Latin American Economy and Foreign Trade

Economy and Integration of Latin America and the Caribbean, Brazil, Mexico, Peru
- Introduction to the Latin American Economy
- Economic Profile of Latin America
- Effects of the COVID in Latin America and the Caribbean
- Post-crisis Scenario
- Key challenges: innovation and technological change
- International Trade of Iberian America
- Economic relations between China and Latin America
- Growing influence of China and other emerging economies
- Regional Integration in Latin America and the Caribbean
- Analysis of the Economic Survey of Latin America and the Caribbean published by the ECLAC
The aims of the subject “Latin American Economy” are the following:
- To analyze the evolution of the Latin American economy
- To assess the global crisis effects in the region
- To analyze the intra-Latin American trade
- To explore the trade relations between China and Latin American Countries
- To evaluate the degree of the Latin American economic integration

The Subject “Economy and Integration of Latin America” belongs to the following Online Programs taught by EENI Global Business School:
Masters: International Business, Foreign Trade.
Doctorate: American Business, World Trade.

Languages:  or
or  America Latina
America Latina
 America
America
 Amérique.
Amérique.
- Credits of the Subject “Latin American Economy”: 2

- Duration: two weeks

Latin American Economy:
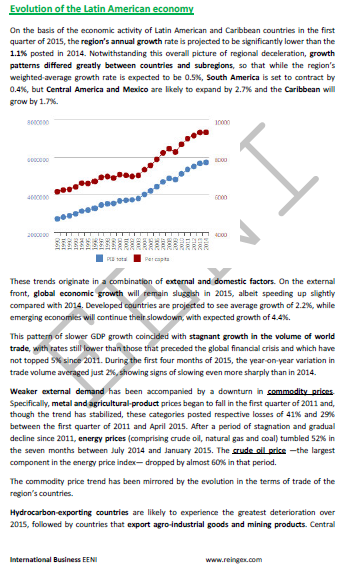
- Regional deceleration. The Latin American economic growth rate: 1.1%
- Mexico and Central America: 2,7%
- Causes: global crisis, world trade reduction, and export commodity prices decline (agricultural, energy, crude oil, and raw materials)
- Financial markets volatility
- Investment reduction
- Unemployment rate: 6%
- The economic slowdown cut into labour demand, unemployment rate is esteemed to rise to 8.3% for the region overall, while the new jobs that have been created are of poorer quality
- The effects of the crisis were channeled through the real sector of the economies, damaging what had been the main engines of regional growth
- exports plunged, while the contraction of the economic activity worldwide, together with the drop in International Trade flows, lowered commodity prices, which hurt the terms of the international trade in Latin America (Iberian America)
- At the same time, revenue from remittances and tourism fell, with Mexico and Central American countries and the Caribbean suffering the most, and Foreign direct investment (FDI) plummeted by 37%
- Economic Growth is esteemed to be slower in some of the most open economies that have a less diversified portfolio of trade partners and a heavier reliance on manufacturing
- The same can be said for the Caribbean Economies, some of which are facing complex financial and exchange-rate situations
- Drop in foreign investment was Generalized in all the subregions in Latin America and the Caribbean
- Brazil continued to be the main foreign direct investment recipient, followed by Chile, Mexico, Colombia and Argentina
- Among the medium-sized and large economies in Latin America, Chile is the economy with the highest proportion of foreign direct investment concerning its GDP (8%)
- As in the past, the services sector received the largest amount of foreign direct investment, while the primary sector (agriculture, mining, and hydrocarbons) experienced a relative drop
- The United States continued to be the largest investor in the region, followed by Spain and Canada
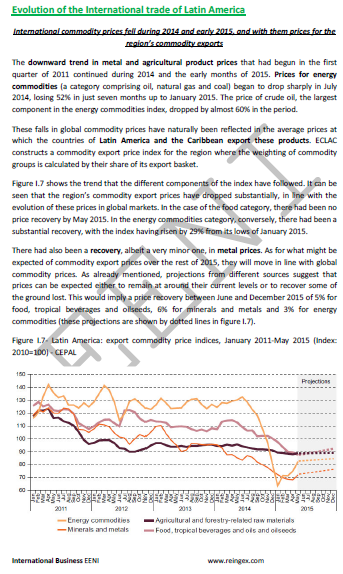
Source: Economic Commission for Latin America and the Caribbean.
(c) EENI Global Business School (1995-2024)
We do not use cookies
Top of this page


