
 Italia
Italia  Italie
Italie  Italia.
Italia.
- Subject Credits “Doing Business in Italy”: 2

EENI Global Business School in Italian Commercio Estero.
International Trade, Logistics and Business in Italy

- Baltic-Adriatic Corridor (Poland, Slovenia)
- Access to the:
- Atlantic Corridor (Portugal-Germany)
- North Sea-Mediterranean Transport Corridor


Italian Preferential Access and Trade Agreements:
- Italy and the European Economic Area
- European Union
- Economic and Monetary Union
- European Customs Union
- European Single Market
- The European Union Services Directive
- European Digital Single Market
- As a member of EU, Italy is a beneficiary of EU Trade Agreements
- Central European Initiative
- Adriatic-Ionian Initiative
- Regional Cooperation Council
- SICA (observer country)

- World Trade Organization (WTO)
- Agreement on Trade in Services (GATS)
- Agreement on Sanitary Measures
- Agreement on Technical Barriers to Trade
- Agreement on Preshipment Inspection
- Agreement on Safeguards
- Trade Facilitation Agreement
- Convention Harmonization of Frontier Controls of Goods
- CMR Convention (UN)
- World Customs Organization (WCO)
- Kyoto Convention
- COTIF Convention (Rail)
- BIC
- Chicago Convention (ICAO)
- International Maritime Organization (IMO)
- Convention for Safe Containers
- Istanbul Convention
- International Road Transport Union (IRU)
- TIR Convention
- Guidelines on Safe Load Securing for Road Transport
- International Chamber of Shipping
- CIM & CIT Rules (Rail Transport)
- Customs Convention on Containers - not a member

- European Union
- European Central Bank
- European Investment Bank
- European Bank for Reconstruction and Development (EBRD)
- European Union-CELAC Summit
- Economic Commission for Europe (UNECE)

- Economic Commission for Latin America (ECLAC)
- Asia-Europe Meeting
- Inter-American Development Bank (Non-borrowing country)
- Asian Development Bank
- African Development Bank
- OECD
- OECD anti-corruption measures
- United Nations
- World Bank
- World Trade Organization (WTO)
- International Monetary Fund
- CPLP (observer country)
Italy is an observer member
- Association of Caribbean States (ACS)
- Latin American Integration Association (LAIA)
- Council of the Baltic Sea States
- Black Sea Economic Cooperation
- IORA (dialogue partner)
- Borders of Italy: France, Switzerland, Austria and Slovenia
- Official Language of Italy: Italian
- Italian Capital: Roma
- Area of Italy: 301,340 km²
- Italian Population: 61 million people
- Government of Italy: Parliamentary Republic
Religion in Italy: Christianity.
- Roman Catholicism is the main religion in Italy
Italy belongs to the European Economic Area.


Italian Foreign Trade
- Main Italian export products are engineering, textiles, industrial machines, vehicles, transport equipment, chemical products, foods, beverages, minerals...
- Top Italian export markets: Germany, France, the United States, Spain, the UK
- Top Italian import partners: Germany, France, the Netherlands, Belgium, Spain
- As a member of EU, Italy is a beneficiary of EU Trade Agreements: South Korea, Tunisia, India, ASEAN, Egypt, Jordan, Lebanon, Ukraine, Moldova, Georgia...
(c) EENI Global Business School (1995-2025)
Top of this page









 WhatsApp
WhatsApp