Business in Portugal. Portuguese Economy

Portuguese Foreign Trade. International Relations of Portugal: Africa, America. Lisbon
- Introduction to the Portuguese Republic
- Portuguese Economy
- Portuguese International Trade
- International relations of Portugal with Europe, Sub-Saharan Africa, America, Asia
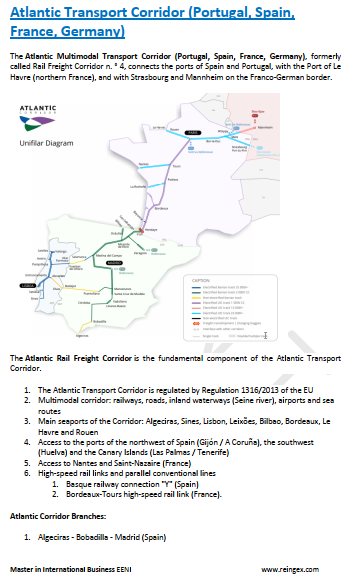
- Atlantic Corridor (Portugal-Germany)
- Importance of the Community of Portuguese-speaking Countries
- Invest in Portugal
- Main Portuguese Companies
- Case Studies:
- PORTUCEL SOPORCEL Group
- Efacec Group
- Portugal Telecom
- Access to the Portuguese Market
- Business Plan for Portugal
The objectives of the subject “International Trade and Business in” Portugal” are the following:
- To analyze the Portuguese economy and global trade
- To know the trade opportunities in the Portuguese Market
- To analyze the trade relations of Portugal with the country of the student
- To understand the importance of the Community of Portuguese-speaking Countries
- To know the Portuguese trade agreements as a member of the EU
- To develop a business plan for the Portuguese Market

The Subject “Foreign Trade and Business in Portugal” belongs to the following Online Programs taught by EENI Global Business School:
Doctorate: European Business, World Trade.
Masters: International Business, Foreign Trade.

 Masters adapted to Portuguese Students.
Masters adapted to Portuguese Students.

Languages:  +
+  Portugal
Portugal  Portugal
Portugal  Portugal.
Portugal.
- Credits of the Subject “Doing Business in Portugal”: 1

- Duration: one week
Business in Portugal.


Portuguese Preferential Access and Trade Agreements:

- Portugal and the European Economic Area
- The EU
- Economic and Monetary Union
- European Customs Union
- European Single Market
- The EU Services Directive
- European Digital Single Market
- As a member of the EU, Portugal is a beneficiary of the EU Free trade agreements
- SELA
- Africa-EU
- ALADI (observer)

- WTO
- GATS
- Agreement on Sanitary Measures
- Agreement on Technical Barriers to Trade
- Agreement on Preshipment Inspection
- Agreement on Safeguards
- Trade Facilitation Agreement
- WCO
- Convention Harmonization of Frontier Controls of Goods
- Hamburg Rules
- CMR Convention (UN)
- IRU
- TIR Convention
- Guidelines on Safe Load Securing for Road Transport
- COTIF Convention (Rail)
- BIC
- Chicago Convention (ICAO)
- IMO
- Convention for Safe Containers
- Istanbul Convention
- ICS
- Customs Convention on Containers - not a member

European Organizations:
- European Union
- Group of States against Corruption
- ECB
- EIB
- UNECE
- OSCE

- Inter-American Development Bank (Non-borrowing country)
- OEA
- Asia-Europe Meeting
- ECLAC
- African Development Bank
- Asian Development Bank
- IMF
- UN
- Community of Portuguese-speaking Countries (CPLP)
- WTO
- OECD
- OECD anti-corruption measures
- WB
- Portuguese Capital: Lisbon
- Area of the Portuguese Republic (Europe): 92,212 km²
- Portuguese Population: 10.46 million people
- Official Language: Portuguese
- Border with Spain
- Portuguese Government: Unitary semi-presidential Constitutional Republic
- The Portuguese Republic has significant cultural and historical with Latin America, especially with Brazil.
- Also to its former colonies: Macau, Mozambique, Angola, Cape Verde and São Tomé and Príncipe
- Abolition of Slavery in Portugal: 1869
Religion: Catholicism (Christianity).

Portugal belongs to the European Economic Area.
Portuguese Economy
- Portuguese GDP (nominal): 229,948 million dollars
- One of the most important features of the economic structure of the Portuguese Republic is the services sector dominance
- The Portuguese Services sector contribute 73.6% to gross value added (GVA) and represent 59.3% of the labour market
- The global economic and financial crisis caused a domestic demand contraction
- The main products of Portugal are textile, footwear, auto parts, chemicals, wood, cork oak, paper, metals, dairy products, wine, porcelain..

Portuguese Foreign Trade
- The Portuguese market has only 10.6 million people, but there are more than 249.6 million people who speak Portuguese worldwide (the fifth most spoken language in the world: Angola, Brazil, Cape Verde, Guinea-Bissau, Mozambique, São Tomé and Príncipe, Macau...)
- These countries have significant trade relations with Portugal
- Foreign companies investing in Portugal can easily access to these markets
- The Portuguese Republic has a nominal growth of 11% in exports of products and services
- The Portuguese largest trading partner is Spain (23.5% of Portuguese exports)
(c) EENI Global Business School (1995-2024)
We do not use cookies
Top of this page


