Business in Poland. Polish Foreign Trade

Invest in Poland (largest Central European market) Warsaw. Polish Economyy
- Introduction to the Republic of Poland (EU)
- Polish Economy.
- Key sectors of the Polish economy
- Business in Warsaw
- Polish Foreign Trade
- International economic relations of Poland
- Invest (FDI) in Poland
- Case Study: The company Mota-Engil Polska
- Access to the Polish Market
- Business Plan for Poland
The objectives of the subject “International Trade and Business in” Poland” are the following:
- To analyze the Polish Economy and Foreign Trade
- To know the trade opportunities in the Polish Market
- To analyze the trade relations of Poland with the country of the student
- To know the Polish trade agreements as a member of the EU
- To develop a business plan for the Polish Market

The Subject “Foreign Trade and Business in Poland” belongs to the following Online Programs taught by EENI Global Business School:
Doctorate: European Business, World Trade.
Masters: International Business, Foreign Trade.
EENI in Polish Magisterskie Handel zagraniczny.
Languages:  +
+  Polonia
Polonia  Pologne
Pologne  Polonia.
Polonia.
- Credits of the Subject “Doing Business in Poland”: 1

- Duration: one week

 Masters adapted to Polish Students.
Masters adapted to Polish Students.
International Trade and Business in Poland

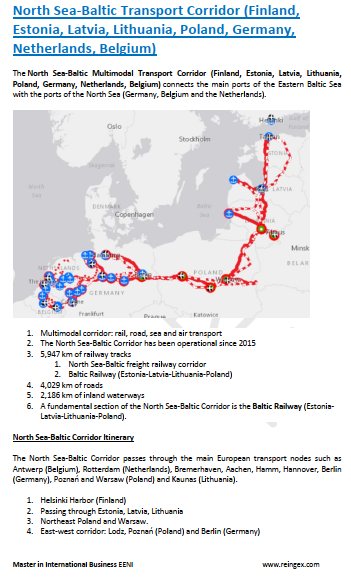
- North Sea-Baltic Corridor (Finland, Belgium)
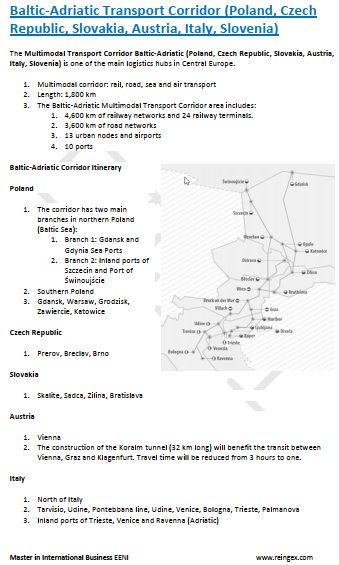
- Baltic-Adriatic Corridor (Poland, Slovenia)
- Pan-European Corridor II (Russia-Germany)
- Access to the
- Trans-Siberian Railway (Russia, Mongolia, China, North Korea)
- Pan-European Corridor IX
- Eurasian Land Transport Initiative


Polish Preferential Access and Trade Agreements:

- Poland and the European Economic Area
- The EU
- European Customs Union
- European Single Market
- The EU Services Directive
- European Digital Single Market
- As a member of the EU, Poland is a beneficiary of the EU Free trade agreements
- Council of the Baltic Sea States
- Central European Initiative
- Regional Cooperation Council
- Organization of the Black Sea Economic Cooperation (observer country)

- WTO
- GATS
- Agreement on Sanitary Measures
- Agreement on Technical Barriers to Trade
- Agreement on Preshipment Inspection
- Agreement on Safeguards
- Trade Facilitation Agreement
- WCO
- Convention Harmonization of Frontier Controls of Goods
- Organization for Cooperation between Railways (OSJD)
- COTIF Convention
- BIC (Containers)
- Chicago Convention (ICAO)
- IMO
- Convention for Safe Containers
- Istanbul Convention
- Customs Convention on Containers
- CMR Convention
- Rotterdam Rules (Sea)
- CIM & CIT Rules (Rail)
- IRU
- TIR Convention
- Guidelines on Safe Load Securing for Road Transport

European Organizations:
- The EU
- ECB
- EIB
- Group of States of the European Council Convention against Corruption
- UNECE
- OSCE

- WTO
- WB
- Asia-Europe Meeting
- OECD
- OECD anti-corruption measures
- IMF
- UN
- The Republic of Poland (Europe) has a population of 38.5 million people (34th largest in the world)
- Borders of Poland: Lithuania, Belarus, Ukraine, the Czech Republic, Slovakia and Germany
- Polish Capital: Warsaw
- Official Language of Poland: Polish
- Polish Area: 312,685 km²
- Polish Government: Parliamentary Republic
Religion in Poland: Catholicism (Christianity).

Poland belongs to the European Economic Area.
Polish Economy.
- Poland is the largest market in Central Europe and the eighth largest European market
- An important privatization and economic liberalization process (1990s)
- Polish Nominal GDP: 531.76 thousand million dollars.
- Agriculture: 4.6%
- Industry: 28.1%
- Services: 67.3%
- GDP per capita of Poland: 26.402 dollars
- The main Polish products are machines, shipbuilding, iron and steel, coal, chemical products, beverages, foods, glass, textile
- Polish Currency: Zloty
- Headquarters of the European Border and Coast Guard Agency (Frontex): Warsaw (Poland)

Polish Foreign Trade
- The Republic of Poland has an important domestic market and a strategic location for Export products for the European market
- Top Polish exports destinations are Germany, Italy, France, the UK, the Czech Republic, Russia, the Netherlands, Ukraine, Sweden, and Hungary
- Main Polish exports: transport equipment, semi-manufactured products and foods
- Main origins of Polish imports: Germany, Russia, Italy, France, the Czech Republic, the Netherlands, the UK, Belgium, South Korea
- Headquarters of the Organization for Cooperation between Railways (OSJD)
(c) EENI Global Business School (1995-2024)
We do not use cookies
Top of this page



