Business in Papua New Guinea

Economy and Foreign Trade of Papua New Guinea, Port Moresby. Agribusiness, mining
- Introduction to the Independent State of Papua New Guinea (Oceania)
- Economy of Papua New Guinea (PNG)
- International Trade of PNG
- Business in Port Moresby
- Investment in Papua New Guinea
- Business Opportunities in Papua New Guinea
- Case Study: Telikom Papua
- Access to the market of Papua New Guinea
- Business Plan for Papua New Guinea
The objectives of the subject “International Trade and Business in the Independent State of Papua New Guinea” are the following:
- To analyze the Papua New Guinean Economy and Global Trade
- To know the trade opportunities in the Independent State of Papua New Guinea
- To explore the Papua New Guinean trade relations with the country of the student
- To know the Papua New Guinean Trade Agreements
- To examine the profile of Papua New Guinean Companies
- To develop a business plan for the Papua New Guinean Market

The Subject “Foreign Trade and Business in Papua New Guinea” belongs to the following Online Programs taught by EENI Global Business School:
Masters: International Business, Foreign Trade.
Languages:  or
or  Papúa Nueva-Guinea
Papúa Nueva-Guinea  Papouasie-Nouvelle-Guinee.
Papouasie-Nouvelle-Guinee.
- Credits of the subject “Doing Business in Papua New Guinea”: 1

- Duration: one week

EENI Masters adapted to  Papua New Guinean students.
Papua New Guinean students.
International Trade and Business in Papua New Guinea.
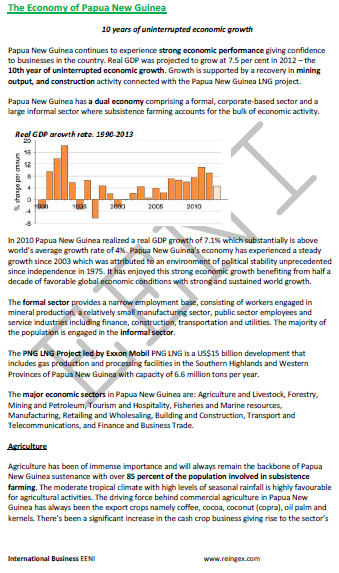
Papua: a decade of uninterrupted economic growth.

Papua New Guinean Market Access and Trade Agreements:
- Papua New and the Economic Area of Oceania
- Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC)
- Pacific Islands Forum
- Pacific Island Countries Trade Agreement (PICTA)
- PICTA Trade in Services Protocol
- Oceania Customs Organization
- UK-Pacific States Free Trade Agreement (Solomon Islands, Papua New Guinea, Samoa)
- Melanesian Spearhead Group (MSG) Trade Agreement
- Australia-Papua New Guinea Free Trade Agreement (PATCRA)
- South Pacific Regional Trade and Economic Cooperation Agreement (SPARTECA)
- ASEAN (observer)

- WTO
- GATS
- Agreement on Sanitary Measures
- Agreement on Technical Barriers to Trade
- Agreement on Preshipment Inspection
- Agreement on Safeguards
- Trade Facilitation Agreement
- WCO
- BIC (Containers)
- Chicago Convention (ICAO)
- International Maritime Organization
- Istanbul Convention - not a member
- Customs Convention on Containers - not a member

- Asian Development Bank
- ESCAP
- Colombo Plan

- PEEC
- UN
- WB
- WTO
- IMF

The Independent State of Papua New Guinea.
- Papua New Guinean Population: 7 million people
- Area of Papua New Guinea: 462,840 km²
- of Papua New Guinea shares a border with Indonesia and Australia by sea
- The capital of Papua New Guinea is Port Moresby (255,000 people)
- English is the official language, while Tok Pisin and Motu are national languages
- Over 800 different languages are spoken in Papua New Guinea
- Independence of Papua New Guinea from Australia: 1975
- Papua New Guinea is a Parliamentary Constitutional Monarchy; the Queen Elizabeth II is the Head of the Independent State of Papua New Guinea
Main religion in Papua is Christianity: Catholicism (1.8 million) and Protestantism (3 million, 61% of the population, Methodists: 1 million).
- In Papua New Guinea, there is a small community of Baha'i

Papua New Guinea belongs to the Economic Area of Oceania.
Papua New Guinean Economy.
- 33% of the Papua New Guinean population lives with less than USD 1.25 a day
- 85% of the population of Papua is related to the agriculture
- The main economic sectors of the Independent State of Papua New Guinea are agriculture, livestock, forestry, mining, Petrol, tourism, hospitality, fisheries, marine resources, manufacturing, retailing and wholesaling, building and construction, international transport, telecommunications, international finance, and trade
- Papua has huge natural resources (petroleum, copper, and gold)
- The currency of Papua is the Kina (PGK)
Global Trade and Business in Papua New Guinea:

International Trade of Papua New Guinea.
- 80% of the exports of Papua New Guinea are composed of three commodities: petroleum, copper, and gold
- Top Exports of Papua New Guinea are gold, silver, copper, crude oil, logs, timber, coffee, palm oil, cocoa, and copra
- Top export markets of Papua New Guinea are Australia, Japan, South Korea, China, Germany, the U.S., the UK, and Singapore
- Top Papua New Guinean import partners are Australia, Japan, the U.S., Singapore, New Zealand, the UK, China, and Hong Kong
The Government of Papua New Guinea is promoting the foreign direct investment. The Investment Promotion Authority of Papua is the agency focused on attracting new foreign investors to Papua New Guinea.

(c) EENI Global Business School (1995-2024)
We do not use cookies
Top of this page



