Business in Vietnam

"Vietnamese Foreign Trade and Economy. Saigon Port (Vietnam). Buddhism
- Introduction to tVietnam
- Business in Saigon
- Vietnamese Economy
- Doi Moi Reform
- International Trade of Vietnam
- Investment in Vietnam
- Case Study:
- Mobilfone
- Zamil Steel
- Access to the Vietnamese market
- Business Plan for Vietnam
The objectives of the subject “International Trade and Business in tVietnam” are the following:
- To analyze the Vietnamese Economy and Global Trade
- To know the business opportunities in tVietnam
- To explore the Vietnamese trade relations with the country of the student
- To know the Vietnamese Trade Agreements
- To examine the profile of Vietnamese companies
- To develop a business plan for the Vietnamese market

The Subject “Foreign Trade and Business in Vietnam” belongs to the following Online Programs taught by EENI Global Business School:
Masters: International Business, Foreign Trade.
Course: Taoism, Confucianism & Business.
Languages:  (or
(or  Vietnam
Vietnam  Vietnam).
Vietnam).
- Credits of the subject “Doing Business in Vietnam”: 2

- Duration: two weeks

Masters adapted to  Vietnamese students.
Vietnamese students.
International Trade and Business in Vietnam

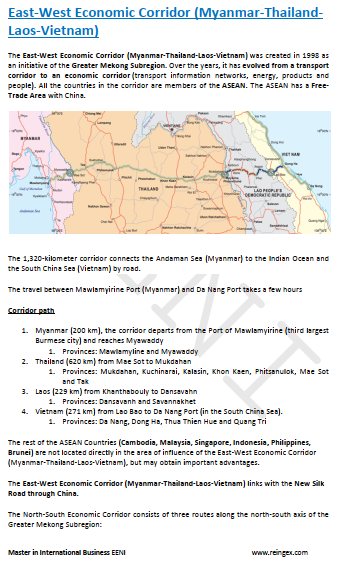

Vietnamese Market Access and Trade Agreements:
- Vietnam and the Buddhist Economic Area
- ASEAN
- ASEAN Free-Trade Area
- ASEAN Economic Community
- Vietnam has trade agreements (as ASEAN Member) with Australia-New Zealand, Canada, China, India, the EU, Japan, Korea, Russia, the U.S., Pakistan
- Mekong River Commission
- APEC
- Regional Comprehensive Economic Association
- Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership
- Mekong Economic Cooperation
- Laos-Vietnam Trade Agreement
- UK-Vietnam Free Trade and Economic Integration Agreement
- EU-Vietnam Agreement
- Japan-Vietnam Agreement
- Eurasian Economic Union (EAEU)-Vietnam Agreement
- Russia-Vietnam Customs Union
- South Korea-Vietnam Agreement
- Chile-Vietnam Agreement
- Greater Mekong Subregion
- Global System of Trade Preferences

- WTO
- WCO
- BIC
- Chicago Convention (ICAO)
- International Maritime Organization
- Organization for Cooperation between Railways (OSJD)

- ESCAP
- Asian Development Bank
- Asia Cooperation Dialogue
- Boao Forum for Asia
- Africa-Asia Partnership
- FEALAC

- UN
- WB
- WTO
- IMF
- WCO
- PEEC

The Socialist Republic of Vietnam
- Vietnamese Population: 91.7 million people
- Capital of Vietnam: Hanoi
- Largest Vietnamese city: Ho Chi Minh City
- Official language of Vietnam: Vietnamese
- Main ethnic group of Vietnam: Kinh (86%)
- Type of Government: One-party Socialist state
- Independence of Vietnam: 1945 (from France)
- Vietnamese Area: 332,698 km²
- Borders of Vietnam: China, Cambodia, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Thailand and the Philippines
Main religion in Vietnam: Mahayana Buddhism (80% of the total Vietnamese population).
- 8 million Vietnamese are followers of Cao Dai
- Confucianism and Taoism influence
- Catholicism: 6 million people
- Vietnam has not an official religion


Vietnam belongs to the Buddhist / Sinic Civilization.
Vietnamese Economy.
- Vietnam will be the 21st largest economy in the World by 2025
- Vietnam is a Frontier Market
- Today, Vietnam is considered to be the less attractive market of the ASEAN-4 and China
- The GDP of tVietnam is only 3% of China, 24% of Thailand, 29% of Indonesia, 38% of Malaysia or 42% of the Philippines
- In 1986, tVietnam set up the “Doi Moi reform policy.” Thenceforth, tVietnam has seen spectacular modifications
- The old centrally-planned Economy of Vietnam was replaced by the new socialist-oriented market Economy
- The Vietnamese economy is based on a multi-sector model based on a market mechanism and state regulations
- Economy of Vietnam is 50% free (Heritage Foundation)
- Nominal Vietnamese GDP: 138 billion USD
- Agriculture: 19% of the GDP
- Industry: 38%
- Services: 42%
- Inflation (CPI) of Vietnam: 1.86%
- Vietnamese Currency: Dong (VND)

In 1993 was created Vietnam Mobile Telecom services Company is a a state-owned company under Vietnam Posts and telecommunications corporation. Vietnam Mobile Telecom has become the first mobile telephony services provider in the brand name MobiFone, marking the beginning momentum of the mobile telephony industry in Vietnam.
In 1997 was created Zamil Steel Vietnam Co., Ltd to design, manufacture and supply top quality pre-engineered steel buildings for use as factory buildings, warehouses, workshops, distribution centers...
Global Trade and Business in Vietnam:


Vietnamese Foreign Trade.
- Top Vietnamese exports products are crude oil, textiles, footwear, fisheries products, and electronics products
- Largest export markets of Vietnam are the U.S., Japan, China, Australia, and Singapore
- Main imports of Vietnam are machinery, refined petroleum, steel, and material for the textile industry
- Top Vietnamese import sources are China, Taiwan, Singapore, South Korea, Thailand, and Malaysia
- Saigon Port (port system of Vietnam Maritime sector) is the largest foreign trade port of Vietnam



