Optional subjects (Master)
Master in Transport and Logistics in Africa (Optional subjects)
Content of the optional subjects of the Master in Transport and Logistics in Africa taught by EENI Global Business School.
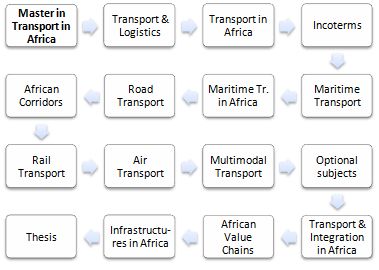
- Detailed content of the modules of the Master
- Download the syllabus (PDF) of the Master
- Download the syllabus (PDF) of Related Subjects to Transport in Africa
ECTS = European Credit Transfer and Accumulation System
 Enrol / Request for Information
Enrol / Request for Information

Optional Subjects of the Master in Transport and Logistics in Africa.
The student must select at least 7 ECTS of the following subjects:
- African Economic Areas
- Western African Economic Area (2 ECTS)
- Central African Economic Area (1 ECTS)
- Southern African Economic Area (1 ECTS)
- Eastern African Economic Area (2 ECTS)
- Maghrebian Economic Area (1 ECTS)
- Foreign Trade Documents (1 ECTS)
- Customs. World Trade Organization (WTO) (4 ECTS)
- International Contracts (3 ECTS)
- International Payment Methods. Documentary credits (4 ECTS)
- Non-tariff measures (4 ECTS)
- Trade Facilitation (2 ECTS)
The selection of the optional subjects is done from the e-campus of EENI, once the Enrollment is formalized.
Recommendable subjects for the African Students
EENI Global Business School recommends that the African students select the African regional economic communities, since all of them have programs related to the transport, economic and customs integration, trade facilitation, etc.
Non-African students can also select one of the following regional economic communities.
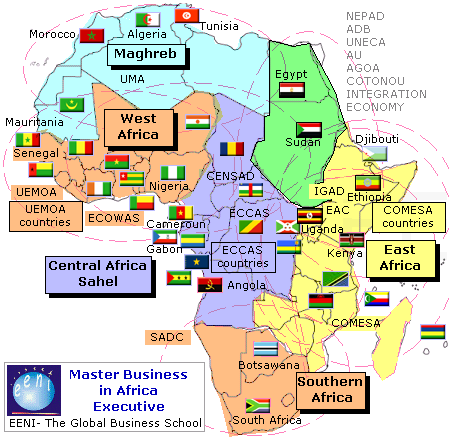

