Module: Business in the Maghreb
Module “Foreign Trade and Business in the Maghreb” (E-learning, 9 ECTS,  )
)

Seven subjects compose the Module “Foreign Trade and Business in the Maghreb” (Morocco, Algeria, Tunisia, Libya, and Mauritania) taught by EENI Global Business School:
- The Maghrebian Economic Area as a part of the Islamic and the African Civilization
- Islam in the Maghreb
- Economic Integration in the Maghreb.
- Arab Maghreb Union (AMU)
- Business in the Maghrebian Countries (Morocco, Algeria, Tunisia, Libya, and Mauritania)
- Maghrebian Businesspeople
- Logistics in the Maghreb
- Trans-African Roads
- Largest Maghrebian Ports
- Other regional economic institutions and trade agreements related to the Maghreb
- Business Plan for the Maghrebian markets

- Credits: 9

- Duration: 2 months It is recommended to dedicate about twelve hours of study per week following a flexible schedule. It is possible to reduce the duration dedicating more hours a week
- Download the syllabus (PDF)
Languages:  .
.
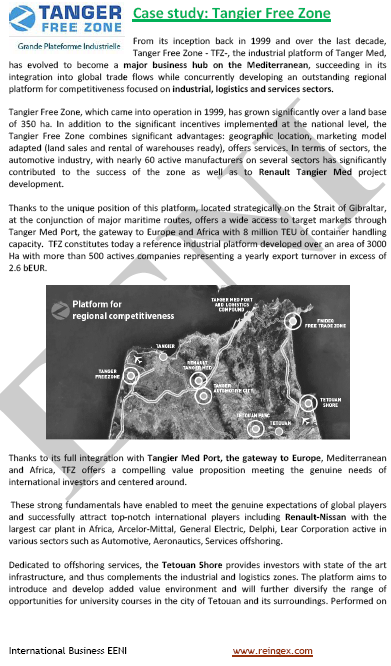
Sample - Sample of the Module - Foreign Trade and Business in the Maghreb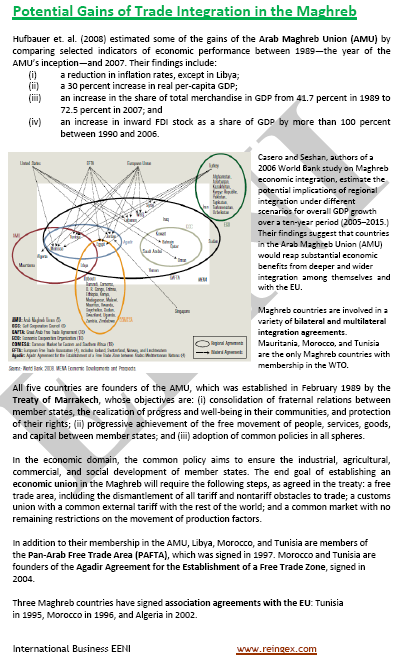
The main objective of the Module is to provide an overview of the Maghrebian Economy and the business opportunities:
- To learn to do business in the Maghreb (Morocco, Algeria, Tunisia, Libya, and Mauritania)
- To know the trade opportunities in the Maghreb
- To understand how to negotiate in the Maghrebian Markets
- To analyze foreign trade and foreign direct investment flows in the Maghreb
- To understand the importance of the AMU (Arab Maghreb Union) and the Agadir Agreement
- To explore the Trade Agreements related to the Maghreb
- To know the largest ports and Trans-African corridors related to the Maghrebian Countries
- To know the main Maghrebian Businesspeople
- To develop a business plan for the Maghreb
Module intended for all those wanting to specialize in the Maghrebian Markets.

This Module belongs to the following Higher Education Programs taught by EENI:
Doctorate in African Business, World Trade, Islamic Business.
Masters: International Business, Foreign Trade.
1- Economic Integration in the Maghreb.

- The Maghrebian Economic Area (PDF)
as a part of the Islamic and the African Civilization
- Islam in the Maghreb
- Why study “Islam and Business”?
- Arab Maghreb Union (AMU)
- Community of Sahel-Saharan States (CEN-SAD)
- Arab Mediterranean Agreement
- Greater Arab Free-Trade Area (GAFTA)

Trade Agreements with the other civilizations:
- Morocco-United States Agreement
- The EFTA has FTAs with Tunisia and Morocco
- Turkey has FTAs with Morocco and Tunisia
- Islamic Trade Preferential System
Trade Relations with the EU
- Economic Partnership Agreements with Algeria, Morocco, and Tunisia
- European Neighborhood Policy (Algeria, Libya, Morocco, and Tunisia)
- Euro-Mediterranean Partnership (Algeria, Morocco, Tunisia, and Mauritania)
- Mauritania is a beneficiary of the Africa-EU Partnership, GSP and AGOA
Note: Libya is a member of the COMESA, the COMESA-EAC-SADC Tripartite Agreement, and the COMESA-United States agreement.
2- Doing Business in the Maghrebian Countries:
- Business in Algeria
- Business in Libya
- Business in Mauritania
- Business in Morocco
- Business in Tunisia
3- Maghrebian Businesspeople
- Othman Benjelloun
- Anas Sefrioui
- Aziz Akhannouch
- Miloud Chaabi
- Mohamed Hassan Bensalah
- Issad Rebrab
- Ali Haddad
- Mohamed Ali Harrath
4- Logistics in the Maghreb.

4.1 African Highways Networks:
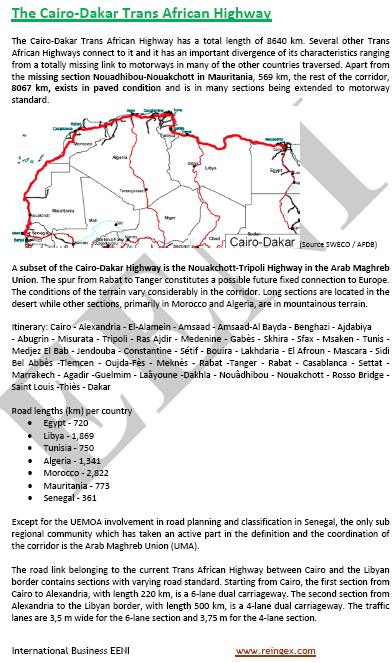
- Cairo-Dakar Corridor
- Algiers-Lagos (Trans-Saharan)
- Tripoli-Windhoek
- Dakar-Lagos
4.2 Largest Maghrebian Ports:
5- Business Plan for the Maghrebian markets.
The Module includes the Market Access Tool:


- Arab League
- OIC
- Islamic Development Bank
- African Development Bank
- Summit of South American-Arab Countries (ASPA)
- Asia-Middle East Dialogue
- Organization for the Development of the Senegal River
- Economic Commission for Africa
- African Union (AU)
- AUDA-NEPAD
- Afro-Arab Cooperation
- Arab Bank for Africa (BADEA)
- African Continental Free-Trade Area
Masters adapted to Libya.
Area of Knowledge: Africa .




Sample
(c) EENI Global Business School (1995-2024)
We do not use cookies
Top of this page






