Business in Slovenia

Foreign Trade and Business in Slovenia. Ljubljana
- Introduction to the Republic of Slovenia (EU)
- Slovenian Economy
- Business in Ljubljana
- Slovenian Foreign Trade: a winter sport products exporter
- Investment in Slovenia
- Top Slovenian companies
- Access to the Slovenian Market
- Business Plan for Slovenia
The objectives of the subject “International Trade and Business in” Slovenia” are the following:
- To analyze the Slovenian Economy and Global Trade
- To know the trade opportunities in the Slovenian Market
- To analyze the trade relations of Slovenia with the country of the student
- To know the Slovenian trade agreements as a member of the EU
- To develop a business plan for the Slovenian Market

The Subject “Foreign Trade and Business in Slovenia” belongs to the following Online Programs taught by EENI Global Business School:
Doctorate: European Business, World Trade.
Masters: International Business, Foreign Trade.

 Masters adapted to Slovenian Students.
Masters adapted to Slovenian Students.
Languages:  +
+  Eslovenia
Eslovenia  Slovenie
Slovenie  Eslovénia.
Eslovénia.
- Credits of the Subject “Doing Business in Slovenia”: 1

- Duration: one week

International Trade and Business in Slovenia

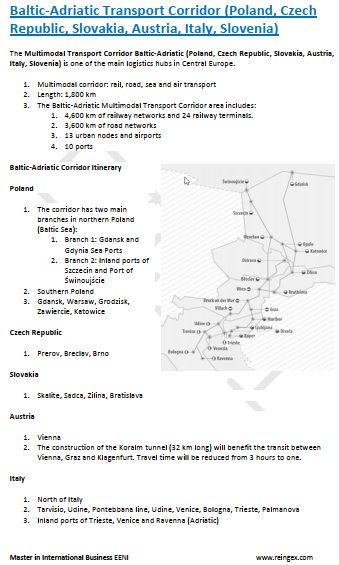
Transport and Logistics in Slovenia
- Port of Koper
- Baltic-Adriatic Corridor (Poland, Slovenia)
Global Trade and Business in Slovenia:


Slovenian Preferential Access and Trade Agreements:

- Slovenia and the European Economic Area
- The EU
- As a member of the EU, Slovenia is a beneficiary of the EU Trade Agreements
- Adriatic-Ionian Initiative
- Central European Initiative
- Regional Cooperation Council

- WTO
- Agreement on Sanitary and Phytosanitary Measures
- GATS
- Agreement on Technical Barriers to Trade
- Agreement on Preshipment Inspection
- Agreement on Safeguards
- Trade Facilitation Agreement
- WCO
- Convention Harmonization of Frontier Controls of Goods
- CMR Convention
- Customs Convention on Containers - not a member
- COTIF Convention (Rail)
- BIC
- Chicago Convention (ICAO)
- IMO
- Convention for Safe Containers
- Istanbul Convention
- CIM, CIT Rail Rules
- IRU
- TIR Convention
- Guidelines on Safe Load Securing for Road Transport
- ICC

- UNECE
- EBRD
- OSCE

- UN
- WB
- Asia-Europe Meeting
- OECD
- WTO
- IMF
- Inter-American Development Bank
- Capital of Slovenia: Ljubljana
- Official Language: Slovenian
- Area of Slovenia: 20,273 km²
- Slovenian Population: 2 million people
- Type of Government: Parliamentary Republic
- Borders of Slovenia: Italy, Croatia, Hungary and Austria
- Independence of Slovenia: 1992 (Yugoslavia)
Religion in Slovenia: Catholicism (Christianity).

Slovenia belongs to the European Economic Area.
Economy of Slovenia.
- Slovenian GDP (nominal): 49,550 million dollars
- GDP per capita of Slovenia: 28,200 dollars
- Slovenian Currency: Euro
- Slovenia joined the EU in 2004
- Slovenia has significant petroleum, zinc and coal reserves
- Slovenia is a major exporter related to winter sports
- About 20% of the world's generic pharmaceuticals have been manufactured in Slovenia
- Slovenian wines are rated as high quality
- Renault has a car factory in Slovenia (Revoz)
- Top Slovenian Industries: iron products and aluminum, trucks, cars, military equipment, wood, textiles, chemical products
- Headquarters of the Agency for the Cooperation of Energy Regulators (ACER): Ljubljana
Main Slovenian Companies:
- Istrabenzl, industrial conglomerate
- Adria Mobil, auto caravans
- Akrapovic, automotive
- Alpine, sport and fashion footwear
- Elan Line, sports
- Goodyear, Dunlop, Sava tires
- Gorenje, household appliances and personal electronic devices
- Tomatoes, mopeds
- Pharmaceutical products Krka
- Pharmaceuticals Lek
- Gorenje Orodjarna, foundry
- Litostroj, heavy machinery
- Slovenija CESTE Tehnika, construction, civil engineering

Slovenian Foreign Trade.
- The main Slovenian exports are manufactured products, machinery and transportation equipment, chemical products, foods
- Top Slovenian exports destinations: Germany, Italy and Croatia
- Top Slovenian suppliers: Germany, Italy and Austria
- As a member of the EU, Slovenia is a beneficiary of the EU trade agreements with the ASEAN, Egypt, Jordan, Lebanon, Ukraine, Moldova, Georgia..
- The Port of Koper is the largest in Slovenia
(c) EENI Global Business School (1995-2024)
We do not use cookies
Top of this page