African transregional organizations.
- COMESA-EAC-SADC Tripartite
- Community of Sahel-Saharan States (CEN-SAD)
- Common Market for Eastern and Southern Africa (COMESA)
- OHADA
- Southern African Development Community (SADC)
Eastern Africa Students (COMESA, EAC, IGAD, Nile, IOC, NC, Tripartite Agreement).
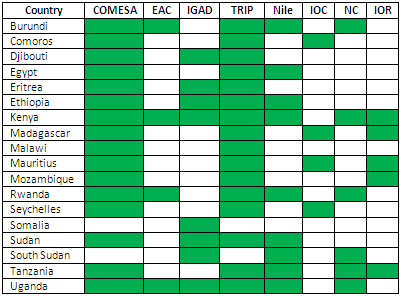
- East African Community (EAC)
- Intergovernmental Authority on Development (IGAD)
- Conference on the Great Lakes
- Indian-Ocean Rim Association
- Nile Basin Initiative
- Indian Ocean Commission
- Economic Community of the Great Lakes Region
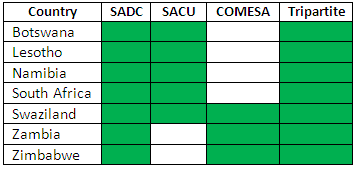
Southern African Students (SADC, SACU, COMESA, Tripartite Agreement).
Western African Students (UEMOA, WAMZ/ZMAO, CEDEAO/ECOWAS, MRU, NBA, CEN-SAD, OHADA).
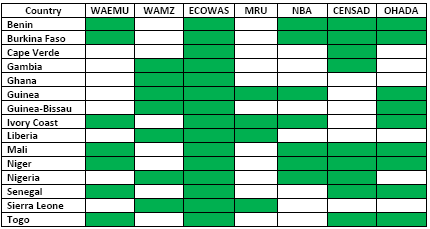
- Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS)
- West African Economic and Monetary Union (WAEMU)
- West African Monetary Zone (WAMZ)
- Niger Basin Authority
- Organization for the Development of the Senegal River
- Mano River Union (MRU)
- G5-Sahel
Central African Students (CEMAC, CEEAC/ECCAS, COMESA, SADC, EAC, Tripartite Agreement, NBA, NBI, CEN-SAD, OHADA).
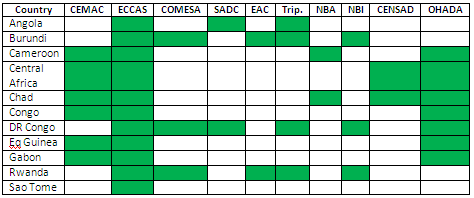
- Central African Economic and Monetary Community (CEMAC)
- Economic Community of Central African States (ECCAS)
Maghrebian Students:
- Arab Maghreb Union (AMU)
African Economic Areas:
- African Economic Areas
- Nigeria and/or South Africa as the Central States of the African Civilization
- Economic Profile of the African Markets
- Eastern African Economic Area (2 ECTS) (PDF)
- Southern African Economic Area (1 ECTS) (PDF)
- Western African Economic Area (2 ECTS) (PDF)
- Central African Economic Area (1 ECTS) (PDF)
- Maghrebian Economic Area (1 ECTS) (PDF)
Objectives:
- To define the economic characteristics of each African economic area
- To know the economic profile of the countries of each economic area
- To understand the processes of the economic integration in the analyzed economic area
- To know the economic relations with the other economic areas of the different civilizations
- To analyze the main Economic Organizations related to the studied economic area

Foreign Trade Documents (1 ECTS).
- The role of the documents in the international transport and International Trade
- International transport documents
- Commercial documents (proforma, invoice, packing list...)
- Other Foreign Trade Documents
The objectives of the module “Documents of International Trade” are the following:
- To know the function of the main foreign trade documents
- To know how to fill them out properly
- To know how to perform the check-list of the import-export documents
Customs. World Trade Organization (WTO) (4 ECTS).
- Customs in International Trade
- Customs regime
- Customs classification
- Customs clearance
- Inspection of products at customs
- Origin of products
- The role of the customs agent
- Introduction to the World Customs Organization
- Harmonized System (HS)
- Rules of Origin
- Trade Facilitation Programs
- Customs Procedures
- Kyoto Convention
- SAFE Package
- Agreement on Rules of Origin of the WTO
- The World Trade Organization and Customs
- Rules for the customs valuation of products
- Customs Valuation Methods:
- Transaction value
- Identical or similar goods
- Deductive or computed method
- Fall-back
- Rules of Origin
- Import licenses
- The WTO Agreements on Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT), Sanitary and Phytosanitary Measures (MSF), Pre-shipment Inspection
The objectives of the module “Customs” are the following:
- To understand the customs procedures in Foreign Trade, the different commercial regimes and the methods of product classification
- To learn about the fundamental concepts related to the customs: customs clearance, customs valuation, non-tariff barriers and obstacles, pre-shipment inspection, origin of goods, Harmonized System, customs processes..
- To know the process of importing a product and the customs regimes
- To understand the functions of the WCO and the WTO in relation to customs
International Contracts (3 ECTS).
- International Contracts in Foreign Trade
- Risks associated to the International Trade
- Risk minimization instruments
- Vienna Convention
- Hague Conference on Private International Law
- United Nations Convention on Contracts for the International Sale of Goods (1980)
- Convention on the Limitation Period in the International Sale of Goods
- Common clauses of an international sales contract
- Anti-corruption clause of the ICC
- International arbitration
- International contracts with distributors, importers, agents..
- Guarantees in Foreign Trade
- Organization for the Harmonization of Business Law in Africa (OHADA)
- The role of the UN Commission on International Trade Law (UNCITRAL) in foreign trade and international transport
- Legislative texts of the Commission for International Trade Law: conventions, model laws and legislative guides
- UNCITRAL Model Law on International Commercial Conciliation
- UNCITRAL Model Law on International Commercial Arbitration
- United Nations Convention on the Carriage of Goods by Sea (Hamburg Rules)
- United Nations Convention on the Liability of Operators of Transport Terminals in International Trade
The objectives of the module “International Contracts” are the following:
- To learn about the fundamentals and functions of the contracts in Foreign Trade
- To explore the main international Organizations, conventions, clauses and laws related to the International Contracts
- To understand how to implement the main clauses of an international sales contract
- To know how to minimise the risks through the clauses of a contract
- To understand the functioning of an international arbitration process

