Business in New Zealand, Auckland, Wellington

New Zealander economy and foreign trade. Agribusiness, manufacturing (New Zealand)
- Introduction to New Zealand (Oceania)
- New Zealander Economy
- Business in Auckland
- New Zealander International Trade
- Investment in New Zealand
- Business Opportunities in New Zealand
- Information Technology
- Infrastructure
- Agribusiness
- Manufacturing
- Case Study: Fonterra
- Access to the New Zealander market
- Business Plan for New Zealand
The objectives of the subject “International Trade and Business in New Zealand” are the following:
- To analyze the New Zealander Economy and Foreign Trade
- To know the trade opportunities in New Zealand
- To explore the New Zealander trade relations with the country of the student
- To know the New Zealander Trade Agreements
- To examine the profile of New Zealander companies
- To develop a business plan for the New Zealander market

The Subject “Foreign Trade and Business in New Zealand” belongs to the following Online Programs taught by EENI Global Business School:
Masters: International Business, Foreign Trade.
Languages: 
 Nueva Zelanda
Nueva Zelanda  Nouvelle-Zelande.
Nouvelle-Zelande.
- Credits of the subject “Doing Business in New Zealand”: 2

- Duration: two weeks

Masters adapted to  New Zealander Students.
New Zealander Students.
International Trade and Business in New Zealand.

Market Access and Trade Agreements of New Zealand
- New Zealand and the Economic Area of Oceania
- APEC
- Pacific Islands Forum
- Oceania Customs Organization
- Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership
- Regional Comprehensive Economic Association
- Australia-New Zealand Closer Economic Relations Agreement
- South Pacific Regional Trade and Economic Cooperation Agreement
- ASEAN-Australia-New Zealand Agreement
- China-New Zealand FTA
- Singapore-New Zealand Agreement
- India-New Zealand Agreement
- New Zealand-Taiwan Agreement
- Thailand-New Zealand Agreement
- New Zealand-Malaysia Agreement
- Hong Kong China-New Zealand Agreement
- South Korea-New Zealand Agreement
- Trade Agreements with Chile, GCC, and Russia
- SICA (observer)
Sample:

- WTO
- GATS
- Agreement on Sanitary Measures
- Agreement on Technical Barriers to Trade
- Agreement on Preshipment Inspection
- Agreement on Safeguards
- Trade Facilitation Agreement
- WCO
- International Road Transport Union (IRU)
- BIC
- Chicago Convention (ICAO)
- IMO
- Customs Convention on Containers
- Istanbul Convention - not a member

- ESCAP
- FEALAC
- ASEM
- Colombo Plan
- Boao Forum for Asia
- Asian Development Bank

- OECD
- OECD anti-corruption measures
- UN
- UNCTAD
- ITC
- WIPO
- WB
- WTO
- IMF
- Commonwealth
- PEEC
- OECD
- New Zealand's capital: Wellington
- Auckland is the largest city and the largest port
- English, Maori, and New Zealand sign language are recognized as official languages
- New Zealand has a diverse multicultural population of over 4.5 million people
- New Zealander Area: 268,680 km²
- New Zealand is a constitutional monarchy. The Queen Elizabeth II (UK) is the Head of State
- New Zealand became independent from the UK in 1853
The main religion in New Zealand is Christianity.
New Zealand belongs to the Economic Area of Oceania.

Economy of New Zealand
- New Zealand has an efficient, market economy, a secure business environment, and excellent infrastructures
- New Zealand ranks fourth in economic freedom (Heritage Foundation) and occupies the second position in the ease of doing business index (WB)
- The main Economic Sectors of New Zealand are manufacturing, services, and agricultural
- Top fast Growing Sectors of New Zealand: creative and food and beverage (10% of the New Zealander GDP)
- Auckland: 30% of the total annual trade of New Zealand and represent 13% of the GDP of NZ
- The currency is the New Zealand dollar (NZD)

International Trade of New Zealand.
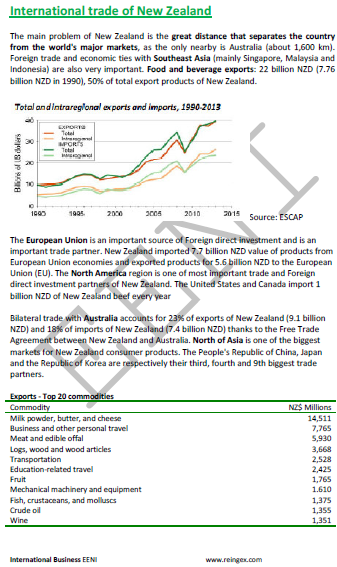
- The principal problem of New Zealand is the great distance that separates the country from the world's largest markets, as the only nearby is Australia (about 1,600 kilometers)
- Food and beverage exports of New Zealand: 22 billion NZD (7.76 billion NZD in 1990), 50% of the total export products of New Zealand
- Top trade partners of New Zealand: Australia, the U.S., Japan, China, and the UK
- The fastest growing export markets of New Zealand are China (43%), Singapore (28%), Egypt (25%), the UAE (18%), and India (16%)
- The EU is a largest foreign direct investment source and is a significant trading partner. New Zealand imported 7.7 billion NZD value of products from the EU economies and exported products for 5.6 billion NZD to the EU
- The North America region is one of the largest trade and investment partners of New Zealand. The U.S. and Canada import 1 billion NZD of New Zealand beef every year
- Bilateral trade with Australia accounts for 23% of the exports of New Zealand (9.1 billion NZD) and 18% of the imports from New Zealand (7.4 billion NZD) thanks to the Free Trade Agreement between New Zealand and Australia
- North of Asia is one of the largest markets for the New Zealander consumer products. China, Japan, and the Republic of Korea are respectively their third, fourth and the ninth largest trade partners
- Foreign Trade and economic ties with Southeast Asia (mainly Singapore, Malaysia, and Indonesia) are also crucial

(c) EENI Global Business School (1995-2024)
We do not use cookies
Top of this page



