India (Bharat): Hinduism, Society

Introduction to India (Religion, Hinduism, Values...)
- Introduction to India (Bharat): population, main cities, Ayurvedic..
- History of India
- India: The “spiritual land”
- Introduction to the Indian religions
- Hinduism
- Jainism
- Sikhism
- Zoroastrianism
- Islam
- Indian society values

The Subject “Introduction to India” belongs to the following Online Programs taught by EENI Global Business School:
Masters: International Business, Foreign Trade.
Course: Hinduism and Business.


Recommendations for the  Indian Students.
Indian Students.

Introduction to India (Bharat).
The Republic of India (Bharat):
- India is one of the oldest civilizations in the World
- India is the Central State of the Hindu Civilization
- India has become self-sufficient in agricultural production
- India is among the ten most industrialized nation in the World
- India is one of the BRICS (Brazil, China, Russia, India, and South Africa) markets
- Indian population: 1,210 million (17% of the world's population)
- Literacy rate in India: 64.84%, 75.26 for males and 53.67 for females
- The Constitution of India recognizes twenty-two different languages
- Hindi is the official language
- English is the language of business in India (Bharat)
- Area of India: 3,287,595 km² (2.4% of the World area)
- The capital of India is New Delhi
- The Indian largest city is Mumbai
- Type of Government: Federal Parliamentary Republic
- Independence of India: 1947 (UK)
- Currency of India: the Indian Rupee (INR)
- Borders of India: Pakistan, China, Nepal, Bhutan, Bangladesh, and Burma
- Nearby island countries: Indonesia, Maldives, and Sri Lanka
Official languages: Hindi and English (*).
India recognizes thirty official languages:
- Assamese (Assam)
- Bengali (Tripura and West Bengal)
- Bodo (Assam)
- Cashmere
- Dogri (Jammu and Kashmir)
- Gujarati (Dadra and Nagar Haveli, Daman and Diu and Gujarat)
- Hindi (Andaman and Nicobar Islands, Bijar, Chandigarh, Chhattisgarh, Delhi, Jariana, Himachal Pradesh, Jharkhand, Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan, Uttar Pradesh, and Uttaranchal)
- Kannada (Karnataka)
- Konkani (Goa)
- Maithili (Bihar)
- Malayalam (Kerala and Lakshadweep)
- Manipuri (Manipur)
- Marathi (Maharashtra)
- Nepali (Sikkim)
- Oriya (Orissa)
- Punjabi (Punjab)
- Sanskrit
- Santali
- Sindhi
- Tamil (Tamil Nadu and Pondicherry)
- Telugu (Andhra Pradesh)
- Urdu (Jammu and Kashmir)
- Punjabi (Punjab)
The capital of India is Delhi, the Indian politics and international embassies centre. Delhi has one of the highest per capita revenue levels in India.
- Mumbai (Bombay) is the commercial capital of India and one of the largest cities in the World (16 million people)
- Bangalore is the “Silicon Valley of India” and a leading Business Process Outsourcing (BPO) centre
- Kolkata (Calcutta) is one of the largest metropolitan cities in India with a strong cultural and literary tradition
- Chennai (Madras) in South India has a strong industrial base, many engineering and technical companies in India are located in Chennai
It is necessary to know the Indian history to know the Indian culture and the form of doing business, especially the influence of Hinduism.
- The history and culture of India begin along the Indus River
- The Republic of India has the most religious diversity in the World. In India, was born Hinduism, Buddhism, Sikhism, and Jainism (Zoroastrianism)
- Religion is vital in India. Hinduism is the religion of 82% of the Indian population
- Hinduism is the third largest religion in the World (after Christianity and Islam): 837 million followers (13% of the population in the World)
- Hinduism is the main religion in India, Nepal, and among the Tamils in Sri Lanka
- Hindu sacred texts are perhaps the most ancient religious texts still surviving today. Primary sacred texts of Hinduism are the Vedas: the Rig Veda, Sama Veda, Yajur Veda, and Atharva Veda
- The Bhagavad-Gita, part of the Mahabharata (400 or 300 B.C.), is a central text of Hinduism, a philosophical dialogue between Krishna and the warrior Arjuna. This is one of the most popular and accessible of all Hindu scriptures, required reading for anyone interested on Hinduism
- Mahatma Gandhi is considered as the Father of the new India and a beacon of light in the last decades of the British colonial rule, promoting the non-violence, justice, and harmony among the people of all faiths
- The Ayurvedic concept is that the organism adapts to the environment and its food and climate. This principle of adaptation is called Satyma. In India, Ayurveda is gaining much prominence as an alternative to the Western medicine
Hindi language:
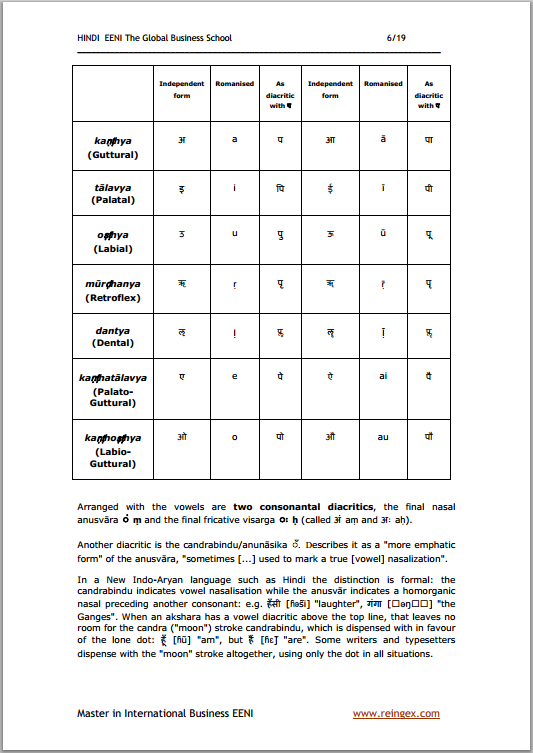





 or
or 