International Payment Methods. Documentary Credits (4 ECTS)
- Introduction to the International Payment Methods
- Clean and Documentary Collections
- The importance of the Documentary Credits in International Trade
- Letter of credit
- Types, modalities and variants of the Documentary Credits
- Analysis of the contents of a letter of credit
- UCP 600
- E-UCP
- United Nations Conventions related to international means of payment
- United Nations Convention on Independent Guarantees and Stand-by Letters of Credit
- United Nations Convention on the Transfer of Credits in International Trade
- United Nations Convention on International Bills of Exchange and International Promissory Notes
- UNCITRAL Model Law on International Credit Transfers
The objectives of the module “Documentary Credits and International Payment Methods” are the following:
- To analyze the different International Payment Methods used in Foreign Trade
- To understand the fundamental role of the Documentary Credits as well as their operation and modalities
- To know how to manage a foreign trade operation through a documentary credit

Non-tariff Measures (4 ECTS)
- Introduction to the Non-tariff Measures in Foreign Trade
- Technical Barriers to Trade
- Sanitary and Phytosanitary Measures
- Non-automatic Import licensing, quotas and prohibitions
- Pre-shipment Inspection
- Contingent trade-protective measures (Anti-dumping Measures, Safeguards)
- Price control measures, including charges and additional taxes
- Other non-tariff measures (financial, investment, distribution, public procurement, rules of origin, exports...)
The objectives of the module “Non-tariff Measures” are the following:
- To know how to identify and distinguish the non-tariff measures in Foreign Trade
- To familiarise the student with the use of the “International Classification Manual of Non-Tariff Measures” of UNCTAD
- To know how to act before a non-tariff measure implemented by a country
- To evaluate the possible impact they may have on exports / imports
Trade Facilitation (2 ECTS)

- Introduction to the foreign trade facilitation programs
- Trade Facilitation Agreement
- Convention Harmonization of Frontier Controls of Goods
- Global System of Trade Preferences
- Trade Negotiations Among Developing Countries
- The pillars of trade facilitation (transparency, simplification, harmonization, standardization)
- Potential gains from the trade facilitation
- Main Domains of trade facilitation (purchases, transport, customs, payments)
- Trade facilitation and international transport
- The global supply chain and the trade facilitation
- Buy-Ship-Pay Model (CEFACT / ONU)
The objectives of the module “Trade Facilitation” are the following:
- To understand the fundamentals of trade facilitation programs
- To learn the WTO Agreement on Trade Facilitation
- To analyze the impact of the trade facilitation programs in the global supply chain
 Master in transport en Afrique
Master in transport en Afrique  Master en Transporte en África
Master en Transporte en África  Mestrado em
Transporte na África.
Mestrado em
Transporte na África.
(c) EENI Global Business School (1995-2024)
We do not use cookies
Top of this page

